


Operational risk An operational risk is defined as a risk incurred by an organisation's internal activities. Operational risk is the broad discipline focusing on the risks arising from the people, systems and processes through which a company operates. It can also include other classes of risk, such as fraud, legal risks, physical or environmental risks. A widely used definition of operational risk is the one contained in the Basel II regulations. Operational risk management differs from other types of risk, because it is not used to generate profit (e.g. credit risk is exploited by lending institutions to create profit, market risk is exploited by traders and fund managers, and insurance risk is exploited by insurers). Background[edit] Since the mid-1990s, the topics of market risk and credit risk have been the subject of much debate and research, with the result that financial institutions have made significant progress in the identification, measurement and management of both these forms of risk.
ISO 31000 ISO 31000 is a family of standards relating to risk management codified by the International Organization for Standardization. The purpose of ISO 31000:2009 is to provide principles and generic guidelines on risk management. ISO 31000 seeks to provide a universally recognised paradigm for practitioners and companies employing risk management processes to replace the myriad of existing standards, methodologies and paradigms that differed between industries, subject matters and regions. Currently, the ISO 31000 family is expected to include: ISO 31000:2009 - Principles and Guidelines on Implementation[1]ISO/IEC 31010:2009 - Risk Management - Risk Assessment TechniquesISO Guide 73:2009 - Risk Management - Vocabulary ISO also designed its ISO 21500 Guidance on Project Management standard to align with ISO 31000:2009.[2] Introduction[edit] ISO 31000 was published as a standard on the 13th of November 2009, and provides a standard on the implementation of risk management. Scope[edit]
Digital marketing Digital marketing is marketing that makes use of electronic devices (computers) such as personal computers, smartphones, cellphones, tablets and game consoles to engage with stakeholders. Digital marketing applies technologies or platforms such as websites, e-mail, apps (classic and mobile) and social networks. Social Media Marketing is a component of digital marketing. Many organisations use a combination of traditional and digital marketing channels. History[edit] The term 'digital marketing' was first used in the 1990s.[1] In the 2000s and the 2010s, digital marketing became more sophisticated as an effective way to create a relationship with the consumer that has depth and relevance.[2] In 2012 and 2013 statistics showed digital marketing remained a growing field.[3][4] Digital marketing is often referred to as 'online marketing' or 'internet marketing'. Types of digital marketing[edit] Two different forms of digital marketing exist:[citation needed] Multi-Channel Communications[edit]
Part 1: Flipping The Classroom? … 12 Resources To Keep You On Your Feet Welcome to another post rich in resources. If you have come here looking for links that will guide you to videos and multimedia to use in a Flipped Classroom that is coming in a future post. Perhaps you have tried a little Flip of your own and want to learn more. If you are beginning to investigate what a Flipped Classroom is, with the thought of possibly trying some kind of Flip yourself… then this is also the right place. Many educators are beginning to become aware of the growing teaching method referred to as “Flipping The Classroom”. You see, at first this definition does make a lot of sense, and like so many “best practices” I see great value in the idea. Yes, I am a proponent of incorporating various multimedia and online learning in a blended environment. The Twelve Resources To Better Understand Flipping the Classroom Learning About The Khan Academy - You have heard about Khan and have possible even used the tutorials. Like this: Like Loading...
Operational risk management The term Operational Risk Management (ORM) is defined as a continual cyclic process which includes risk assessment, risk decision making, and implementation of risk controls, which results in acceptance, mitigation, or avoidance of risk. ORM is the oversight of operational risk, including the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes and systems; human factors; or external events. Four Principles of ORM[edit] The U.S. Accept risk when benefits outweigh the cost.Accept no unnecessary risk.Anticipate and manage risk by planning.Make risk decisions at the right level. Three Levels of ORM[edit] In Depth In depth risk management is used before a project is implemented, when there is plenty of time to plan and prepare. Deliberate Deliberate risk management is used at routine periods through the implementation of a project or process. Time Critical Time critical risk management is used during operational exercises or execution of tasks. ORM Process[edit] In Depth[edit] 1. 2.
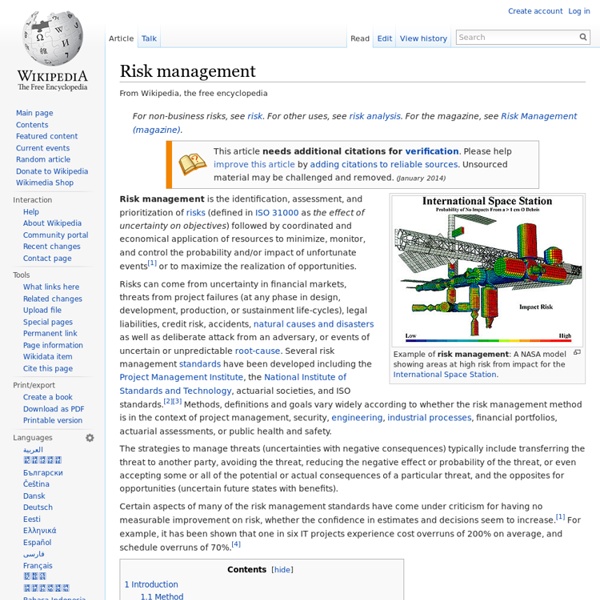
Enterprise risk management Enterprise risk management (ERM) in business includes the methods and processes used by organizations to manage risks and seize opportunities related to the achievement of their objectives. ERM provides a framework for risk management, which typically involves identifying particular events or circumstances relevant to the organization's objectives (risks and opportunities), assessing them in terms of likelihood and magnitude of impact, determining a response strategy, and monitoring progress. By identifying and proactively addressing risks and opportunities, business enterprises protect and create value for their stakeholders, including owners, employees, customers, regulators, and society overall. (ERM) ERM can also be described as a risk-based approach to managing an enterprise, integrating concepts of internal control, the Sarbanes–Oxley Act, and strategic planning. ERM frameworks defined[edit] Casualty Actuarial Society framework[edit] Hazard risk Financial risk Operational risk
Risk management: Five steps to risk assessment This is not the only way to do a risk assessment, there are other methods that work well, particularly for more complex risks and circumstances. However, we believe this method is the most straightforward for most organisations. Follow the five steps in our leaflet: Five steps to risk assessment Don’t overcomplicate the process. If you run a small organisation and you are confident you understand what’s involved, you can do the assessment yourself. Download the Risk Assessment and Policy Template [7]. If you work in a larger organisation, you could ask a health and safety adviser to help you. a hazard is anything that may cause harm, such as chemicals, electricity, working from ladders, an open drawer, etc; and the risk is the chance, high or low, that somebody could be harmed by these and other hazards, together with an indication of how serious the harm could be. Step 1: Identify the hazards[9]
How Khan Academy Is Changing the Rules of Education | Magazine Matthew Carpenter, age 10, has completed 642 inverse trigonometry problems at KhanAcademy.org.Photo: Joe Pugliese “This,” says Matthew Carpenter, “is my favorite exercise.” I peer over his shoulder at his laptop screen to see the math problem the fifth grader is pondering. It’s an inverse trigonometric function: cos-1(1) = ? Carpenter, a serious-faced 10-year-old wearing a gray T-shirt and an impressive black digital watch, pauses for a second, fidgets, then clicks on “0 degrees.” Carpenter, who attends Santa Rita Elementary, a public school in Los Altos, California, shouldn’t be doing work anywhere near this advanced. But last November, Thordarson began using Khan Academy in her class. Initially, Thordarson thought Khan Academy would merely be a helpful supplement to her normal instruction. “I’m able to give specific, pinpointed help when needed,” she says. The result is that Thordarson’s students move at their own pace. Khan’s videos are anything but sophisticated. Not everyone agrees.