

Optimism. Berlin Wall Monument (West view) – the west side of the Wall is covered with graffiti that reflects the hope and optimism post-1989 The word is originally derived from the Latin optimum, meaning "best.
" Being optimistic, in the typical sense of the word, ultimately means one expects the best possible outcome from any given situation. This is usually referred to in psychology as dispositional optimism. Researchers sometimes operationalize the term differently depending on their research, however. Endurance. Endurance may also refer to an ability to keep going through a tough situation involving hardship, stress, etc.
(see patience) See also[edit] References[edit] External links[edit] Compassion. Compassion personified: a statue at the Epcot center in Florida.
Determination. Background/Overview[edit] Determination is a positive emotion that involves persevering towards a difficult goal in spite of obstacles.[1][2] Determination occurs prior to goal attainment and serves to motivate behavior that will help achieve one’s goal.
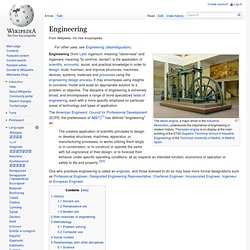
Empirical research suggests that people consider determination to be an emotion; in other words, determination is not just a cognitive state, but rather an affective state.[3] In the psychology literature, researchers have studied determination under other terms, including challenge and anticipatory enthusiasm.[4][5] Current emotions research is heavily focused on negatively valenced emotions and the action-tendencies they produce.[6] Positive emotions, such as determination, call this focus into question. Engineering. The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (ECPD, the predecessor of ABET)[1] has defined "engineering" as: The creative application of scientific principles to design or develop structures, machines, apparatus, or manufacturing processes, or works utilizing them singly or in combination; or to construct or operate the same with full cognizance of their design; or to forecast their behavior under specific operating conditions; all as respects an intended function, economics of operation or safety to life and property.[2][3] One who practices engineering is called an engineer, and those licensed to do so may have more formal designations such as Professional Engineer, Designated Engineering Representative, Chartered Engineer, Incorporated Engineer, Ingenieur or European Engineer.
Indian religions. Ganesha, a deity common to Hindus, Jains, and Buddhists.
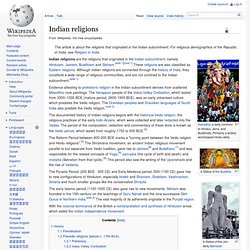
Primarily a widely-worshipped Hindu deity. Indian religions are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent; namely Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism and Sikhism. [web 1][note 1] These religions are also classified as Eastern religions. Although Indian religions are connected through the history of India, they constitute a wide range of religious communities, and are not confined to the Indian subcontinent. [web 1] Evidence attesting to prehistoric religion in the Indian subcontinent derives from scattered Mesolithic rock paintings. Unionism in Ireland. Unionists today want Northern Ireland to remain a part of the United Kingdom with England, Scotland and Wales In Ireland, unionism is an ideology which favours the continuation of some form of political union between the Ireland and Great Britain.

Since the partition of Ireland, unionism in Ireland has focused primarily on maintaining and preserving the place of Northern Ireland within the United Kingdom. In this context, or in the context of the historical events that led to the creation of Northern Ireland, a distinction may be made between Ulster unionism and unionism and unionists elsewhere on Ireland. The political relationship between England and Ireland dates from the 12th century Norman invasion.
In the Act of Union 1800, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was created. Unionism and its opposing ideology, Irish nationalism, are associated with particular ethnic and/or religious communities. Orangism (Netherlands) Prisoner. A prisoner, also known as an inmate or detainee, is a person who is deprived of liberty against their will.
This can be by confinement, captivity, or by forcible restraint. The term applies particularly to those on trial or serving a prison sentence.[1] English law[edit] "Prisoner" is a legal term for a person who is imprisoned.[2] Thanksgiving. History Prayers of thanks and special thanksgiving ceremonies are common among almost all religions after harvests and at other times.[2] The Thanksgiving holiday's history in North America is rooted in English traditions dating from the Protestant Reformation.
Halloween. Halloween or Hallowe'en (/ˌhæləˈwiːn, -oʊˈiːn, ˌhɑːl-/; a contraction of "All Hallows' Evening")[5] also known as All Hallows' Eve,[6] is a yearly celebration observed in a number of countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christian feast of All Hallows' Day.

It initiates the triduum of Hallowtide, the time in the liturgical year dedicated to remembering the dead, including saints (hallows), martyrs, and all the faithful departed believers.[7] According to many academic scholars, All Hallows' Eve is a Christianized feast initially influenced by Celtic harvest festivals,[8][9] with possible pagan roots, particularly the Gaelic Samhain.[6][10][11] Other academic scholars maintain that it originated independently of Samhain and has solely Christian roots.[12] Etymology[edit] History[edit] Gaelic and Welsh influence[edit] Snap-Apple Night, painted by Daniel Maclise in 1833, shows people feasting and playing divination games on Halloween in Ireland. Fire. The ignition and extinguishing of a pile of wood shavings Slow motion fire sequence 1000 frame/s. Desire. Desire is a sense of longing or hoping for a person, object, or outcome.
The same sense is expressed by emotions such as "craving" or "hankering". When a person desires something or someone, their sense of longing is excited by the enjoyment or the thought of the item or person, and they want to take actions to obtain their goal. The motivational aspect of desire has long been noted by philosophers; Thomas Hobbes (1588–1679) asserted that human desire is the fundamental motivation of all human action. While desires are often classified as emotions by laypersons, psychologists often describe desires as different from emotions; psychologists tend to argue that desires arise from bodily structures, such as the stomach's need for food, whereas emotions arise from a person's mental state. Marketing and advertising companies have used psychological research on how desire is stimulated to find more effective ways to induce consumers into buying a given product or service.
Autumn. Autumn, interchangeably known as fall in the US and Canada,[1] is one of the four temperate seasons. Autumn marks the transition from summer into winter, in September (Northern Hemisphere) or March (Southern Hemisphere) when the arrival of night becomes noticeably earlier and the temperature cools. One of its main features is the shedding of leaves from deciduous trees as they pave way for further growth.
The equinoxes might be expected to be in the middle of their respective seasons, but temperature lag (caused by the thermal latency of the ground and sea) means that seasons appear later than dates calculated from a purely astronomical perspective. The actual lag varies with region. In North America, autumn is usually considered to start with the September equinox.[5] In traditional East Asian solar term, autumn starts on or around 8 August and ends on about 7 November. Warning. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Warning may refer to: