

Top scientists warn of 'ghastly future of mass extinction' and climate disrup... Antarctica melting: Journey to the 'doomsday glacier' The images are murky at first.
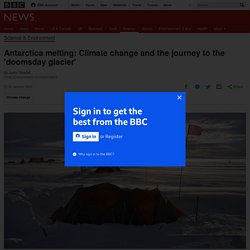
Sediment sweeps past the camera as Icefin, a bright yellow remotely operated robot submarine, moves tentatively forward under the ice. Then the waters begin to clear. Sea Level Rise! - CounterPunch.org. Photograph Source: BrendelSignature – CC BY 3.0 Sea level has been stable, at current levels, throughout recorded history for 5,000 years.
That’s about to change. Still, it’s very difficult for people to imagine a change in sea level after 5,000 years of rock solid stability. Flood Maps. People say climate change is the '10-year challenge' that matters. 'Abrupt thaw' of permafrost beneath lakes could significantly affect climate change models. Methane released by thawing permafrost from some Arctic lakes could significantly accelerate climate change, according to a new University of Alaska Fairbanks-led study.
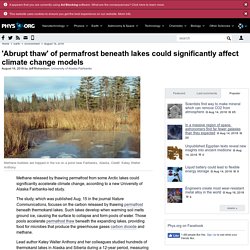
The study, which was published Aug. 15 in the journal Nature Communications, focuses on the carbon released by thawing permafrost beneath thermokarst lakes. Such lakes develop when warming soil melts ground ice, causing the surface to collapse and form pools of water. Those pools accelerate permafrost thaw beneath the expanding lakes, providing food for microbes that produce the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane. What will Earth look like if all its land ice melts? Here's your answer. NASA Satellite Sees Overheated Tropical Forests Oozing with Carbon Dioxide. NASA's latest carbon dioxide-mapping satellite has detected a dramatic spike in the amount of the greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, measuring the largest annual increase Earth has seen in at least 2,000 years.
Carbon Emissions From Soil Could Lead To ‘Unstoppable’ Global Warming. The Doomsday Glacier - Rolling Stone. In the farthest reaches of Antarctica, a nightmare scenario of crumbling ice – and rapidly rising seas – could spell disaster for a warming planet.

Thwaites Glacier in West Antarctica is so remote that only 28 human beings have ever set foot on it. Knut Christianson, a 33-year-old glaciologist at the University of Washington, has been there twice. A few years ago, Christianson and a team of seven scientists traveled more than 1,000 miles from McMurdo Station, the main research base in Antarctica, to spend six weeks on Thwaites, traversing along the flat, featureless prairie of snow and ice in six snowmobiles and two Tucker Sno-Cats.
Future - How Western civilisation could collapse. This story is featured in BBC Future’s “Best of 2017” collection.
Discover more of our picks. The political economist Benjamin Friedman once compared modern Western society to a stable bicycle whose wheels are kept spinning by economic growth. Scientists to EPA head: You don’t know what you’re talking about. Last week, newly appointed EPA head Scott Pruitt made some comments about climate change that were clearly at odds with a basic scientific understanding of the climate.
Since then, various groups of scientists have pointed out just how wrong he was and have offered to help out if he decides to come to grips with reality. Super-warm seas wiped out an entire underwater forest in Australia, scientists report. This year, the tragic die-off of large volumes of coral at the treasured Great Barrier Reef has provided a climate change shock like few others.
The cause was too much warm water — which seems to have pushed the corals past a thermal survival threshold. And that warm water, in turn, is tied to climate change. Now, however, a team of researchers has revealed that another Australian coastal ecosystem that gets less attention — Australia’s kelp-dominated Great Southern Reef, which covers a huge expanse along its more temperate southern and southwestern coast — saw an equally dramatic ecosystem upheaval five years ago.
New Study indicates Sea Level Rise is a Bigger Problem than Previously Estimated. Humans are being wide off the mark regarding severity of global sea level rise, said a team of researchers in a new study published this week in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics.
The study team informed that the planet could experience much more rise in sea levels than previously estimated, thanks to climate change which is going to worsen in the future. The research team said that 2 degree Celsius target set by climate scientists and policymaker isn’t enough. Several nations around the globe have pledged to curb greenhouse gas emissions and limit planet’s warming to 2 degrees Celsius by the next century, but these efforts are not sufficient to control sea level rise, suggested the study published in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. “We are in a position of potentially causing irreparable harm to our children, grandchildren and future generations. This is a complex story, but one with important practical implications”, as per Hansen.
Massive fossil fuels cut is last chance to limit global warming, researchers say. The Point of No Return: Climate Change Nightmares Are Already Here. Historians may look to 2015 as the year when shit really started hitting the fan. InsideClimate News. Surging Seas: Mapping Choices. What | When | Which | How | Who | Legal What Carbon pollution casts a long shadow.
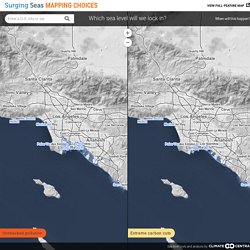
When people burn fossil fuels or clear forests today, the extra carbon we put in the atmosphere stays long enough to add to global warming for thousands of years. Warming won’t just stop when we stop polluting, and neither will sea level rise. The Big Read: Climate change and the fate of Antarctica. A world-renowned climate scientist visiting New Zealand will this week present new evidence suggesting a behemoth "sleeping giant" ice sheet is more sensitive to climate change than we ever thought. To climate scientists, the vast East Antarctic Ice Sheet represents something of the elephant in the room in terms of what it could contribute to global sea level rise. If all of it melted, the ice sheet, which forms most of Antarctica, would contribute an equivalent of around 50 metres of sea level rise - the vast majority of the total 58 metres that could come from the frozen continent. The part of the ice sheet that rests on bedrock below sea level is most vulnerable and holds an equivalent of 19 metres of sea level rise.