

Roman Empire - Livius. Perseus Search Results. Titus Livius (Livy), The History of Rome, Book 9, chapter 9. 9. then said Postumius: "meanwhile, surrender us, who are unconsecrate, as you may do without offence to Heaven; [2] afterwards you shall surrender also those sacrosanct ones, when once they have retired from their magistracy; but, if you should listen to me, before surrendering them you would have them scourged here in the Comitium, that they might receive in advance this extra punishment, by way of interest. [3] for when they deny that the people can be freed of their obligation by surrendering us, who is so unacquainted with the fetial law as not to be aware that they say this, more that they may not be surrendered than because the case is so?
[4] and yet, Conscript Fathers, I do not dispute the fact that guarantees as well as treaties are sacred in the eyes of those who cherish honour among men on an equal footing with obligations due to the gods; but I deny that without the people's authorization any sanction can be given which shall be binding on the people. [5] what! Facts about Roman History. The Romans came to Britain nearly 2000 years ago and changed our country.
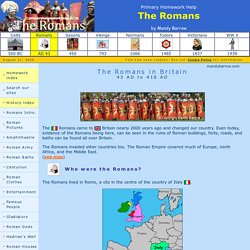
The Colosseum. History >> Ancient Rome The Colosseum is a giant amphitheatre in the center of Rome, Italy.
It was built during the Roman Empire. When was it built? Construction on the Colosseum was started in 72 AD by the emperor Vespasian. It was finished eight years later in 80 AD. Timeline - Romans leave Britain. Roman Invasions of Britain. Why were the Roman armies so successful? Hadrian's Wall. Ealy Rome. Julius Caesar. Julius Caesar is assassinated. Biographies >> Ancient Rome Occupation: Roman general and dictator Born: July 100 BC in Rome, Italy Died: 15 March 44 BC in Rome, Italy Best known for: Being the dictator of Rome and putting an end to the Roman Republic Julius Caesar by Unknown Biography: Where did Caesar grow up?
Julius Caesar was born in Subura, Rome in the year 100 BC. Did Caesar go to school? At around the age of six, Gaius began his education. Becoming an Adult Caesar's father died when he was sixteen years old. Early Career Young Caesar soon found himself in the middle of a power struggle between two factions in the government. When Sulla died, Caesar returned to Rome. Consul and General At the age of 40 Julius Caesar was elected to consul. As governor of Gaul, Caesar was in charge of four Roman legions. Civil War Politics in Rome became increasingly hostile while Caesar was in Gaul. Caesar announced that he was going to return to Rome and run for consul again. Fall of Rome. Honorius When Theodosius died in 395 AD, he left the Roman Empire to his two sons, Honorius and Arcadius.

Honorius took the West and Arcadius the East. But like other emperors who had been brought up at court, neither of them was very good at ruling, or even very interested. Most of the actual work was done by their advisors. Stilicho Most of Honorius' work was done by a Vandal named Stilicho. It didn't take long for the Germans and Goths to realize that the new young emperors were weak and so this was a good time to attack. But while Constantine III was doing this, nobody was watching the border. Meanwhile Constantine III was trying to take over Spain. End of the Roman Empire. Rome Burns. The capital of a great empire, Rome was a center of art and culture that spanned hundreds of years.
It was also the home city of a long series of emperors who ruled the Mediterranean. One of these was a man named Nero. A ruthlessly ambitious man, Nero came to the throne at age 16 with big plans. After allegedly killing his own mother, Nero proposed a plan to tear down a third of the city and build a series of palaces that he wanted to call Neropolis.
The Roman senate, which retained power even though the land was ruled by an emperor, refused to agree to the building project. On July 18, 64 A.D., a fire broke out in Rome’s chariot stadium. History has blamed Nero for the fire, and it certainly gave him what he wanted—he took the opportunity to begin building a huge palace where part of the city had once stood. Empire byzantin. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
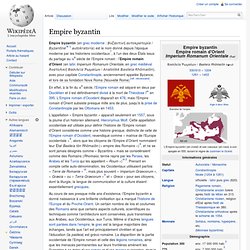
Empire byzantin Empire romain d'OrientImperium Romanum Orientale (la) Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων / Basileía Rhōmaíōn (grc) L'Empire byzantin (en violet) et ses vassaux (en rose) à son apogée en 555, durant le règne de Justinien le Grand. Empire romain. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Cet article traite d'une période de l'histoire de la Rome antique. Pour les territoires administrés par Rome, voir l'article Province romaine. Empire romain L'Empire fut fondé par Auguste, qui mit fin à la dernière guerre civile, dans la toute fin de la République romaine. Contrairement au régime républicain, qui était oligarchique, l'Empire fut une autocratie, tout en conservant durant le principat des apparences républicaines : le pouvoir politique était principalement détenu par un seul homme, l'empereur, qui s'appuya sur une bureaucratie sans cesse plus développée, sur une administration territoriale importante et sur un puissant appareil militaire.
En effet, à partir de la fin du IIe siècle, Rome est confrontée à ce que l'historiographie ultérieure a appelé les invasions barbares. À cette époque, le pouvoir était devenu un régime absolu, avec une cour et un protocole de type oriental. Octave devient empereur[modifier | modifier le code] ROMAINS. Top 10 Myths About the Romans. History For many, the only exposure to Ancient Rome comes from what they have seen in the movies or on television.
Unfortunately, films like Gladiator, Spartacus, Barabbas, and Demetrius and the Gladiators don’t present a very accurate depiction of life in Rome and the arena. Considering the fact that the Roman Empire existed for so long, and so much of our own Western society has derived from it, it is no surprise that we all have at least one or two misconceptions about the Empire and its people.
For this reason, we have put together a list of the most misconceptions people hold about the Ancient Roman society and customs. Fortunately most are easily proven wrong as you will see when you read on: Contrary to popular belief, the emperor did not give a thumbs up or down for a gladiator as a signal to kill his enemy.