

The Waugul: State Library of Western Australia. To the Noongar traditional owners and custodians, Western Australia’s Swan River, the Derbal Yerrigan has remained at the heart of their culture and heritage for more than 40,000 years.

SBS Audio and Language : Aboriginal : Highlight: Swan-Valley-Home-of-the-Waugal. Spirituality. Spirituality for Indigenous Australians takes many forms.
Its forms and practices have been profoundly influenced by the impact of colonialism, both past and present. Carl Bento © Australian Museum Some Indigenous Australians share the religious beliefs and values of religions introduced into Australia from other cultures around the world, particularly Europe. But for most people religious beliefs are derived from a sense of belonging-to the land, to the sea, to other people, to one's culture. Freedom Rider: Aboriginal Righteous Anger. Printer-friendly version by BAR editor and senior columnist Margaret Kimberley Australia’s aboriginals – her original people – were nearly wiped out by the invading British, starting in 1788.
“Their lands were stolen, they were killed by new diseases, and even their children were taken from them as late as the 20th century.” A recent aboriginal demonstration frightened Australia’s prime minister, prompting accusations that the aboriginals were showing bad manners. But, “What are bad manners in comparison to genocide?” The Koori History Website. SBS: First Australians. Sorry Day and the Stolen Generations.
Warning.

This article may contain the names and images of Aboriginal and Islander people now deceased. It also contains links to sites that may use images of Aboriginal and Islander people now deceased. Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission, report. The history of the Aboriginal Tent Embassy. Updated 27 Jan 2012, 2:50amFri 27 Jan 2012, 2:50am Gallery: Aboriginal Tent Embassy The Aboriginal Tent Embassy was founded on Australia Day in 1972 to protest the decision by the McMahon Liberal government to reject a proposal for Aboriginal Land rights.
The government instead planned to implement a lease system, conditional on the ability of Indigenous people to make economic and social use of the land, and excluding rights to mineral and forestry resources. Four Indigenous activists - Michael Anderson, Billy Craigie, Bertie Williams and Tony Coorey - set up the protest at 1.00am under a beach umbrella on the lawns of Parliament House (Old Parliament House). The movement quickly gained traction, with more and more tents being erected and numbers at one point swelling to 2,000. On July 20, after the Government modified a law relating to trespass on Commonwealth lands, Police moved in and forcibly dismantled the embassy. Collaborating for Indigenous Rights 1957-1973. Mission Voices. Koorie Heritage Trust. Indigenous_res010_0802. What are Aboriginal Ceremonies about? Aboriginal Ceremonies have been the means of keeping the Australian Aboriginal culture intact for thousands of years.
They are used to pass on rules and laws that are believed to have been handed down by the Dreamtime spirits. They are a part of life for those where the culture remains intact in the Northern Territory, Western and Eastern Desert tribes, Tiwi Islanders and in the Kimberley tribes of Western Australia. Although they take different forms in different areas Aboriginals believe Creation sprits took human and animal form and left rules and laws. They created features of the landscape as they moved across it. They also left ancestral teachings about tools, hunting laws, ceremonies and a totemic system among the tribes. OzOutback - The Real Australia: Aboriginal Ceremonies from Northern Australia. Weird, Wacky and Wonderful : Aboriginal Dreaming.
Indigenous Australiana Beliefs. Aboriginal Culture. When discussing specific ceremonies it is important to have a local Aboriginal person present.
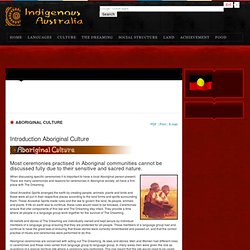
There are many ceremonies and reasons for ceremonies in Aboriginal society, all have a firm place with The Dreaming. Great Ancestral Spirits arranged the earth by creating people, animals, plants and birds and these were all put in their respective places according to the land forms and spirits surrounding them. These Ancestral Spirits made rules and the law to govern the land, its people, animals and plants. If life on earth was to continue, these rules would need to be followed. Heritage and Culture - Welcome to DIA - Department of Indigenous Affairs. An Interview with Ray Minniecon By Brenda Paik Sunoo. Aboriginal Culture and Grief: An Interview with Ray Minniecon By: Brenda Paik Sunoo December 2001 My name is Ray Minniecon.

I come from the Kabi Kabi people in Queensland And I'm head of Indigenous Programs for World Vision, Australia. You've asked: What are some Aboriginal beliefs/customs of death, dying, grief and the afterlife? It varies place to place. The Dreaming. Aboriginal dancers telling Dreamtime stories at the Sydney Olympics opening ceremony.
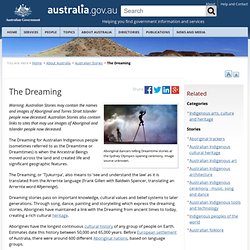
Image source unknown. Warning. Aboriginal Culture - About this site. Welcome to aboriginalculture.com.au Australian Aboriginal culture varies throughout the continent and people from different regions have different Ancestral Beings, different tools, weapons, basketry and different art styles.

Since the arrival of Macassan (Indonesian) on northern Australian shores after 1700 AD, and later European colonisation in 1788, Aboriginal culture has evolved and changed further. This site looks at how Aboriginal culture was at the time of European arrival, beginning with the record of a man who was shipwrecked in 1846 and survived 17 years with Aborigines in northern Queensland. This account is combined with images from the same region taken from the 1890s. Click on “Regional Studies” to see how people lived at this time. Aboriginal Spirituality: Aboriginal Culture & People at Central Art - Aboriginal Art Store.
Aboriginal spirituality lies in the belief in a cultural landscape. Everything on the vast desert landscape has meaning and purpose. The land is both an external landscape and an 'in scape' – an internal relationship with the Creator. Landmarks are both metaphysical and physical. As an example Uluru can be seen as an epic poem, a source of sacred law, a physical landmark and a repository of knowledge. Aboriginal people view life as a web of inter relationships where man and nature are partners. The acrylic paintings reflect this spirituality. The Desert Art ultimately is religious art, a document that maintains the records of complex belief system.