


http://www.brainexplorer.org/neurological_control/Neurological_Neurotransmitters.shtml
Autism and Neuropsychology, by Marisa Marzillo Autism is a lifelong disorder that has become the discussion of many media outlets; it is a disorder that causes abnormal neurological development. It seems that lately autism prevalence is increasing, which is causing a demand for professionals to investigate on what causes autism. Autism disorder is characterized by different behavior including social impairments, difficulty in communication, and restrictive patterns of behavior. Individuals living with autism don’t have a lower IQ than most people, but it is common that they have weak social interaction. How To Boost Brain Power and Memory Until just a few years ago, doctors believed that the brain stopped making new neural connections - meaning that the memory began to get irreversibly worse - when the body stopped developing, usually in the early 20s. And doctors knew that, like any other part of the body, neurons weaken as people age. Loss of brain function due to neural breakdown was assumed to be a normal, unavoidable part of aging. It turns out they were wrong.
6 Virtual Tours Of The Human Body For Free Interactive Anatomy Lessons When it comes to interactive virtual views, we have gone to space and around the globe. So, it’s not surprising that we are also going within ourselves on a virtual journey of the human body. One of the finest tools available online is Visible Body. Unfortunately, it’s not free anymore. Chapter 12: Attention and Consciousness Attention involves top-down (voluntary) goal-directed processes and bottom-up (reflexive), stimulus-driven mechanisms. They influence the way information is processed in the brain and can occur early during sensory processing. Balint's syndrome is a visual attention and awareness deficit. Is Alzheimer's a Form of Diabetes? When the body refuses to make insulin, the condition is called type 1 diabetes; when the body mismanages the hormone, it's known as type 2. Now, scientists report new evidence linking insulin to a disorder of the brain: when the brain prevents the hormone from acting properly, the ensuing chemical imbalance may help trigger Alzheimer's disease. The correlation is so strong that some researchers are calling Alzheimer's disease "type 3" diabetes. In the body, insulin helps convert food into cellular energy. But the brain has other uses for insulin, namely as a means to learn and make new memories.
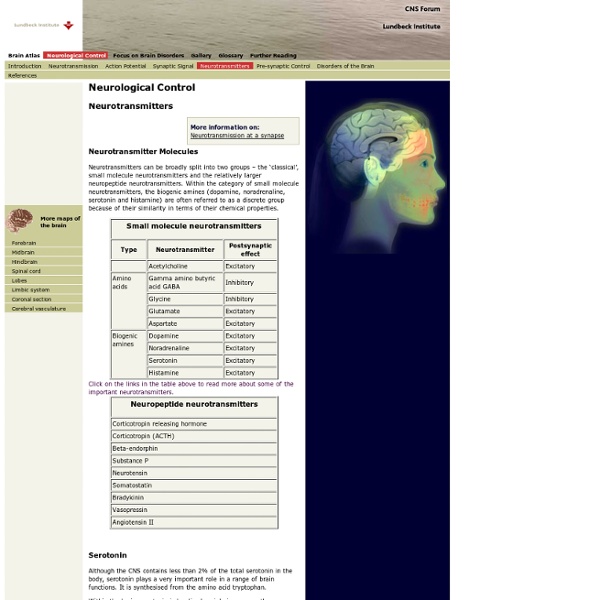
Memory strengthened by stimulating key site in brain Ever gone to the movies and forgotten where you parked the car? New UCLA research may one day help you improve your memory. UCLA neuroscientists have demonstrated that they can strengthen memory in human patients by stimulating a critical junction in the brain. List all the essential neurotransmitters Acetylcholine - synthesized from Choline, Lecithin, and panthothenic acid (B5), or Diethylaminoethanol (DMAE) - Arousal and orgasm - voluntary muscular control and proper tone - enhance energy and stamina - memory - long-term planning - mental focus Dopamine - synthesized from amino acid Levodopa - Alertness - Motivation - motor control - immune function - Ego hardening, confidence, optimism - Sexual Desire - Fat gain and loss - lean muscle gain - Bone density - ability to sleep soundly - Inhibits prolactin - thinking, planning, and problem solving - Aggression - Increase psychic and creative ability - Reduction of compulsivety - Salience and paranoia - Processing of pain - Increase sociability Serotonin (5-HT) - Synthesized from amino acid L-tryptophan with co-factor Niacin (B3), through the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) Norepinephrine - Synthesized from Dopamine with co-factor of vitamin C through the intermediate DOPAC.
How Our Brains Make Memories Sitting at a sidewalk café in Montreal on a sunny morning, Karim Nader recalls the day eight years earlier when two planes slammed into the twin towers of the World Trade Center. He lights a cigarette and waves his hands in the air to sketch the scene. At the time of the attack, Nader was a postdoctoral researcher at New York University. He flipped the radio on while getting ready to go to work and heard the banter of the morning disc jockeys turn panicky as they related the events unfolding in Lower Manhattan. Nader ran to the roof of his apartment building, where he had a view of the towers less than two miles away. He stood there, stunned, as they burned and fell, thinking to himself, “No way, man.
Alzheimer's is really just 'type-3' diabetes, new research shows (NaturalNews) Emerging research on the widespread degenerative brain disease known as Alzheimer's suggests that this prevalent form of dementia is actually a type of diabetes. Published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, a recent study out of Rhode Island Hospital (RIH) confirms that Alzheimer's is marked by brain insulin resistance and corresponding inflammation, a condition that some researchers are now referring to as type-3 diabetes. Dr. Suzanne de la Monte from RIH is the one responsible for making this fascinating connection, having found in her research that diabetes is closely associated with several key neuronal factors implicated in dementia.
The Brain-Information about the Brain - StumbleUpon 1 Introduction “I think, therefore I am.” —René Descartes, 17th-century philosopher bodies-in-motion - scott-eaton.com 30 second sequences from BiM Not long ago, I had twelve artists from Natural Motion (of Morpheme and Clumsy Ninja fame) into Somerset House, my home away from home, for a four day anatomy workshop. At the end of each day we would take about 20 minutes to draw from the Bodies in Motion library.
Magnetic manipulation of the sense of morality : Neurophilosophy WHEN making moral judgements, we rely on our ability to make inferences about the beliefs and intentions of others. With this so-called “theory of mind”, we can meaningfully interpret their behaviour, and decide whether it is right or wrong. The legal system also places great emphasis on one’s intentions: a “guilty act” only produces criminal liability when it is proven to have been performed in combination with a “guilty mind”, and this, too, depends on the ability to make reasoned moral judgements. MIT researchers now show that this moral compass can be very easily skewed. B-complex vitamins may help slow progression of dementia Oct. 28, 2010 — Large doses of B-complex vitamins could reduce the rate of brain shrinkage by half in elderly people with memory problems and slow the progression of dementia. A two-year clinical trial in England has shown that B vitamins, including B-6, B-12 and folic acid, slow down mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a condition which is a major risk factor for Alzheimer disease and other forms of dementia. Dr.
22 Ways to Overclock Your Brain “I just found out that the brain is like a computer. If that’s true, then there really aren’t any stupid people. Just people running DOS.” - Anonymous The brain is a three-pound supercomputer. It is the command and control center running your life.