

Systems of Photosynthesis. The Ecology of Photosynthetic Pathways. The Light-Dependent and Light-Independent Reactions - Shmoop Biology. The light reactions, or the light-dependent reactions, are up first.
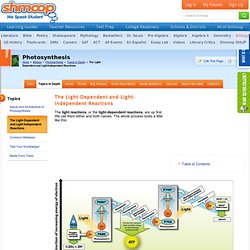
We call them either and both names. The whole process looks a little like this: Do not freak out or fill your head with all the complicated names in that diagram. No—stop right there. All in all, the process is simpler than it looks. Here again is our friend the chloroplast. Image source Even though the two photosystems absorb different wavelengths of light, they work similarly. The absorption pigments transfer the energy from sunlight to another pigment; at each transfer, the absorption pigments pass the photon energy to another pigment that absorbs a similar or lower wavelength of light. Anyway, eventually, the energy makes it to the reaction center, or action pigment. The positively charged photosystem creates a scenario similar to one that might occur if Twilight stars Robert Pattinson and Kristen Stewart made a surprise appearance at your local high school.
Back to regularly scheduled programming. Guess what? Photosynthesis. The free chemical energy required for life processes is derived from organic food materials by a process called biological oxidation.
If organisms are allowed to utilize the existing food materials on this planet, it will be exhausted in no time. However, nature has devised a unique mechanism by means of which it replenishes the organic food materials in excess and this is achieved by harnessing the solar energy by plants. Definition: Photosynthesis can be defined as a “series of processes in which solar electro magnetic radiation energy (SEMR) is captured, converted and conserved in the form of chemical energy by green plants”. Read or download Photosynthesis: The Green Miracle. As you know, plants and some bacteria and single-celled organisms use energy from the Sun in order to produce sugar from carbon dioxide and water.
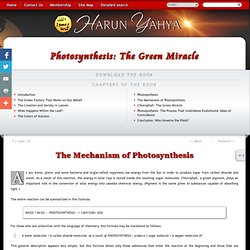
As a result of this reaction, the energy in solar rays is stored inside the resulting sugar molecules. Chlorophyll, a green pigment, plays an important role in the conversion of solar energy into useable chemical energy. (Pigment is the name given to substances capable of absorbing light.) The entire reaction can be summarized in this formula: For those who are unfamiliar with the language of chemistry, this formula may be translated as follows: 6 water molecules + 6 carbon dioxide molecules –as a result of PHOTOSYNTHESIS— produce 1 sugar molecule + 6 oxygen molecules 67 This general description appears very simple, but this formula shows only those substances that enter the reaction at the beginning and those that are obtained at the end.
Components of the Photosynthesis Process Grana: Thylakoids combine together to form grana. ent wavelengths. Cell Biology Archives. A,C, G, and T.
Every biology student learns that the information to construct a cell is contained in those four letters, and each corresponds to a chemical nucleotide. The Cell Cycle. Plant Cell Vs. Animal Cell. The bodies of both plants and animals are made up of cells.
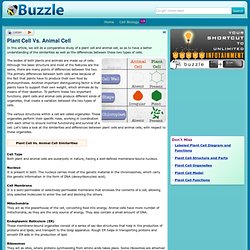
Although the basic structure and most of the features are the same, there are many points of differences between the two. The primary differences between both cells arise because of the fact that plants have to produce their own food by photosynthesis. Another important distinguishing factor is that plants have to support their own weight, which animals do by means of their skeleton. To perform these two important functions, plant cells and animal cells produce different kinds of organelles, that create a variation between the two types of cells.
The various structures within a cell are called organelles. Plant Cell Vs. Cell Type Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic in nature, having a well-defined membrane-bound nucleus. Nucleus It is present in both. Mitochondria They act as the powerhouse of the cell, converting food into energy. Ribosomes They act as sites, where proteins synthesizing from amino acids takes place. Cell Differences: Plant Cells. Figure %: Generalized Plant Cell Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells.
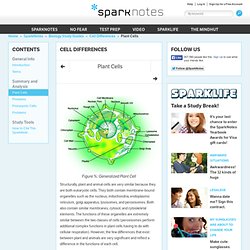
They both contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes. Both also contain similar membranes, cytosol, and cytoskeletal elements. The functions of these organelles are extremely similar between the two classes of cells (peroxisomes perform additional complex functions in plant cells having to do with cellular respiration). Cell Energy Cycle Gizmo. Cellular Respiration. Electron Transport System and Formation of ATP. Animation: How Glycolysis Works.