

Egyptian pyramids. A view of the pyramids at Giza from the plateau to the south of the complex.
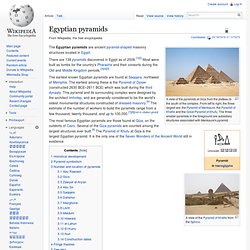
From left to right, the three largest are: the Pyramid of Menkaure, the Pyramid of Khafre and the Great Pyramid of Khufu. The three smaller pyramids in the foreground are subsidiary structures associated with Menkaure's pyramid. There are 138 pyramids discovered in Egypt as of 2008.[1][2] Most were built as tombs for the country's Pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.[3][4][5] The earliest known Egyptian pyramids are found at Saqqara, northwest of Memphis. The Wisdom of the Egyptians: Chapter III: The Ptah-Hotep And The Ke'gemni: The Oldest Books In The World. Sacred Texts Egypt Index Previous Next p. 93 THE Instructions of Ptah-hotep and of Ke'gemni possess, apart from the curious nature of their contents, a feature of the greatest interest, and an adequate claim on the notice of all persons interested in literature and its history.

For if the datings and ascriptions in them be accepted as trustworthy--there is no reason why they should not be accepted--they were composed about four thousand years before Christ, and three thousand five hundred and fifty years before Christ, respectively. The Light of Egypt or the Science of the Soul and the Stars. Great Sphinx of Giza. The Great Sphinx of Giza, 2008 It is the largest monolith statue in the world, standing 73.5 metres (241 ft) long, 19.3 metres (63 ft) wide, and 20.22 m (66.34 ft) high.[1] It is the oldest known monumental sculpture, and is commonly believed to have been built by ancient Egyptians of the Old Kingdom during the reign of the Pharaoh Khafra (c. 2558–2532 BC).[1][2] Origin and identity The Great Sphinx partly under the sand, ca. 1870's.
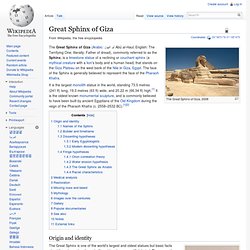
The Great Sphinx is one of the world's largest and oldest statues but basic facts about it, such as when it was built, and by whom, are still debated. Ancient Egyptian creation myths. The sun rises over the circular mound of creation as goddesses pour out the primeval waters around it Ancient Egyptian creation myths are the ancient Egyptian accounts of the creation of the world.
The Pyramid Texts, tomb wall decorations and writings, dating back to the Old Kingdom (2780 – 2250 B.C.E) have given us most of our information regarding early Egyptian creation myths.[1] These myths also form the earliest religious compilations in the world.[2] The ancient Egyptians had many creator gods and associated legends. History of ancient Egypt. The history of Ancient Egypt spans the period from the early predynastic settlements of the northern Nile Valley to the Roman conquest in 30 BC.
The Pharaonic Period is dated from around 3200 BC, when Lower and Upper Egypt became a unified state, until the country fell under Greek rule in 332 BC. Chronology[edit] Note For alternative 'revisions' to the chronology of Egypt, see Egyptian chronology. Egypt's history is split into several different periods according to the ruling dynasty of each pharaoh.
Predynastic Period (Prior to 3100 BC)Protodynastic Period (Approximately 3100–3000 BC)Early Dynastic Period (1st–2nd Dynasties)Old Kingdom (3rd–6th Dynasties)First Intermediate Period (7th–11th Dynasties)Middle Kingdom (12th–13th Dynasties)Second Intermediate Period (14th–17th Dynasties)New Kingdom (18th–20th Dynasties)Third Intermediate Period (21st–25th Dynasties) (also known as the Libyan Period)Late Period (26th–31st Dynasties) Neolithic Egypt[edit] Neolithic period[edit] Dynastic Egypt[edit] The Ancient Egypt Site - The History, Language and Culture of Ph. The Relationship Between The Great Pyramid and the Book of the D. The Relationship Between The Great Pyramid and The Book of the Dead It has been proposed that the Great Pyramid of Giza is the Egyptian “Book of the Dead” symbolized in stone.

Marsham Adams first proposed this in 1895. “The intimate connection between the secret doctrine of Egypt’s most venerated books, and the secret significance of her most venerable monument, seems impossible to separate, and each form illustrates and interpenetrates the other. Alexander Ancient Art - An Amulet of Ptaikos on Crocodiles.
This is a relatively rare Egyptian amulet showing Ptaikos, a god (or perhaps a member of a whole group of similarly looking gods) who gave protection.

Ptaikos is generally depicted as a dwarf with a fat belly and short crooked legs. In many cases, like on this amulet, he is shown standing on crocodiles (a symbol of his triumph over them) and having snakes or other dangerous animals in his hands. Wadjet. Two images of Wadjet appear on this carved wall in the Hatshepsut Temple at Luxor.
Ptah. Ptah, the Universal Architect God The Memphis triad consisted of the universal architect god, Ptah, patron of masons, his consort Sekhmet, the lion-headed one (sometimes Bast the cat goddess), and Nefertum/Imhotep, their son, who was also a healer god.

Ra. Ra /rɑː/[1] or Re /reɪ/ (Egyptian: 𓂋ꜥ, rˤ) is the ancient Egyptian solar deity.
By the Fifth Dynasty (2494 to 2345 BC) he had become a major god in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the midday sun. The meaning of the name is uncertain, but it is thought that if not a word for 'sun' it may be a variant of or linked to words meaning 'creative power' and 'creator'.[2] In later Egyptian dynastic times, Ra was merged with the god Horus, as Re-Horakhty ("Ra, who is Horus of the Two Horizons"). He was believed to rule in all parts of the created world: the sky, the earth, and the underworld.[3] He was associated with the falcon or hawk.
When in the New Kingdom the god Amun rose to prominence he was fused with Ra as Amun-Ra. All forms of life were believed to have been created by Ra, who called each of them into existence by speaking their secret names. Role[edit] Eye of Horus. The Wedjat, later called The Eye of Horus The Eye of Horus is an ancient Egyptian symbol of protection, royal power and good health. The eye is personified in the goddess Wadjet (also written as Wedjat,[1][2][3] or "Udjat",[4] Uadjet, Wedjoyet, Edjo or Uto[5]). Egyptian God-Thoth. Ptah - Wepwawet Wiki.