

Quantum Entanglement May Link Wormholes In Universe, Physicists Say. Wormholes — shortcuts that in theory can connect distant points in the universe — might be linked with the spooky phenomenon of quantum entanglement, where the behavior of particles can be connected regardless of distance, researchers say.
These findings could help scientists explain the universe from its very smallest to its biggest scales. Scientists have long sought to develop a theory that can describe how the cosmos works in its entirety. Currently, researchers have two disparate theories, quantum mechanics and general relativity, which can respectively mostly explain the universe on its tiniest scales and its largest scales. Peter Higgs interview: 'I have this kind of underlying incompetence'
The story of the physicist who gave his name to the Higgs boson particle is a charming tale about a quintessentially British national treasure.
Ever since Peter Higgs was named as this year's Nobel prize winner, the tale has been endlessly retold, and goes like this. Higgs struck upon his theory while walking in the Cairngorms one weekend in 1964. An unworldly and donnish academic, he has been cloistered away in an ivory tower since, so immersed in particle physics research that when his first son was born he was miles away in a university library, and so remote from contemporary reality that to this day he owns neither a TV nor mobile phone, and only acquired his first computer on his 80th birthday.
On the day of the Nobel announcement he wasn't home to take the call, and when a former neighbour stopped to congratulate him in the street, his first response was a puzzled, "What prize? " But when we meet this week in London, this sugary tale turns out to be largely untrue. Dark Matter's Dark Horse.
LUX results: Dark matter hunt nears final phase. 30 October 2013Last updated at 12:26 ET By Rebecca Morelle Science reporter, BBC World Service.
Did a hyper-black hole spawn the Universe? Higgs and Englert Are Awarded Nobel Prize in Physics. What Is the Higgs? - Interactive Graphic. Higgs boson scientists win Nobel prize in physics. 8 October 2013Last updated at 10:01 ET By James Morgan Science reporter, BBC News The Nobel committee decided Englert and Higgs should jointly take the accolade for the boson, discovered at Cern in 2012 Two scientists have won the Nobel prize in physics for their work on the theory of the Higgs boson.
Peter Higgs, from the UK, and Francois Englert from Belgium, share the prize. In the 1960s, they were among several physicists who proposed a mechanism to explain why the most basic building blocks of the Universe have mass. Universe May Have Formed From Debris When Star Collapsed Into Black Hole, Cosmologists Say. It could be time to bid the Big Bang bye-bye.
NASA Starts Building Faster-than-light Warp Engine. Researchers at NASA’s Texas-based Johnson Space Center are trying to prove that it is possible to travel faster than the speed of light, and hope to one day build an engine that resembles the fictional Starship Enterprise.
NASA physicist and engineer Dr. Harold G. White, 43, believes it is possible to bend the rules of time and space that Albert Einstein constructed when he postulated that it is impossible to exceed the speed of light. White's research is based on the theories of Mexican physicist Miguel Alcubierre, who in 1994 theorized that exceeding Einstein’s galactic speed limit was possible if scientists discovered a way to harness the expansion and contraction of space. And Harold and his team are trying to do just that. Physicists Show Time Flows Asymmetrically at the Electron Level.
[This article originally appeared in print as "Time Asymmetry Finally Found.
"] At the level of tiny particles, the laws of physics are symmetrical in time. A reaction that proceeds in one direction (such as particle A transforming into particle B) is just as likely to occur in the reverse direction (particle B transforming into A). It’s not too strange a concept: A video showing a billiard ball’s initial bounce off a pool table’s cushion would look the same whether it was running backward or forward in time. The physics works just as well, and identically, either way. Yet experiments since the 1960s have suggested there should be exceptions to this rule — special cases of so-called “time-reversal violation.” [1303.1521] Double-Disk Dark Matter. The Possible Parallel Universe of Dark Matter. I am a light-matter chauvinist.
Don’t snicker; you’re probably one, too. Almost all of us are. We think of ourselves, and the world immediately around us, as something special. News in Brief: Under magnet's sway, fluids form simple structures. View the video Dollops of magnetic fluid can assemble themselves into both simple structures and constantly changing complex formations, researchers report in the July 19 Science.
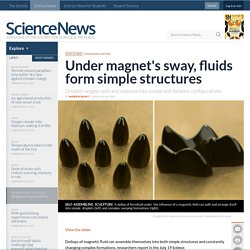
In nature, molecules such as proteins can autonomously warp and fold themselves into new arrangements. Scientists want to create self-assembling synthetic structures that are as dynamic and versatile as the natural ones that drive life. Neutrino 'Flavor' Changes May Help Solve Antimatter Mystery. Exotic particles called neutrinos have been caught in the act of shape-shifting, switching from one flavor to another, in a discovery that could help solve the mystery of antimatter.
Neutrinos come in three flavors — electron, muon and tau — and have been known to change, or oscillate, between certain flavors. 'Schrodinger's Cat' Thought Experiment Put To Test By Physicists In Canada, Switzerland.