

The physical, sexual, cognitive, social, and emotional changes that happen during this transition phase can bring about anticipation and anxiety to both the child and the parents. Therefore parents should better understand what to expect at different developmental stages so as to prepare themselves to deal with the situations that arise. The Stages of Adolescence. Prenatal Pregnancy is a time of anticipation, excitement, preparation, and, for many new parents, uncertainty.
The nine months of pregnancy will give you time to have your questions answered, calm your fears, and prepare yourself for the realities of parenthood. This section contains some guidelines to help you with the most important of these preparations. Baby: 0-12 mos. Operant Conditioning. Operant Conditioning. What does Reinforcement and Punishment means?
Reinforcement and Punishment. Learning Objectives Explain the difference between reinforcement and punishment (including positive and negative reinforcement and positive and negative punishment)Define shapingDifferentiate between primary and secondary reinforcers In discussing operant conditioning, we use several everyday words—positive, negative, reinforcement, and punishment—in a specialized manner.
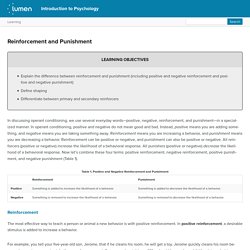
In operant conditioning, positive and negative do not mean good and bad. Instead, positive means you are adding something, and negative means you are taking something away. Reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. Reinforcement & Punishment. Reinforcement vs Punishment Psychology [Examples] Reinforcement and punishment are often used as parenting tools to modify children’s behavior.
![Reinforcement vs Punishment Psychology [Examples]](http://cdn.pearltrees.com/s/pic/th/reinforcement-punishment-183049524)
Let’s review the difference between positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement, and the difference in outcomes between them. The Difference Between Positive And Negative Reinforcement In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is the introduction of a favorable condition that will make the desired behavior more likely to happen, continue or strengthen in the future1. Because the favorable condition acts as a reward, reinforcement is a reward-based operant conditioning. There are two types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement. What Is Reinforcement in Operant Conditioning? One of the many different ways in which people can learn is through a process known as operant conditioning (also known as instrumental conditioning).1 This involves learning through reinforcement or punishment.

The type of reinforcement used can play an important role in how quickly a behavior is learned and the overall strength of the resulting response. Understanding Reinforcement Reinforcement is a term used in operant conditioning to refer to anything that increases the likelihood that a response will occur. Psychologist B.F. Positive Reinforcement and Operant Conditioning. In operant conditioning, positive reinforcement involves the addition of a reinforcing stimulus following a behavior that makes it more likely that the behavior will occur again in the future.

When a favorable outcome, event, or reward occurs after an action, that particular response or behavior will be strengthened. One of the easiest ways to remember positive reinforcement is to think of it as something being added. Example of Positive Reinforcement. Positive Reinforcement - Tips for teaching and parenting. Parenting Children with Positive Reinforcement (Examples + Charts) Children don’t come with instructions and discipline is often experienced by parents and children alike as an arena where our will and wits are tested.
Positive reinforcement is only one of many forms of discipline, but from the perspective of positive psychology, it may as well be the most important one as it focuses on amplifying what is already good in our children and in ourselves as their caretakers. Positive reinforcement as a form of positive discipline allows us to tap into our children’s individual strengths, draw attention to their personality traits and interests, and as a result give us an opportunity to connect, communicate effectively, and ultimately empower them to be more of themselves. Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our 3 Positive Psychology Exercises for free. Negative Reinforcement and Operant Conditioning.
Negative reinforcement is a term described by B.

F. Skinner in his theory of operant conditioning. Example of Negative Reinforcement. Negative Reinforcement: What Is It and How Does It Work? What is negative reinforcement?

Negative reinforcement is a method that can be used to help teach specific behaviors. With negative reinforcement, something uncomfortable or otherwise unpleasant is taken away in response to a stimulus. Positive Punishment and Operant Conditioning. Positive punishment is a concept used in B.F.

Skinner's theory of operant conditioning. How exactly does the positive punishment process work? Example of Positive Punishment. What is Positive Punishment? Real-Life Examples of Positive Punishment. “Positive” and “punishment” seem like two words that you wouldn’t use together.
However, positive punishment will make complete sense once you learn the definition and explore some examples of positive punishment. Review how positive punishment is different from negative punishment and which is more effective. Understanding Positive Punishment. What is Negative Punishment (Examples and Effectiveness) In this article, we will review negative punishment, its definition, examples, and drawbacks. American psychologist B.F. Skinner developed the theory of operant conditioning, which stated that a person or animal’s behavior could be increased or decreased by adding or removing appropriate stimuli after the behavior is exhibited. The difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning is that classical affects unconscious behavior, while operant affects conscious behavior. Within operant, punishment aims to reduce a behavior while reinforcement increase a behavior. Example of Negative Punishment.
Negative Punishment Examples and Scenarios. Nobody ever wants their stuff taken away. That is the main concept behind negative punishment. Using negative punishment example scenarios, gain an understanding of the concept and its effectiveness. Then, go on to explore the difference between positive and negative punishment. Disrespectful teenage behaviour: what to do. About disrespectful behaviour in teenagers Sometimes you might feel that interactions with your child all seem a bit like this: You – ‘How’s that project going?’
Your child – ‘Why are you checking up on me? Don’t you trust me? I always get good marks, so why ask me about it?’