


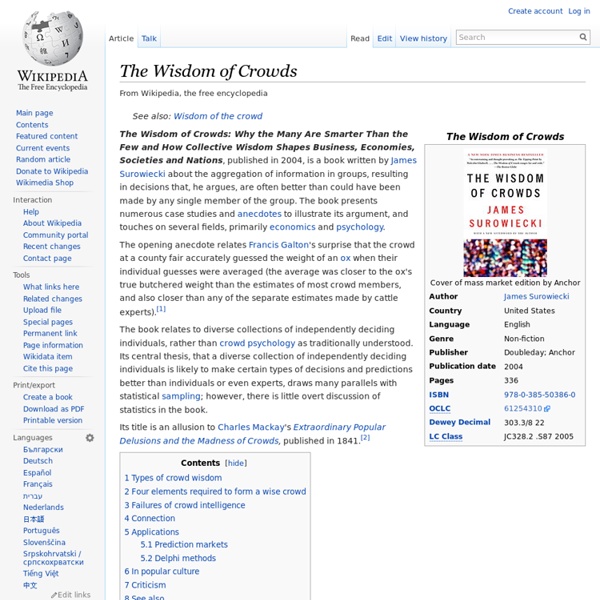
Open innovation Open innovation is a term promoted by Henry Chesbrough, adjunct professor and faculty director of the Center for Open Innovation at the Haas School of Business at the University of California,[1] in a book of the same name,[2] though the idea and discussion about some consequences (especially the interfirm cooperation in R&D) date as far back as the 1960s[citation needed]. Some instances of open innovation are Open collaboration,[3] a pattern of collaboration, innovation, and production. The concept is also related to user innovation, cumulative innovation, know-how trading, mass innovation and distributed innovation. “Open innovation is a paradigm that assumes that firms can and should use external ideas as well as internal ideas, and internal and external paths to market, as the firms look to advance their technology”.[2] Alternatively, it is "innovating with partners by sharing risk and sharing reward Advantages[edit] Disadvantages[edit] Models of open innovation[edit] See also[edit]
Swarm intelligence Swarm intelligence (SI) is the collective behavior of decentralized, self-organized systems, natural or artificial. The concept is employed in work on artificial intelligence. The expression was introduced by Gerardo Beni and Jing Wang in 1989, in the context of cellular robotic systems.[1] The application of swarm principles to robots is called swarm robotics, while 'swarm intelligence' refers to the more general set of algorithms. Example algorithms[edit] Particle swarm optimization[edit] Ant colony optimization[edit] Artificial bee colony algorithm[edit] Artificial bee colony algorithm (ABC) is a meta-heuristic algorithm introduced by Karaboga in 2005,[5] and simulates the foraging behaviour of honey bees. Bacterial colony optimization[edit] The algorithm is based on a lifecycle model that simulates some typical behaviors of E. coli bacteria during their whole lifecycle, including chemotaxis, communication, elimination, reproduction, and migration.[6] Differential evolution[edit]
Politiek zegt massaal af voor debat bij toespraak Griffin - DeepJournal Alle fracties in de Tweede Kamer hebben dinsdag en woensdag afgezegd nadat zij eerder (op D66 na, dat een partijcongres heeft) hadden toegezegd vrijdag 8 september iemand te zullen afvaardigen voor het debat na afloop van de toespraakvan David Ray Griffin, aldus de organisator van de avond.Professor Griffin, een van de belangrijkste auteurs over 9/11, zal morgen in Amsterdam een toespraak houden over 11 september. Hij is in Nederland uitgenodigd door uitgeverij Lemniscaat dat zijn boek The New Pearl Harbor heeft vertaald: 11 september - Een onderzoek naar de feiten. Download [MP3, 17 Mb] het interview van DeepJournal met Jesse Goossens. Lees hier een ander interview met Goossens.Jesse Goossens, vertaalster van het boek en organisatrice van de avond met Griffin in een gesprek met Daan de Wit van DeepJournal, op woensdagavond 6 september: 'CDA, Partij van de Arbeid, SP, GroenLinks, VVD; ze zouden allemaal iemand afvaardigen en het is allemaal gecancelled.'
Ontology of Folksonomy Thomas Gruber TomGruber.org and RealTravel.com Published in Int’l Journal on Semantic Web & Information Systems, 3(2), 2007. Ontologies are enabling technology for the Semantic Web. A while ago, the Artificial Intelligence research community got together to find a way to “enable knowledge sharing” (Neches et al., 1991). In the context of the Semantic Web, “ontology” is an enabling technology — a layer of the enabling infrastructure — for information sharing and manipulation. Not so long ago, keen observers of the Internet (Vander Wal, 2004),(Sterling, 2005), (Mieszkowski, 2005) and inventors of social software (Shachter, 2003), (Fake and Butterfield, 2003) began to notice that people who don’t write computer programs were happily “tagging” with keywords the content they created or encountered. Like all vague but evocative terms, both of the words ontology and folksonomy have taken on many senses. Yes, we agree, tags are cool. How to proceed? Let us focus on the ontology layer here.
Living lab A living lab is a research concept. A living lab is a user-centred, open-innovation ecosystem,[1][2] often operating in a territorial context (e.g. city, agglomeration, region), integrating concurrent research and innovation processes[3] within a public-private-people partnership.[4] The concept is based on a systematic user co-creation approach integrating research and innovation processes. User centred research methods,[6] such as action research, community informatics, contextual design,[7] user-centered design, participatory design,[8] empathic design, emotional design,[9][10][11] and other usability methods, already exist but fail to sufficiently empower users for co-creating into open development environments. Description[edit] William J. In 2010, Mitchell, Larson and Pentland, formed the first US-based living labs research consortium. The convergence of globalization, changing demographics, and urbanization is transforming almost every aspect of our lives. How it works[edit]
Craig Reynolds (computer graphics) Craig W. Reynolds (born March 15, 1953), is an artificial life and computer graphics expert, who created the Boids artificial life simulation in 1986.[1] Reynolds worked on the film Tron (1982) as a scene programmer, and on Batman Returns (1992) as part of the video image crew. Reynolds won the 1998 Academy Scientific and Technical Award in recognition of "his pioneering contributions to the development of three-dimensional computer animation for motion picture production.
Education: Money is made of Nothing (Republished from I.P.C.O. Education) 200bc. Rome Rome was having trouble with the money changers. 2 early Roman Emperors were assassinated because of their attempts to diminish the power of the money changers by reforming Usury laws and limiting land ownership to 500 acres. 48bc. Julius Caesar took back the power to coin money from the money changers and minted coins for the benefit of all, building great public works projects and making money plentiful which won him the love of the common man. With the of death of Caesar came the demise of plentiful money in Rome. 1100ad. King Henry 1st finally resolved to take the power away from the gold smiths and introduced the ‘Tally Stick System’ (accepted for the payment of taxes1100ad -1826ad.) 1500's King Henry 8th King Henry 8th finally relaxed the laws of Usury. 1553 Queen Mary 1st Queen Mary 1st took the throne and tightened the Usury Laws again, the money changers renewed the hording of gold and silver coins forcing the economy to plummet.
Text Clouds: A New Form of Tag Cloud? During 2006, tag clouds moved beyond their well-known role as navigation mechanisms and indicators of activity within social media experiences, emerging as a standard visualization technique for texts and textual data in general. This use of tag clouds does not commonly involve tags, social networks, emergent architectures, folksonomies, or metadata. "Text cloud" might be a more accurate label for these visualizations than tag cloud. In addition to recognizing fundamental differences - text clouds differ from tag clouds in composition (no tags at all) and purpose (predominantly comprehension, rather than access or navigation) - distinguishing the two types of clouds will make it much easier to assess their abilities to support user experience needs and business goals. The emergence of this new form of text cloud looks like a good example of speciation in action (though it's too early to tell whether the end result will be cladogenesis or anagenesis). The Economist's Text cloud
Cloud computing Cloud computing metaphor: For a user, the network elements representing the provider-rendered services are invisible, as if obscured by a cloud. Cloud computing is a computing term or metaphor that evolved in the late 1990s, based on utility and consumption of computer resources. Cloud computing involves application systems which are executed within the cloud and operated through internet enabled devices. Purely cloud computing does not rely on the use of cloud storage as it will be removed upon users download action. Clouds can be classified as public, private and hybrid.[1][2] Overview[edit] Cloud computing[3] relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and economies of scale, similar to a utility (like the electricity grid) over a network.[2] At the foundation of cloud computing is the broader concept of converged infrastructure and shared services. Cloud computing, or in simpler shorthand just "the cloud", also focuses on maximizing the effectiveness of the shared resources.