

Goldman Sachs. Morgan Stanley. Martian Government Bond Issue as a default idea. Government bond. The terms on which a government can sell bonds depend on how creditworthy the market considers it to be.
International credit rating agencies will provide ratings for the bonds, but market participants will make up their own minds about this. Bond (finance) In contrast, government bonds are usually issued in an auction.
In some cases both members of the public and banks may bid for bonds. In other cases only market makers may bid for bonds. The overall rate of return on the bond depends on both the terms of the bond and the price paid.[4] The terms of the bond, such as the coupon, are fixed in advance and the price is determined by the market. In the case of an underwritten bond, the underwriters will charge a fee for underwriting. An alternative process for bond issuance, which is commonly used for smaller issues and avoids this cost, is the private placement bond. Historically an alternative practice of issuance was for the borrowing government authority to issue bonds over a period of time, usually at a fixed price, with volumes sold on a particular day dependent on market conditions.
Jerry McMahan - Funding the First Colony - 19th Annual International Mars Society Convention. Early American currency - Wikipedia. Early American currency went through several stages of development in colonial and post-Revolutionary history of the United States.
Because few coins were minted in the thirteen colonies that became the United States in 1776, foreign coins like the Spanish dollar were widely circulated. Colonial governments sometimes issued paper money to facilitate economic activity. The British Parliament passed Currency Acts in 1751, 1764, and 1773 that regulated colonial paper money. Colonial currency[edit] There were three general types of money in the colonies of British America: specie (coins), paper money and commodity money.[1] Commodity money was used when cash (coins and paper money) was scarce. Planetary Currency for Mars. Help bootstrap Mars exploration and colonization, mine and use Marscoin today.
A Planetary Bitcoin Revolution Since 2009 a new invention, a peer-to-peer decentralized secure payment and monetary system, bitcoin, has demonstrated quite powerful how a future planetary economic and financial system could look like [7].
Indeed, as many observers have noted, the most difficult part in using bitcoin is actually the "legacy system" of our established old banking and financial industry. Business Model Innovation. Credit union. Worldwide, credit union systems vary significantly in terms of total system assets and average institution asset size,[6] ranging from volunteer operations with a handful of members to institutions with assets worth several billion US dollars and hundreds of thousands of members.[7] Credit unions operate alongside other mutual and/or co-operative organisations engaging in cooperative banking, such as building societies.
Differences from other financial institutions[edit] Credit unions differ from banks and other financial institutions in that those who have accounts in the credit union are its members and owners,[8] and they elect their board of directors in a one-person-one-vote system regardless of their amount invested.[9] Credit unions see themselves as different from mainstream banks, with a mission to be "community-oriented" and "serve people, not profit".[10][11][12][13][14][15] Not-for-profit status[edit] Global presence[edit] History[edit] In the United States, St.
The Mars Society. The History of Foreign Investment in the United States to 1914 - Mira Wilkins.
Largest global insurers by market cap 2016. This statistic presents the leading insurance companies worldwide as of March 2016, ranked by market capitalization.
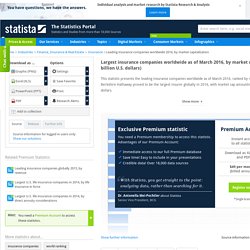
Berkshire Hathaway proved to be the largest insurer globally in 2016, with market cap amounting to 346.5 billion U.S. dollars. Global insurance industry - additional information Insurance is a form of risk management, where a person, called the insured or policy holder, signs a contract with a company, which is called insurer or insurance carrier, in order to protect themselves from sudden losses. Top 100 Global Corporations ranked by Current Market Capitalization (U.S.$ millions) SWFI - Sovereign Wealth Fund Institute. Sovereign Wealth Fund Rankings Largest Sovereign Wealth Funds by Assets Under Management What is a Sovereign Wealth Fund?
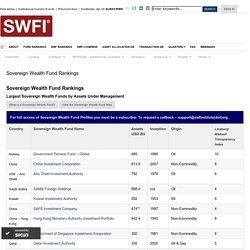
View the Sovereign Wealth Fund Map. Top 10 Largest Global IPOs Of All Time. Alibaba Group’s staggering initial public offering of $25 billion shattered all records and became the largest IPO ever.
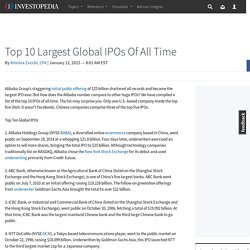
Forbes Welcome. Underwriting - Wikipedia. "Underwriter" redirects here.
For the United States Navy ships, see USS Underwriter. Underwriting services are provided by some large specialist financial institutions, such as banks, insurance or investment houses, whereby they guarantee payment in case of damage or financial loss and accept the financial risk for liability arising from such guarantee.
Crowdfunding. Crowdfunding is the practice of funding a project or venture by raising monetary contributions from a large number of people, typically via the internet.[1] One early-stage equity expert described it as “the practice of raising funds from two or more people over the internet towards a common Service, Project, Product, Investment, Cause, and Experience, or SPPICE.”[2] The crowdfunding model is fueled by three types of actors: the project initiator who proposes the idea and/or project to be funded; individuals or groups who support the idea; and a moderating organization (the "platform") that brings the parties together to launch the idea.[3] In 2013, the crowdfunding industry grew to be over $5.1 billion worldwide.[4] History[edit] Types[edit]

Sponsor - Wikipedia. Sweepstakes - Wikipedia. Sweepstakes are a type of contest where a prize or prizes may be awarded to a winner or winners.[1] Sweepstakes began as a form of lottery that were tied to products sold.[2] In response, the FCC and FTC refined U.S. broadcasting laws (creating the anti-lottery laws).[3] Under these laws sweepstakes became strictly "No Purchase Necessary to Enter or Win", especially since many sweepstakes companies skirted the law by stating only "No Purchase Necessary to Enter",[4] removing the consideration (one of the three legally required elements of gambling)[5] to stop abuse of sweepstakes.[5] Today, sweepstakes in the USA are used as marketing promotions to reward existing consumers, and to draw attention to a product.[2] By definition, the winner is determined by luck rather than skill.[6] Marketing[edit]
List of lotteries - Wikipedia. Benefactor - Wikipedia. Patronage - Wikipedia. Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows to another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists such as musicians, painters, and sculptors. Angel investor - Wikipedia. An angel investor or angel (also known as a business angel, informal investor, angel funder, private investor, or seed investor) is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start-up, usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity. A small but increasing number of angel investors invest online through equity crowdfunding or organize themselves into angel groups or angel networks to share research and pool their investment capital, as well as to provide advice to their portfolio companies.[1] Etymology and origin[edit]
Assurance contract - Wikipedia. An assurance contract, also known as a provision point mechanism, is a game theoretic mechanism and a financial technology that facilitates the voluntary creation of public goods and club goods in the face of the free rider problem. The free rider problem is that there may be actions that would benefit a large group of people, but once the action is taken, there is no way to exclude those who did not pay for the action from the benefits.
This leads to a game theoretic problem: all members of a group might be better off if an action were taken, and the members of the group contributed to the cost of the action, but many members of the group may make the perfectly rational decision to let others pay for it, then reap the benefits for free, possibly with the result that no action is taken. The result of this rational game play is lower utility for everyone. Assurance contracts operate as follows: Seed money. Seed money, sometimes known as seed funding, is a form of securities offering in which an investor purchases part of a business. The term seed suggests that this is a very early investment, meant to support the business until it can generate cash of its own, or until it is ready for further investments. Seed money options include friends and family funding, angel funding, and crowdfunding.[1] List of highest funded crowdfunding projects - Wikipedia. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This is an incomplete list of the highest funded crowdfunding projects, either successful or not.
Over 10 million[edit] Threshold pledge system - Wikipedia. Escrow - Wikipedia. Horizontalidad - Wikipedia. Distributism - Wikipedia. Doctrine in opposition to both socialism and capitalism Distributism is an economic theory asserting that the world's productive assets should be widely owned rather than concentrated.[1] It was developed in Europe in the late 19th and early 20th centuries based upon the principles of Catholic social teaching, especially the teachings of Pope Leo XIII in his encyclical Rerum novarum (1891) and Pope Pius XI in Quadragesimo anno (1931).[2][3][4] It views both capitalism and socialism as equally flawed and exploitative, and it favors economic mechanisms such as small-scale cooperatives and family businesses, and large-scale antitrust regulations. Some Christian Democratic political parties have advocated distributism in their economic policies.
Cooperative. Mondragon Corporation. Financing railroads. In November 1879, private banking firm Drexel, Morgan & Co. successfully sold a block of William Vanderbilt's New York Central Railroad stock when he decided to liquidate his inheritance from his father, Cornelius Vanderbilt. Gilles Herard, Jr. Merchant Banker. © 2010 Company Name. All rights reserved. 390 N. Member States' Assessed Share of the UN Budget. Countries reach historic agreement to generate financing for new sustainable development agenda - United Nations Sustainable Development. Financing for Development. Funding NATO. Global Financing Facility. What we do - New Rules for Global Finance Coalition.
The Secret Story of WWII Japanese & Nazi Gold By David Guyatt. Goldman Sachs report on space mining for platinum with 'asteroid-grabbing spacecraft' Chapter 1: An Introduction to Multinational Finance - Multinational Finance, 6th Edition. Financing the Multinational Corporation and Its Cost of Capital. The Capital Structure for a Multinational Corporation. Sources of Finance Available to a Global Business. UFOs, the Tower of Babel Moment and Space Collateralization. MOVE OVER SWIFT... BUT IS SPACE THE REAL REASON? A trillion-dollar space industry will require new markets. GOLDMAN SACHS, PLATINUM, AND ASTEROID MINING.
ASTEROID MINING AND SPACE MILITARIZATION. THE GRAND DUCHY OF LUXEMSPACE IS AT IT AGAIN...