

Biosensing Machine That Can Smell and Differentiate Odors Developed. Researchers from The University of Manchester and the University of Bari have developed a biosensor that can differentiate smells that are similar to each other.
The machine can distinguish the smell of two similar objects such as spearmint or caraway. The scientists have found a way to manufacture odorant binding proteins in quantities that can be used in the biosensor. Odorant binding proteins helps the nose perceive the different smells by reacting to the different type of chemicals around The biosensor incorporate the proteins using a transistor. By doing so, the team were able to detect and measure the changes in current as the proteins reacted to odors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.Smelling Machines. Warm Light LED Lamp Using Single Yellow Phosphor Ideal For Indoor Lighting Developed. A warm white LED has been developed by scientists using a single yellow phosphor.
This is ideal for indoor lighting as it doesn't give out the usual bright white-blue light current LED lamps do. Low energy lighting options can be found almost anywhere these days. The two most common are Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL) and LED lamps. A 9 watt CFL lighting fixture has an equivalent brightness as that of a regular 45 watt incandescent lamp.
An 11 watt CFL is equal to 60 watts and an 18/20 watt lamp will give an equivalent incandescent brightness of 100 watts. A newer form of low energy lighting is the LED (Light Emitting Diode) lamp. LED lamps can give out light equivalent to a 50 watt halogen lamp at a fraction of the energy needed (around 7 watts). High Temperature Superconductivity Achieved Using Ordinary Scotch Tape. Superconductivity occurs when objects or materials that are super cooled or cooled below a certain temperature achieves no (zero) electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields.
Required temperatures usually approaches absolute zero. This phenomenon is quantum mechanical in nature and is characterized by the Meissner effect. The Meissner effect is an expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state. The electrical resistance of a material slowly goes down as temperature is lowered. When it is cooled below its critical temperature, a superconductor's resistance drops to zero.
Quantum Day : Magnetic Topological Insulator Eliminate Loss In Electrical Power Transmission. The quantum Hall effect (QHE) describes the quantized transport in two dimensional electron gases placed in a transverse magnetic field: the longitudinal resistance vanishes while the Hall resistance is quantized to a rational multiple of h/e2.
The effect was discovered in 1879 by Edwin Hall. But since the electron has not yet been experimentally discovered, application and understanding of the effect had to wait. In 1985, Klaus von Klitzing won the Noble Prize in Physics for discovering that the Hall conductivity was exactly quantized. This phenomenon, referred to as "exact quantization", has allowed for the definition of a new practical standard for electrical resistance.
The quantum Hall effect also provides an extremely precise independent determination of the fine structure constant, a quantity of fundamental importance in quantum electrodynamics. Inexpensive Rectenna and Advances in Near Field Communication For Fast and Efficient Mobile Transactions. Near Field Communication (NFC) is a set of rules, guidelines and standards implemented by smartphones and similar mobile devices to establish radio communication with each other by touching them together or bringing them into close proximity.
Some applications that utilizes NFC are wireless or contactless transactions, data exchange, and wi-fi. Contactless payments are usually transactions that involve payment through the smartphone (usually called "smart wallets"). Near field communication (NFC) technology also lets smartphones and other enabled devices communicate with other devices that are not powered through a NFC tag.
This is similar in nature to QR codes that smart phones are able to use and read. Next Generation Solar Cell Produced With Record Highest Efficiency Rating Using Colloidal Quantum Dots (CQD) Quantum dots are parts of matter whose excitons are bound in all three spatial dimensions.
An exciton is formed when a photon (light particle) is absorbed by a semiconductor. To put it simply, a quantum dot is a nano-scale semiconductor that captures light and converts it into energy. Since they are very small, quantum dots can be applied to surfaces such as plastic by just spraying it to form a flexible layer of quantum dot nano-film semiconductor. This allows the production and manufacture of solar cells that are more economical, durable, and efficient than standard silicon based ones. Some quantum dots are even just a few atoms thick, allowing for micro-sized devices to be produced. Aside from solar cells, quantum dots are also used in transistors, LEDs, diode lasers, and even for quantum computers. Breakthrough by U of T-led research team leads to record efficiency for next-generation solar cells. World Smallest Semiconductor Laser - Breakthrough in Photonic Technology. Semiconductor lasers are eyed to be the next generation in laser technology.
These lasters are compact, can be mass produced, easily integrated into applications, their properties are being improved constantly, they are becoming more and more powerful and efficient and they have found a widespread use as pumps for solid–state lasers. The active medium of the laser is a semiconductor. This is similar to the ones found in an LED. The most common of this is formed from a p-n junction and powered by injected electric current. The former devices are sometimes referred to as injection laser diodes to distinguish them from optically pumped laser diodes. MIT News: Microchips Using Self Assembling Polymers.
Researchers at MIT have developed a new approach to creating the complex array of wires and connections on microchips, using a system of self-assembling polymers. The work could eventually lead to a way of making more densely packed components on memory chips and other devices. The new method — developed by MIT visiting doctoral student Amir Tavakkoli of the National University of Singapore, along with two other graduate students and three professors in MIT’s departments of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) and Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) — is described in a paper published this August in the journal Advanced Materials; the paper is available online now. Graphene Promises New Levels of Technology in Photonic Chips. Graphene comes from graphite. Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov used the weak bond between the layers of graphite to isolate the three strong bonded carbon atoms and discovered graphene.
Without the layer of weak bonds, graphene is a structure that is only one atom thick. Hence, it is a two dimensional object. It is one of the thinnest and strongest material ever measured. The structure resembles chicken wire when viewed on the atomic scale. Geim and Novoselov shared the 2010 the Nobel Prize for Physics for the discovery. New OLED Developed: Spin Polarized Organic LED (Spin OLED) Light Emitting Diodes (LED) uses a standard semiconductor to generate light in different colors.
Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLED) uses an organic polymer or plastic semiconductors to generate light. They produce light on their own, do not generate heat, and are thin and flexible. OLEDs are currently used as display units in small devices such as mobile phones, digital cameras, and MP3 players. Not to be confused with LCD screens, these type of dispaly screens do not need to be backlit with LEDs or lamps. Some commercial visual displays also use OLED screens. MIT News: 3D TV Without Glasses One Step Closer to Holograms. As striking as it is, the illusion of depth now routinely offered by 3-D movies is a paltry facsimile of a true three-dimensional visual experience.
In the real world, as you move around an object, your perspective on it changes. But in a movie theater showing a 3-D movie, everyone in the audience has the same, fixed perspective — and has to wear cumbersome glasses, to boot. Despite impressive recent advances, holographic television, which would present images that vary with varying perspectives, probably remains some distance in the future. But in a new paper featured as a research highlight at this summer’s Siggraph computer-graphics conference, the MIT Media Lab’s Camera Culture group offers a new approach to multiple-perspective, glasses-free 3-D that could prove much more practical in the short term.
“Holography works, it’s beautiful, nothing can touch its quality,” says Douglas Lanman, a postdoc at the Media Lab and one of the new paper’s co-authors. Spin Seebeck Effect Lead To Engines With No Moving Parts And Infinitely Reliable. The Seebeck effect is a phenomenon in which a temperature difference between two dissimilar electrical conductors or semiconductors produces a voltage difference between the two substances.
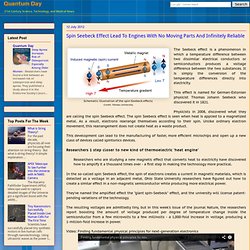
It is simply the conversion of the temperature differences directly into electricity. 320 Tons of Gold Worth US$21B Used Annually For Electronic Devices. Urban Mining is the process of reclaiming compounds and elements from products, buildings and waste. The term is synonymous to recycling but generally refers to recycling of industrial and electronic products for minerals and metals.
Urban mining is gaining interest now since its yield of metals per ton is higher than in traditional mining. Gold for instance yields around 150 grams per ton in cell phone circuitry while traditional mining only yields 5 grams per ton of gold ore. Nanotechnology And Vacuum Tube Technology For Faster And More Efficient Electronics.
A vacuum tube is simply a sealed glass tube or container. The inside of the tube is a space that is empty of any matter or gas; a vacuum. The vacuum tube is a device that controls the current through the vacuum. Vacuum tubes are used for rectification, amplification, switching, or creation of electrical signals. Thomas Edison discovered this when experimenting with light bulbs. He discovered that when an electric contacts are introduced to both ends, the current jumps from the hot filament of the bulb to a metal plate at the bottom.