

Qin Dynasty, Qin Dynasty History, History of Ancient China. Era Information Time: 221 B.C.-207B.C.Location of Capital: Xianyang City in Shanxi Province, not far from Xian Emperors: Ying Zheng, Fushu, Zi Ying Replaced by:Han Dynasty In 221 B.C.,Chinese were unified for the first time to construct a great country that ended the long era of disunity and warring.

In that year the western frontier state of Qin, the most aggressive of the Warring States, subjugated the last of its rival state.Centralization and autarchy were achieved by ruthless methods and focused on standardizing legal codes, bureaucratic procedures, the forms of writing and coinage, and the pattern of thought and scholarship. To silence criticism of imperial rule, the kings banished or put to death many dissenting Confucian scholars and confiscated and burned their books.
Qin expansionism was aided by frequent military expeditions pushing forward the frontiers in the north and south. A number of public works projects were also undertaken to consolidate and strengthen imperial rule. Ancient China Life History Facts:Dynasties,Discoveries,Religions,Crossbow,Sports,Chopsticks. Ancient China - The Ancient Chinese Civilization.
Chinese Historical Accounts the Forbidden City, the home of the Chinese emperors until the last dynasty was overthrown in the 20th century Chinese history, until the twentieth century, was written mostly by members of the ruling scholar-official class and was meant to provide the ruler with precedents to guide or justify his policies.
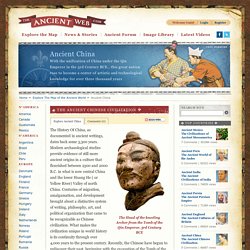
These accounts focused on dynastic politics and colorful court histories and included developments among the commoners only as backdrops. The historians described a Chinese political pattern of dynasties, one following another in a cycle of ascent, achievement, decay, and rebirth under a new family. Of the consistent traits identified by independent historians, a salient one has been the capacity of the Chinese to absorb the people of surrounding areas into their own civilization.
Chinese Dynasty Guide - The Art of Asia - History and Maps. Chinese history, which dates back more than 5,000 years, is extraordinarily rich, complex-and potentially confusing.
Understanding at least its basic chronology and some of its most notable events and developments is made somewhat easier by virtue of its ancient system of dynasties. Chinese History - Common Core. From at least 1766BCE to the twentieth century of the Common Era, China was ruled by dynasties.

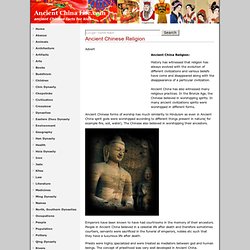
A dynasty is a family that passes control from one generation to the next. A dynasty does not have to last for a long time. One Chinese dynasty lasted more than 800 years while another lasted only fifteen years. Ancient China Religions, Ancient Chinese Religious Beliefs. Advert Ancient China Religion: History has witnessed that religion has always evolved with the evolution of different civilizations and various beliefs have come and disappeared along with the disappearance of a particular civilization.
Ancient China Crossbow Facts, Ancient Chinese Crossbow History. Advert Ancient Chinese Crossbow: A crossbow is a weapon which is used to shoot the projectile, also referred to as bolts.
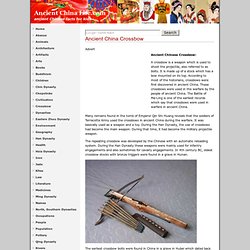
It is made up of a stock which has a bow mounted on its top. Ancient History Encyclopedia. The Qin dynasty was brief in duration (221-206 BCE) but very important in Chinese history.
It followed the Zhou dynasty (1046-256 BCE) and it ended when Liu Bang became the king of Han in 206 BCE (the formal beginning of the Han dynasty). Despite its brevity, the Qin dynasty left important marks on Chinese culture. In fact, the name "China" is derived from the name Qin (“Ch’in” in former Romanization systems). Following the Zhou Dynasty, China became involved in a seemingly endless conflict between the various regions for supreme control of the country. Ancient China Social Classes. Ancient China Government. Ancient China had monarchy, i.e. government headed by an emperor and a royal family.
Chinese rulers also called monarchs based their government on the Confucian model, which taught that the ruler was a virtuous man who led by example… China like many other countries at that time was an agriculture based country with the river Yangtze as its lifeline. During the ancient period the king would be the leader and would be more of a dictator than a king for the people who would take decisions beneficial to them. He had unsurpassing power in all areas be it economy or governance or agriculture which was the livelihood of the people.
The earliest incident of despotic leadership could probably be traced back to the Hsia dynasty (2200 – 1750 BC) when the emperor Yao picked Shun as his successor to help his people who were burdened by the regular floods. Shun can be given credit for being an enlightened leader in some respects, but he was very harsh on his people. Military. Ancient China Geography. Ancient China Religion. Crime and Punishment in Ancient China. See, also, China: A Legal History.

It was both the spirit and the intent of Han Fei’s legalism, as it came, from time to time, to dominate Chinese law, that punishment for all crimes would be harsh and universal. With seemingly no exceptions, every nation and culture in world history has experimented with cruel and unusual punishment; some still doing so, but most free and democratic societies now banning the practice. China is unusual in that a state policy of isolation, right up to the mid-1970s, made it difficult for Chinese people and policymakers to compare and evolve their law. A century of considerable political unrest starting in the mid-nineteenth century (and eventually leading to Communism) exacerbated matters. Ancient China Economy. Interested in the ancient Chinese economy?

Want to know about economic factors that prevailed in ancient China? Read our guide for more facts & information… Ancient China Clothing. Do you want to know what was in fashion in Ancient China? Have you ever wondered what cultural significance Ancient Chinese Clothing had? Read our guide for more facts and information... Ancient China Inventions. China has contributed many modern technological advances; but, have you ever wondered about ancient Chinese inventions? Do you want to know which of Ancient China’s inventions are in use today? Are you interested in how each invention shaped Chinaâ As China grows into a modern day superpower, it is important to remember that China as a civilization has existed for more than six millennia and contributed countless inventions that shaped China’s evolution and amazingly continue to shape the modern world.
Ancient Chinese inventions such as gunpowder, silk, paper, and the compass were and still are prominent pieces of Chinese and global life. Today gunpowder is associated with military use; however, gunpowder was actually invented by Taoist monks in Ancient China who were searching through alchemy for the answer to human immortality. Compass Paper. Invention of Paper, Paper use in Han Dynasty History, History of Ancient China. Daily Life In Ancient China. Daily life in Ancient China is as mysterious as it is old. Shang Dynasty. China History: Chronology, Dynasty Qin Han Tang Song Yuan Ming Qing.
Formation of the Chinese Civilization.