

Khufu ship. The reconstructed "solar barge" of Khufu Model of the solar barge, from the boat museum.
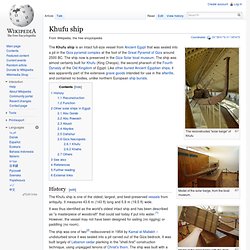
Model of the solar barge with the deck removed, showing the rope stitching that holds the planks together. The Khufu ship is an intact full-size vessel from Ancient Egypt that was sealed into a pit in the Giza pyramid complex at the foot of the Great Pyramid of Giza around 2500 BC. The ship now is preserved in the Giza Solar boat museum. Khufu. Khufu (/ˈkuːfuː/ KOO-foo), originally Khnum-Khufu (/ˈknuːmˈkuːfuː/ KNOOM-koo-foo), is the birth name of a Fourth Dynasty ancient Egyptian pharaoh, who ruled in the first half of the Old Kingdom period (26th century BC).
Khufu was the second pharaoh of the 4th dynasty; he followed his possible father, king Sneferu, on the throne. He is generally accepted as having built the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, but many other aspects of his reign are rather poorly documented.[4][9] Khufu is well known under his Hellenized name Khêops or Cheops (/ˈkiːɒps/, KEE-ops; Greek: Χέοψ, by Diodor and Herodotus) and less well known under another Hellenized name, Súphis (/ˈsuːfɨs/ SOO-fis; Greek: Σοῦφις, by Manetho).[4][9] A rare version of the name of Khufu, used by Josephus, is Sofe (/ˈsɒfiː/ SO-fe; Greek: Σοφe).[10] Arab historians, who wrote mystic stories about Khufu and the Giza pyramids, called him Saurid or Salhuk.[11] Family[edit] Khufu's origin[edit]
The Pyramids. The Pyramids - 3D Virtual Tour The Pyramids virtual tours can be started by clicking the preview window or by downloading the stand-alone versions.

Just drag the mouse to the direction you want to look. Use the scroll wheel to zoom at the details. Press F9 to get a list of the 3D sites you downloaded (residing in the same directory). To install the listed sites as a screensaver press F5. 3D virtual reality tour of Great Pyramid of Cheops, or Khufu. Great Pyramid of Giza. The Great Pyramid of Giza (also known as the Pyramid of Khufu or the Pyramid of Cheops) is the oldest and largest of the three pyramids in the Giza Necropolis bordering what is now El Giza, Egypt.
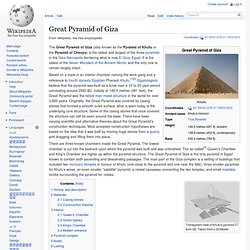
It is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one to remain largely intact. Based on a mark in an interior chamber naming the work gang and a reference to fourth dynasty Egyptian Pharaoh Khufu,[1][2] Egyptologists believe that the pyramid was built as a tomb over a 10 to 20-year period concluding around 2560 BC. Initially at 146.5 metres (481 feet), the Great Pyramid was the tallest man-made structure in the world for over 3,800 years. Originally, the Great Pyramid was covered by casing stones that formed a smooth outer surface; what is seen today is the underlying core structure. Some of the casing stones that once covered the structure can still be seen around the base. There are three known chambers inside the Great Pyramid. History and description[edit] Giza Necropolis. The Giza Necropolis (Arabic: أهرامات الجيزة, IPA: [ʔɑhɾɑˈmɑːt elˈɡiːzæ], "pyramids of Giza") is an archaeological site on the Giza Plateau, on the outskirts of Cairo, Egypt.
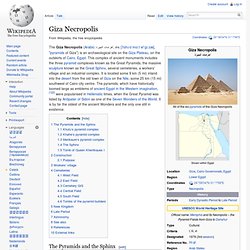
This complex of ancient monuments includes the three pyramid complexes known as the Great Pyramids, the massive sculpture known as the Great Sphinx, several cemeteries, a workers' village and an industrial complex. It is located some 9 km (5 mi) inland into the desert from the old town of Giza on the Nile, some 25 km (15 mi) southwest of Cairo city centre. The pyramids, which have historically loomed large as emblems of ancient Egypt in the Western imagination,[1][2] were popularised in Hellenistic times, when the Great Pyramid was listed by Antipater of Sidon as one of the Seven Wonders of the World. It is by far the oldest of the ancient Wonders and the only one still in existence.