

Yahoo - Connexion. The dystopian lake filled by the world’s tech lust. From where I'm standing, the city-sized Baogang Steel and Rare Earth complex dominates the horizon, its endless cooling towers and chimneys reaching up into grey, washed-out sky.
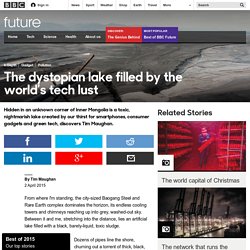
Between it and me, stretching into the distance, lies an artificial lake filled with a black, barely-liquid, toxic sludge. Best of 2015 Our top stories Dozens of pipes line the shore, churning out a torrent of thick, black, chemical waste from the refineries that surround the lake. The smell of sulphur and the roar of the pipes invades my senses. Welcome to Baotou, the largest industrial city in Inner Mongolia. You may not have heard of Baotou, but the mines and factories here help to keep our modern lives ticking.
Element of success Rare earth minerals have played a key role in the transformation and explosive growth of China's world-beating economy over the last few decades. In 1950, before rare earth mining started in earnest, the city had a population of 97,000. Quiet plant. The Bolivian women who knit parts for hearts - BBC News. Traditional craft skills are helping to save the lives of children born with heart defects in Bolivia.
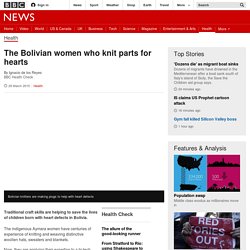
The indigenous Aymara women have centuries of experience of knitting and weaving distinctive woollen hats, sweaters and blankets. Now, they are applying their expertise to a hi-tech medical product - which is used to seal up a "hole in the heart" which some babies are born with. "We are very happy, we are doing something for someone so they can live," says knitter Daniela Mendoza, who weaves the tiny device in a special "clean room". It takes her about two hours to make the Nit Occlud device which was designed by cardiologist Franz Freudenthal.
He set up his clinic in La Paz to help children born with heart problems and so far he has saved hundreds of lives. The device, known as an occluder, looks similar to a top hat and is used to block the hole in the patient's heart. So he enlisted an army of Bolivia's traditional craft knitters to make them by hand. A device with memory. Earth - Ten shocking animal diseases that may threaten species. It's not just humans that have to deal with epidemics.
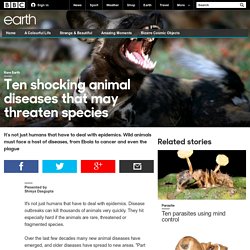
Disease outbreaks can kill thousands of animals very quickly. They hit especially hard if the animals are rare, threatened or fragmented species. Over the last few decades many new animal diseases have emerged, and older diseases have spread to new areas. "Part of this is due to increased trade and travel, which brings pathogens to new regions," says A. Marm Kilpatrick of the University of California, Santa Cruz. The biggest threat to wildlife is still loss of habitat, often triggered by the growth of farmland. Here are ten diseases that are taking a heavy toll on wild animals. 1. We think of Ebola as a human disease, and with good reason. In the early 1990s, the disease ravaged groups of chimpanzees living in Taï National Park in Côte d'Ivoire.
The ebola virus strikes both species hard. Ebola's effects can be particularly devastating when combined with other threats like hunting and deforestation. Earth - Ten sinister parasites that control their hosts' minds. Zombie ant fungus (Ophiocordyceps unilateralis) Ants are great navigators, following highly efficient paths as they forage for food.
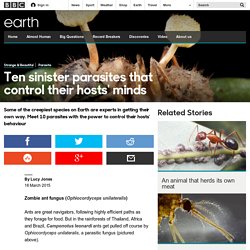
But in the rainforests of Thailand, Africa and Brazil, Camponotus leonardi ants get pulled off course by Ophiocordyceps unilateralis, a parasitic fungus (pictured above). A spore first infects an ant foraging on the rainforest floor, then spends 3-9 days developing inside its body. When the fungus is ready to complete its life cycle, it manipulates the worker to plod blindly away from safety, like a zombie. A study in 2009 found that the ants always went to similar locations: around 25 cm up a tree, in a spot with just the right amount of humidity for the fungus to grow. Within 24 hours, fungal threads emerge from the corpse. Kamikaze horsehair worm (Paragordius tricuspidatus) One of these worms can grow up to a foot long, and look like a cooked piece of spaghetti. Environmental Sex Determination - Developmental Biology - NCBI Bookshelf.
Where Is Our Charlie Hebdo? Americans Don’t Know Real Satire. In one of the last interviews he granted, the late novelist talked about everything from fiction to the varying definitions of faith.
Until he died in his sleep on Saturday, at the age of 77, Robert Stone was my favorite living American author. The Sex of Offspring Is Determined by Particular Chromosomes. By the 1880s, scientists had established methods for staining chromosomes so that they could be easily visualized using a simple light microscope.
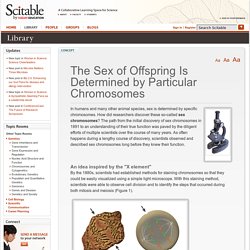
With this staining method, scientists were able to observe cell division and to identify the steps that occurred during both mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). The first indication that sex chromosomes were distinct from other chromosomes came from experiments conducted by German biologist Hermann Henking in 1891. While using a light microscope to study sperm formation in wasps, Henking noticed that some wasp sperm cells had 12 chromosomes, while others had only 11 chromosomes. Biology and life science. Environmental Sex Determination - Developmental Biology - NCBI Bookshelf. Environmental Sex Determination - Developmental Biology - NCBI Bookshelf.