

MNIST Demos on Yann LeCun's website. Convolutional Neural Networks are are a special kind of multi-layer neural networks.

Like almost every other neural networks they are trained with a version of the back-propagation algorithm. Where they differ is in the architecture. Convolutional Neural Networks are designed to recognize visual patterns directly from pixel images with minimal preprocessing. They can recognize patterns with extreme variability (such as handwritten characters), and with robustness to distortions and simple geometric transformations. LeNet-5 is our latest convolutional network designed for handwritten and machine-printed character recognition. Many more examples are available in the column on the left: Several papers on LeNet and convolutional networks are available on my publication page:[LeCun et al., 1998]Y. Xabier.barandiaran.net. Logistic function. Standard logistic sigmoid function A logistic function or logistic curve is a common "S" shape (sigmoid curve), with equation: where For values of x in the range of real numbers from −∞ to +∞, the S-curve shown on the right is obtained (with the graph of f approaching L as x approaches +∞ and approaching zero as x approaches −∞).
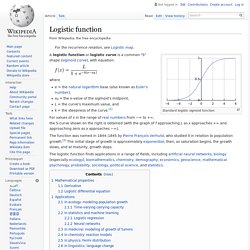
The function was named in 1844–1845 by Pierre François Verhulst, who studied it in relation to population growth.[2] The initial stage of growth is approximately exponential; then, as saturation begins, the growth slows, and at maturity, growth stops. The logistic function finds applications in a range of fields, including artificial neural networks, biology (especially ecology), biomathematics, chemistry, demography, economics, geoscience, mathematical psychology, probability, sociology, political science, and statistics.
Mathematical properties[edit] Derivative[edit] The standard logistic function (k = 1, x0 = 0, L = 1) has an easily calculated derivative: Category:Neural networks. LARAL - index_it. About Ronja. What is Ronja?

Ronja (Reasonable Optical Near Joint Access) is an User Controlled Technology (like Free Software) project of optical point-to-point data link. The device has 1.4km range and has stable 10Mbps full duplex data rate. Ronja is an optoelectronic device you can mount on your house and connect your PC, home or office network with other networks. Or you can use it as a general purpose wireless link for building any other networking project. The design is released under the GNU Free Documentation License: you get all the necessary documentation and construction guides free. User Approach Output of Ronja project is a design.
If you are interested in the device, then visit the homepage, buy components and make the device yourself. The device One Ronja device is a single long-distance optical transceiver that is capable of running against the same or compatible device on the other side of the link. Ronja is somewhat labour expensive. But there are also certain conveniences: LUGS Slides. Eliezer S. Yudkowsky. MNIST handwritten digit database, Yann LeCun and Corinna Cortes. Of handwritten digits Yann LeCun, Courant Institute, NYU Corinna Cortes, Google Labs, New York Christopher J.C.

Burges, Microsoft Research, Redmond The MNIST database of handwritten digits, available from this page, has a training set of 60,000 examples, and a test set of 10,000 examples. It is a good database for people who want to try learning techniques and pattern recognition methods on real-world data while spending minimal efforts on preprocessing and formatting. MNIST Demos on Yann LeCun's website. Convolutional Neural Networks are are a special kind of multi-layer neural networks.

Like almost every other neural networks they are trained with a version of the back-propagation algorithm. Where they differ is in the architecture. Convolutional Neural Networks are designed to recognize visual patterns directly from pixel images with minimal preprocessing. They can recognize patterns with extreme variability (such as handwritten characters), and with robustness to distortions and simple geometric transformations. LeNet-5 is our latest convolutional network designed for handwritten and machine-printed character recognition. Many more examples are available in the column on the left: Several papers on LeNet and convolutional networks are available on my publication page:[LeCun et al., 1998]Y. Education robot. CoDE Department, Université Libre de Bruxelles. Artificial Autonomy Workshop (AlifeX) ITALK - Integration and Transfer of Action and Language Knowledge in Robots.
Nathaniel Virgo. Journal of Machine Learning Research Homepage.