

Vinyl, Art, DJs, Living Rooms, Studios, Collections and News. Understanding dance music structure. Introduction : dance music structure : Understanding Dance Music Structure I am referencing demo mp3 files that can be streamed at each stage of the tutorial.

These have been recorded in 8-bit mono to keep download times to a minimum so even if you are on dial up, and need some assistance it should be relatively painless. I have constructed them in a very simplistic manner to speed the learning of DJ-ing concepts and are purely for reference only. I would only recommend listening to them if you are unclear of my descriptions. It should be noted that this is a general tutorial and is not the basis for every tune ever released on vinyl.
Each coloured square represents the Bar number which will each contain four beats. Introduction So you want to get on your decks and mix away like the billy-o. Like a car, dance music is structured in a very ordered fashion. A record can be split into six sections, which in some instances can be broken down further into stages: Stage 1 Open mp3 demo (1 bar) Electronic Music Production. A dance track usually has a looser structure than a hip-hop or pop song — but it does have a structure.
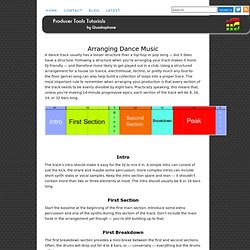
Following a structure when you’re arranging your track makes it more DJ-friendly — and therefore more likely to get played out in a club. Using a structured arrangement for a house (or trance, electrohouse, techno, or pretty much any four-to-the-floor genre) song can also help build a collection of loops into a proper track. The most important rule to remember when arranging your production is that every section of the track needs to be evenly divisible by eight bars. Practically speaking, this means that, unless you’re making 14-minute progressive epics, each section of the track will be 8, 16, 24, or 32 bars long: Intro The track’s intro should make it easy for the DJ to mix it in.
First Section Start the bassline at the beginning of the first main section. Song Structure in Electronic Music and Dubstep. Developing a song is more than just the pieces placed together.
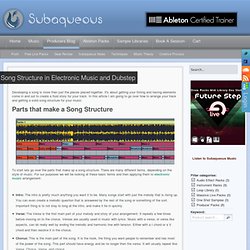
It's about getting your timing and having elements come in and out to create a fluid story for your track. In this article I am going to go over how to arrange your track and getting a solid song structure for your music. Parts that make a Song Structure To start lets go over the parts that make up a song structure. There are many different terms, depending on the style of music. Intro: The intro is pretty much anything you want it to be. The Structure of a Song A typical Pop Song Structure goes Intro, Verse, Chorus, Verse, Chorus, Bridge, Outro. It is fairly simple arrangement starting with intro, repeating main section with some breaks. EQ Frequency Chart For Electronic Music. When talking about well balanced mix, each instrument should have it’s own ‘space’ in the frequency range.
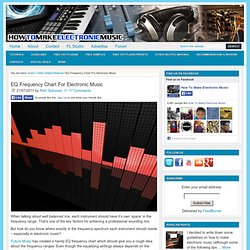
That’s one of the key factors for achieving a professional sounding mix. But how do you know where exactly in the frequency spectrum each instrument should reside – especially in electronic music? Future Music has created a handy EQ frequency chart which should give you a rough idea about the frequency ranges. Even though the equalizing settings always depends on the sounds/melodies you’re using (and your ears), this chart might help you get started.
Guide to Electronic Music. Music Map - La mappa della musica. Generi di musica elettronica. Da Wikipedia, l'enciclopedia libera.
Questo è un elenco dei generi e stili di musica elettronica, di cui molti con relativo approfondimento. Breakbeat/Breaks/Big Beat[modifica | modifica sorgente] Disco/Dance[modifica | modifica sorgente] Downtempo/IDM[modifica | modifica sorgente] The Evolution of Western Dance Music! Definitions of Tempos. What is your natural tempo?
History of Electronic Music. Compiled and annotated by Dr.
Kristine H. Burns 2nd century, BC. The Hydraulis was invented by Ktesibios sometime in the second century B.C. Ktesibios, the son of a Greek barber, was fascinated by pneumatics and wrote an early treatise on the use of hydraulic systems for powering mechanical devices. Greek Aeolian harp. 5th-6th centuries BC, Pythagorus discovered numerical ratios corresponding to intervals of the musical scale. 890 AD Banu Musa was an organ-building treatise; this was the first written documentation of an automatic instrument. ca. 995-1050, Guido of Arezzo, a composer, developed an early form of solmization that used a system of mnemonics to learn "unknown songs. " 1400s The hurdy-gurdy, an organ-grinder-like instrument, was developed. Isorhythmic motets were developed.
Soggetto cavato, a technique of mapping letters of the alphabet into pitches, was developed. 1500s The first mechanically driven organs were built; water organs called hydraulis were in existence. Styles and Tempo of Electronic Music.