

Tai Dam. Tai Dam, also known as Black Tai (Thai: ภาษาไทดำ; pronounced [pʰāːsǎː tʰāj dām]; "Black Tai language"; Chinese: 傣担语; pinyin: Dǎidānyǔ) is a Tai language spoken by the Tai Dam in Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and China (mostly in the Jinping Miao, Yao, and Dai Autonomous County).
The Tai Dam language is similar to Thai and Lao, but it is not close enough to be readily understood by most Thai and Lao speakers. In particular, the Pali and Sanscrit additions to Thai and Lao are largely missing from Tai Dam.[2] Tai Dam speakers in China are classified as part of the Dai nationality along with almost all the other Tai peoples.
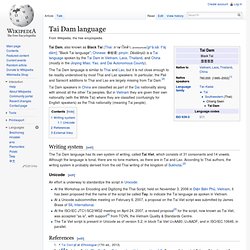
But in Vietnam they are given their own nationality (with the White Tai) where they are classified (confusingly for English speakers) as the Thái nationality (meaning Tai people). Writing system[edit] The Tai Dam language has its own system of writing, called Tai Viet, which consists of 31 consonants and 14 vowels. Unicode[edit] References[edit] External links[edit] Dhivehi. Maldivian ( ދިވެހި divehi) is an Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by about 350,000 people in the Maldives where it is the national language. Spanish. Spanish is a Romance language with approximately 470 million speakers, 410 of whom speak it as a first language, while the remainder speak it as a second language.

A significant number of people also speak Spanish as a foreign language. Uzbek. Uzbek is a Turkic language with about 16.5 million speakers mainly in Uzbekistan. but also in Australia, China, Germany, Israel, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkey (Asia), Turkmenistan, Ukraine and the USA.
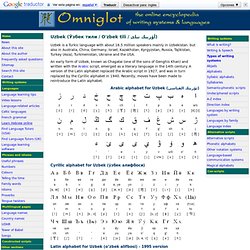
An early form of Uzbek, known as Chagatai (one of the sons of Genghis Khan) and written with the Arabic script, emerged as a literary language in the 14th century. A version of the Latin alphabet replaced the Arabic script in 1927, and was in turn replaced by the Cyrillic alphabet in 1940. Recently, moves have been made to reintroduce the Latin alphabet. Arabic alphabet for Uzbek (ئۇزبېك الفباسى) Cyrillic alphabet for Uzbek (ўзбек алифбоси) Latin alphabet for Uzbek (o’zbek alifbosi) - 1995 version Uzbek sample text. Thai. Thai is a Tai-Kadai language spoken by about 65 million people mainly in Thailand (ประเทศไทย), and also in the Midway Islands, Singapore, the UAE and the USA Thai is closely related to Lao, and northern dialects of Thai are more or less mutually intelligible with Lao, particularly the Lao spoken in northern Thailand.
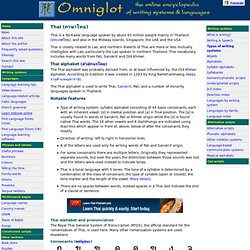
Thai vocabulary includes many words from Pali, Sanskrit and Old Khmer. Thai alphabet (ตัวอักษรไทย) The Thai alphabet was probably derived from, or at least influenced by, the Old Khmer alphabet. According to tradition it was created in 1283 by King Ramkhamhaeng (พ่อขุนรามคำแหงมหาราช). Dzongkha. Dzongkha or Bhutanese is spoken by about 130,000 people in Bhutan, where it is the national language, and also in Nepal and India.
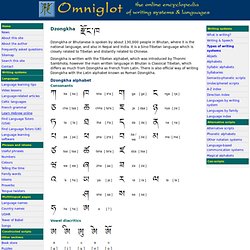
It is a Sino-Tibetan language which is closely related to Tibetan and distantly related to Chinese. Dzongkha is written with the Tibetan alphabet, which was introduced by Thonmi Sambhota, however the main written language in Bhutan is Classical Tibetan, which differs as much from Dzongkha as French from Latin. There is also official way of writing Dzongkha with the Latin alphabet known as Roman Dzongkha. Dzongkha alphabet Consonants Vowel diacritics Conjunct consonants This is a small selection of conjunct consonants, which are used when two consonants occur without a vowel between them.
Sample text in Dzongkha Translation All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. Links. Bengali. Origin The Bengali alphabet is derived from the Brahmi alphabet.
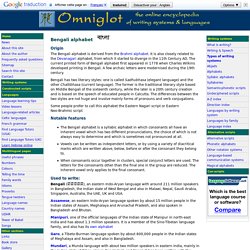
It is also closely related to the Devanagari alphabet, from which it started to diverge in the 11th Century AD. The current printed form of Bengali alphabet first appeared in 1778 when Charles Wilkins developed printing in Bengali. A few archaic letters were modernised during the 19th century. Bengali has two literary styles: one is called Sadhubhasa (elegant language) and the other Chaltibhasa (current language). Some people prefer to call this alphabet the Eastern Nagari script or Eastern Neo-Brahmic script Notable features The Bengali alphabet is a syllabic alphabet in which consonants all have an inherent vowel which has two different pronunciations, the choice of which is not always easy to determine and which is sometimes not pronounced at all.
Used to write: Manipuri, one of the official languages of the Indian state of Manipur in north-east India and has about 1.1 million speakers. Vowels and vowel diacritics Numerals. Hindi. Hindi is an Indo-Aryan language with about 545 million speakers, 425 million of whom are native speakers.
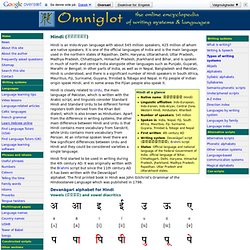
It is one of the official languages of India and is the main language used in the northern states of Rajasthan, Delhi, Haryana, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand and Bihar, and is spoken in much of north and central India alongside other languages such as Punjabi, Gujarati, Marathi or Bengali. In other parts of India, as well as in Nepal, Bangladesh and Pakistan, Hindi is understood, and there is a significant number of Hindi speakers in South Africa, Mauritius, Fiji, Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad & Tobago and Nepal. In Fiji people of Indian origin speak Hindi, and in some areas the Fijian people also speak it. Hindi at a glance Hindi first started to be used in writing during the 4th century AD. Devanāgarī alphabet for Hindi Vowels (स्वर) and vowel diacritics Consonants (व्यंजन) Numerals More Hindi numbers Downloads. Turkish.