

ZH: Greatest Naval Explorer You Never Knew? China's Zheng He. Age of Exploration. The Silk Road: Connecting the ancient world through trade - Shannon Harris Castelo. Ancient Shipwrecks In The Mediterranean Provide Insights Into The Start Of Global Trade Kids News Article. Historians have long suspected that the Eastern Mediterranean Sea, a popular ancient shipping route, is home to numerous shipwrecks.
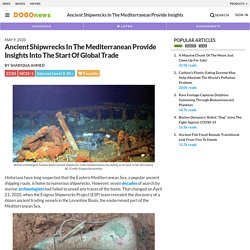
However, seven decades of search by marine archeologists had failed to unveil any traces of the boats. That changed on April 21, 2020, when the Enigma Shipwrecks Project (ESP) team revealed the discovery of a dozen ancient trading vessels in the Levantine Basin, the easternmost part of the Mediterranean Sea. Even more exciting, the shipwrecks comprise a mix of Hellenistic, Roman, early Islamic, and Ottoman boats dating back between the 3rd century B.C. to the 19th century, providing historians new insights into the evolution of trade along one of the world's most popular ancient shipping routes.
Sean Kingsley, director of the Centre for East-West Maritime Exploration and one of ESP's lead archeologists, said: "This is truly ground-breaking, one the most incredible discoveries under the Mediterranean. " First Contacts. LisaHillSchoolStuff - Frances Drake. Sir Frances Drake was an English sea captain who is famous for being the second person to sail all the way around the world and for defeating the Spanish Armada in a war against Spain.
He was a hero to the English but the Spanish thought he was a pirate. This is because he attacked many of their ships and towns and stole their treasure. The English government liked him doing this because they were at war with Spain and so they made it legal for him to do it, as long as he gave some of the treasure to them. LisaHillSchoolStuff - Willem Janszoon. Willem Janszoon (sometimes spelt Jansz) (c. 1570–1630) was a Dutch navigator and he was the first European known to have seen the coast of Australia.
In 1606 he made the first recorded European landing on the Australian continent, but he did not know that he had done this. He thought he was in New Guinea. {*style:<br>*}{*style:<br>*}{*style:<b>*}First voyage to Australia{*style:</b>*}{*style:<br>*}In 1603 he set sail aboard the {*style:<i>*}Duyfken{*style:</i>*} (or {*style:<i>*}Duijfken{*style:</i>*}, meaning “Little Dove”), and went to search for new places to trade in New Guinea and other places which the Dutch thought existed but did not know where they were. {*style:<br>*} From New Guinea Janszoon sailed into the Gulf of Carpentaria on the northern tip of Queensland. In 1606 he became the first European to set foot on Australian land when he landed on the western shore of Cape York in Queensland, near where Weipa is now.
Janszoon maps northern Australian coast. Dutch East India Company During the 16th and early 17th centuries, European competition for control of trade in Asia was fierce.

Until the late 1500s, the Portuguese dominated trade in South-East Asia with the help of Spanish and other international interests. However, in 1568, 17 of the northern Dutch provinces went to war with the Spanish. This led to instability between the Portuguese and the Dutch and, after 1590 while Portugal was briefly controlled by the Spanish, Portuguese traders were forced to close their ports to Dutch merchants. To undermine the Spanish and find a way to make independent trade profits, Dutch traders began to compete with the Portuguese, sending private fleets of vessels to the ‘East Indies’ (now Indonesia) to forcibly take over Portuguese settlements, create new Dutch ports and trade with local people.
LisaHillSchoolStuff - William Dampier. William Dampier was an English buccaneer*.
He was also a sea captain, and a naturalist (someone who studies plants and animals) and he wrote books about his travels which were very popular.First landing in Australia He was the first Englishman to make landfall in Australia, landing on the North West coast of Western Australia near King Sound in 1688 in a ship called the Cygnet. He stayed there for a while because his ship needed repairs. When he got back to England and wrote a book about his travels, the king and queen were so impressed that he was given command of a Royal Navy ship called the Roebuck and sent back to discover more about Australia.Second landing in Australia He returned in 1699 in a ship called HMS Roebuck. His mission was to explore the east coast of Australia (which was called New Holland in those days). He landed at Shark Bay in Western Australia and started exploring. References. Navigation in Ancient Times.
Explorers at sea. Ancient mariners navigated around the ocean using various tools!

Check out these great sites related to navigation during the Age of Exploration: : Create some of your own tools for navigation. astrolabe compass quadrant. Digital Classroom: Cuyp portrait of Tasman and family. LisaHillSchoolStuff - Ferdinand Magellan.
Hartog. Maps.