

Beach, Sea and Ocean. Sea Shepherd International. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration - Ocean. The ocean covers 71 percent of the Earth's surface and contains 97 percent of the planet's water, yet more than 95 percent of the underwater world remains unexplored.

The ocean and lakes play an integral role in many of the Earth's systems including climate and weather. One of every six jobs in the United States is marine-related and over one-third of the U.S. Gross National Product originates in coastal areas. The ocean is key to transportation, recreation and its resources may hold the cures to many diseases. NOAA protects, preserves, manages and enhances the resources found in 3.5 million square miles of coastal and deep ocean waters.
Monitoring and Understanding NOAA is the lead federal agency for implementing a national Integrated Ocean Observing System that will be part of the greater Global Earth Observation System of Systems - or GEOSS. Exploration and Research Understanding ocean ecosystem dynamics is critical for sustainable management of marine resources. Stewardship Education. Beaches Caribbean Family Resorts: All Inclusive Caribbean Vacations for the Whole Family.
Beach Environmental Awareness Campaign Hawai`i. Ocean surface. Ocean Floor. Beach. Wave. Coral reef. Fish. Smithsonian Institution. National Geographic. Seawater. Seawater or salt water is water from a sea or ocean.
On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, or 599 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one litre by volume) of seawater has approximately 35 grams (1.2 oz) of dissolved salts (predominantly sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) ions). Average density at the surface is 1.025 g/ml. Seawater is denser than both fresh water and pure water (density 1.0 g/ml @ 4 °C (39 °F)) because the dissolved salts add mass without contributing significantly to the volume. The freezing point of seawater decreases as salt concentration increases. Geochemistry[edit] The thermal conductivity of seawater is 0.6 W/mK at 25 °C and a salinity of 35 g/kg.[4] The thermal conductivity decreases with increasing salinity and increases with increasing temperature.[5] Salinity[edit] Examples of water salinity (values in parts per thousand) Human impacts[edit] Compositional differences from freshwater[edit] Microbial components[edit]
Salt water. Salt water or saltwater may refer to:
Seawater. Sea. The sea, the world ocean, or simply the ocean, is the connected body of salty water that covers over 70 percent of the Earth's surface.
It moderates the Earth's climate and has important roles in the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle. Sea Life. Beach. Wild beaches are beaches that do not have lifeguards or trappings of modernity nearby, such as resorts, camps, and hotels.
They are sometimes called undeclared, undeveloped, or undiscovered beaches. Wild beaches can be valued for their untouched beauty and preserved nature. They are most commonly found for example in parts of Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic, Thailand, the Philippines and Indonesia. Also found in parts of Australia and New Zealand as well. Overview[edit] Although the seashore is most commonly associated with the word beach, beaches are found by lakes and alongside large rivers. Beach may refer to: small systems where rock material moves onshore, offshore, or alongshore by the forces of waves and currents; orgeological units of considerable size. The former are described in detail below; the larger geological units are discussed elsewhere under bars. Beach. Ocean. An ocean (from Ancient Greek Ὠκεανός, transc.
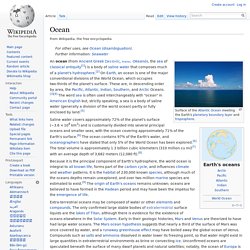
Okeanós, the sea of classical antiquity[1]) is a body of saline water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere.[2] On Earth, an ocean is one of the major conventional divisions of the World Ocean, which occupies two-thirds of the planet's surface. These are, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans.[3][4] The word sea is often used interchangeably with "ocean" in American English but, strictly speaking, a sea is a body of saline water (generally a division of the world ocean) partly or fully enclosed by land.[5] Earth's global ocean[edit] Global divisions[edit] Various ways to divide the World Ocean The major oceanic divisions are defined in part by the continents, various archipelagos, and other criteria.
Physical properties[edit] The bluish color of water is a composite of several contributing agents. Zones with depth[edit] Ocean Life.