

The tools involved are positive and negative reinforcement and positive and negative punishment. Operant Conditioning (Halonen, 2020) Reinforcement & Punishment. The Difference between Positive/Negative Reinforcement and Positive/Negative Punishment. February 5, 2013 7:40 pm Published by Kelley Prince M.A., BCBA.
What is Reinforcement? What Is Reinforcement? Psychology, Definition, And Applications. By: Toni Hoy Updated February 11, 2021 Medically Reviewed By: Whitney White, MS.
CMHC, NCC., LPC Reinforcement psychology is the study of the effect of reinforcement techniques on behavior. Much of reinforcement psychology is based on the early research of B.F. Source: rawpixel.com. Positive vs Negative Reinforcement: Which Is More Effective? The central premise of Pavlok is getting the user to take action and create a new habit — or change an existing one.
To do this, we built “pattern interrupts” — jarring but effective stimuli — into the device that encouraged users to change their routines. We then faced a difficult question that’s challenged behavioral psychologists for decades. What is Positive Reinforcement? Parenting Children with Positive Reinforcement (Examples + Charts) Children don’t come with instructions and discipline is often experienced by parents and children alike as an arena where our will and wits are tested.
Positive reinforcement is only one of many forms of discipline, but from the perspective of positive psychology, it may as well be the most important one as it focuses on amplifying what is already good in our children and in ourselves as their caretakers. Positive reinforcement as a form of positive discipline allows us to tap into our children’s individual strengths, draw attention to their personality traits and interests, and as a result give us an opportunity to connect, communicate effectively, and ultimately empower them to be more of themselves.
Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our 3 Positive Psychology Exercises for free. You can download the free PDF here. Parenting A Teen Through Positive Reinforcement - Back On Track. Most parents can agree: the teenage years can be rough!
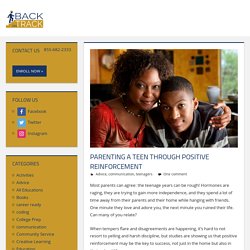
Hormones are raging, they are trying to gain more independence, and they spend a lot of time away from their parents and their home while hanging with friends. One minute they love and adore you, the next minute you ruined their life. The value of reinforcing positive behaviour for our teens. As children approach adolescence, they sometimes begin testing limits, bending the rules and otherwise going against the grain.

While this is normal behaviour for teens, it can be incredibly trying for you, as a parent. Teenagers may also be dealing with the stresses that come with trying to fit in with their peers and assert their growing independence. However, at the same time, they are looking for validation from the adults around them. It's crucial, therefore, for parents and teachers to provide as much guidance and positive reinforcement as possible, rather than simply tightening the rules. While it may be challenging to reward and praise a teen, who may appear to be indifferent to us, it's well worth the effort. BYU Study: a need for positive reinforcement among teens. There are countless publications describing the best ways to raise a child in the hopes of them becoming successful adults.
Between the books, magazines and video tutorials, parents may be finding themselves overwhelmed on more than one occasion. But a group of researchers at Brigham Young University have found the answer to helping children through life may be less complicated than it seems. The BYU study found bad behavior can be discouraged among children by simply encouraging good behavior. The study, Flourishing During the Teen Years: Why “Not Being Bad” Isn’t Good Enough, used information from a 10-year project that followed 500 families in order to see where the individuals struggled and what actions helped them become successful.
When the study began, the children in the families were 11 years old. “For this brief we didn’t look at how these effects changed over time,” wrote Laura Walker, BYU professor and lead researcher of the study. What is Negative Reinforcement? Negative Reinforcement and Operant Conditioning. Negative reinforcement is a term described by B.

F. Skinner in his theory of operant conditioning. What Is 'negative Reinforcement'? Definition And Real-World Examples. You've heard of negative reinforcement, but how do you put it into practice?
These 4 negative reinforcement examples will explain how. Examples in Parenting. What is Punishment? The Study of Punishment in Psychology. Punishment is a term used in operant conditioning to refer to any change that occurs after a behavior that reduces the likelihood that that behavior will occur again in the future.

While positive and negative reinforcements are used to increase behaviors, punishment is focused on reducing or eliminating unwanted behaviors. Punishment is often mistakenly confused with negative reinforcement. The difference: Reinforcement increases the chances that a behavior will occur and punishment decreases the chances that a behavior will occur. Positive vs Negative Punishment - Psychestudy. Punishment is a fundamental concept of Operant Conditioning, whose major objective is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior from occurring again. Punishment can be further classified into two major parts These two different types of punishment have got both similarities and differences, as the major purpose of both these punishment types is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior.
By introducing the concept of punishment to an individual, the individual gets the idea that what he/she is doing, is wrong. Positive and negative punishment, generally speaking, is the concept of adding certain unfavorable consequence or depriving the individual of certain favored item or advantage, in order to decrease the behavior. What Is Punishment Psychology, And Should You Use It? Updated February 01, 2021 Medically Reviewed By: Tanya Harell Source: rawpixel.com We were all punished when we were younger at one time or another.
However, it is how we are punished that can shape how we will behave in the future. Believe it or not, whether you got a spanking for hitting your sister or a pat on the back can decide what kind of person you will be. The Law Of Effect Dr. The Law of Effect was a theory that satisfying responses cause an individual's actions to be repeated, and unwelcome responses cause these actions to occur less often. What is Positive Punishment. Positive Punishment: What It Is, Benefits, and Examples. Positive punishment is a form of behavior modification. In this case, the word “positive” doesn’t refer to something pleasant. Positive punishment is adding something to the mix that will result in an unpleasant consequence. The goal is to decrease the likelihood that the unwanted behavior will happen again in the future. This approach may be effective in certain circumstance, but it’s only one part of the equation.
Guiding your child toward alternative behaviors that are more appropriate to the situation are also needed. Examples in Parenting. 7 Guidelines for using positive punishment. What is Negative Punishment? Negative Punishment - Psychestudy. Negative Punishment Examples and Scenarios.
Nobody ever wants their stuff taken away. That is the main concept behind negative punishment. Which one to use? Adolescent learning: rewards, punishments, and the importance of context. Adolescents’ unique sensitivity to rewards is thought to be due to increased activity in and communication between areas of the brain that respond to rewards. However, we also know that many of the same brain areas also respond to punishment and that there are dynamic changes occurring throughout the brain during adolescence. Much like the complexity of brain development, the story about how adolescents learn from reinforcement might not be so simple. “The way that adolescents learn from the choices that they have made in the past will ultimately influence their future choices and actions.”
An in-depth review of studies examining how we learn from reinforcement across age shows mixed results. Contrary to the idea that adolescents may learn best from rewards, some studies find that adolescents actually learn more from punishment. The context in which learning takes place may be key. Studies conducted to date have subtly varied the learning context in different, specific ways. Which Is Better, Rewards or Punishments? Neither. “I feel a sense of dread as bedtime rolls around. Here we go again.” A dad said this in our family therapy office one day, describing his son’s pre-bed antics. The child would go wild as bedtime approached, stubbornly ignoring his parents’ directions and melting down at the mention of pajamas.
The parents felt frustrated and stumped. Rewarding behavior is key to parenting teens, study suggests. Parenting is hard, and parenting teens brings about an entirely new set of challenges, from keeping their rooms clean to getting them home before curfew. But, a new study suggests parents who want their teenagers to keep their grades up could have better success if they focus more on rewarding good behavior and less on threatening to punish the bad. According to the report, published in PLOS Computational Biology, British researchers have found that adolescents focus well on positive incentives, but have difficulty staying motivated to avoid penalties. The study shows that teens and adults learn in different ways, according to the study’s lead author Stefano Palminteri, a researcher with the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London. It suggests that “in some cases positive feedback may have more of an effect than negative feedback on learning” in adolescents.
Discipline for Teens: Strategies and Challenges. When your child becomes a teenager, your parenting role is likely to shift. You may find yourself becoming more of a guide, rather than an enforcer. That’s not to say your child won’t need you to intervene when there are safety issues or that your teen won’t need consequences. But, by now, it’s OK to let your child make some choices on their own, even when you think it’s a bad choice. References.