

The Thousand-Year Graveyard. Badia Pozzeveri Churchyard, Altopascio, Italy—On a hot afternoon in July 2012, Giuseppe Vercellotti was digging up bones near the wall of an abandoned medieval church here, thinking about getting a cold drink, when he heard his students call his name. Faces glistening with sweat, they told him that they had found something strange buried half a meter down. Vercellotti took a look and saw a layer of lime, used in ancient times to squelch the stench of rotting corpses. When he tapped the hard layer with his trowel, it sounded hollow. “We immediately thought it was a mass grave,” says Vercellotti, a biological anthropologist at Ohio State University, Columbus, who co-leads a field school here. “We instructors were all excited and hopeful.” But the students were apprehensive: “They all started talking about possible contagion,” Vercellotti says.
It was the end of the summer field season. Ancient History. Long Time Gone. A Long Time Ago. Bygone Days. Once Upon A Time. Ancient cultures. CIVILISATION. Ancient Society Research Resources. Ancient Civilizations. Ancient Civilizations. Civilizations. Source Evaluation. Readings & Flowcharts. Search.
History Timeline. Timelines of History, Today in History, World History. History: a timeline. Visualise the key events of stories. Antiquity. Moyen-Orient. Protohistoire. Internet History Sourcebooks Project. Best of History Web Sites. L'Histoire à la carte : un atlas historique multimédia constitué de cartes animées pour mieux comprendre l'Histoire. L'Histoire par l'image.
World History : HyperHistory. Dead Ideas: The History of Extinct Thoughts and Practices – The Weird World History of Ideas Once Believed To Be True, From Ancient History to Modern History. Histoire. Histoire. Histoire Mondiale. Storia. History.
History. History. History. Histoire. History and Historians. Divers histoire. History (H&G) History. History Map Archive. Browse the Map Archive The art and history of cartography, aka mapmaking, goes back to ancient times.
Or at least what they thought it could look like. Our English word map derives from the Latin word mappa, meaning napkin or cloth on which maps were drawn. The Map Archive This map collection is indexed chronologically and by continent. Periodis Web - Maps to be Used for the History of Europe. Euratlas Periodis Web shows the history of Europe through a sequence of 21 historical maps, every map depicting the political situation at the end of each century.
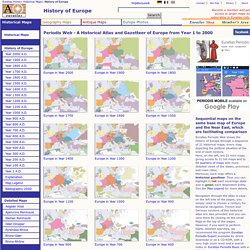
Here, on the left, are 21 mini-maps giving access to 21 full maps and to 84 quarters of maps with more detailed views of the states, provinces and main cities.Moreover, each map offers a historical gazetteer. Thus you can highlight in red each sovereign state and in green each dependent entity. See the Map Legend for more details. Navigation through the atlas is easy: on the left side of the pages, you simply need to choose a century for temporal navigation.
Ancient Society Research Resources. Reconstructing the story of humanity's past. Ancient History Encyclopedia. Aryan migration: New genetic study makes Out of India theory backed by Hindutva supporters unlikely. A new paper authored by 92 scientists from around the globe that was posted online this weekend could settle some major questions about the subcontinent’s history and what that means for various theories of Indian civilisation.

The paper, titled “The Genomic Formation of South and Central Asia” which still has to go through peer review, uses genetics to examine the ancestry of ancient inhabitants of the subcontinent. Below is a quick summary of what you need to know. Who authored the study? AWOL - The Ancient World Online: From Bactria to Taxila: A database of resources on Hellenistic and Imperial Central Asian studies. [First posted in AWOL 24 July 2012, updated 31 March 2017] From Bactria to Taxila: A database of resources on Hellenistic and Imperial Central Asian studies By Antoine Simonin About the projectThe web is a fantastic tool, whose applications and implications are progressing at an exponential rate.

So are the studies on Hellenistic and Imperial Central Asia, that really have begun to develop in the 70s and are increasing since the last twenty years. Impero di Alessandro Magno. Ancient Athens. Vari House, Greece - archaeological recreations and simulations - The Institute for the Visualization of History. Combien d'humains ont vécu sur Terre au total ?La Géothèque. Si tous les humains ressuscitaient, les humains d’aujourd’hui seraient-ils dispersés au milieu d’une foule d’hommes préhistoriques ?

Le chiffre total d’êtres humains à s’être succédé sur la Terre n’est pas très intéressant, en raison d’une mortalité infantile très élevée jusqu’aux périodes récentes. History of Spices - McCormick Science Institute. Abundant anecdotal information documents the historical use of herbs and spices for their health benefits (1).
Early documentation suggests that hunters and gatherers wrapped meat in the leaves of bushes, accidentally discovering that this process enhanced the taste of the meat, as did certain nuts, seeds, berries, and bark. Over the years, spices and herbs were used for medicinal purposes. Spices and herbs were also used as a way to mask unpleasant tastes and odors of food, and later, to keep food fresh (2).
Ancient civilizations did not distinguish between those spices and herbs used for flavoring from those used for medicinal purposes. The 10 oldest cities in the world. There’s a certain aesthetic attached to the oldest cities in the world: bustling souks beneath a bright blue sky, flowing garments made of whispery white cotton, stone masonry painted yellow by the sun.
In reality, however, the oldest cities in the world have faced deep unrest throughout their long histories. Top 10 Worst Plagues In History. Health History is dotted with epidemics and plagues, but a certain number of them stand out as unique for their severity and impact on future generations.
This is a list of the worst plagues in man’s recorded history. Historical Kingdoms/Names. Le projet symogih.org : un système modulaire de gestion de l'information historique. Data for History Consortium. ETRUSQUES. Tages - studi sulla Tuscia. The Roman Domus. The Roman domus was much more than a place of dwelling for a Roman familia.
It also served as a place of business and a religious center for worship. The size of a domus could range from a very small house to a luxurious mansion. Crash Course: Evolution of the Roman Military. Accorded by some as being the most effective and long-lived military institution known to history, Rome’s military was the key to its rise from a relative backwater settlement in Italy to the most dominant power of the ancient world. Throughout its millennia-spanning history, Rome’s military underwent substantial changes as it contended with challenges both within its expanding borders and from neighboring adversaries who threatened to harm the integrity of its borders.
Here is a crash course on the evolution of the Roman military. Phase I (c. 753 BC – c. 578 BC) Phase II (578 BC – c. 315 BC) The Etruscans occupied the cow stealing menace and brought civilization. Roman Army - Recruitment, Legions, Siege Warfare & More. Evolution of the Roman Army: Recruitment of Soliders for the Roman Army: The Roman army changed over time. The consuls had the power to recruit troops, but in the last years of the Republic, provincial governors were replacing troops without the approval of the consuls.
Johnstons' Private Life of the Romans. Food in the Roman World. The ancient Mediterranean diet revolved around four staples, which, even today, continue to dominate restaurant menus and kitchen tables: cereals, vegetables, olive oil and wine. Seafood, cheese, eggs, meat and many types of fruit were also available to those who could afford it. The Romans were also adept at processing and conserving their food using techniques from pickling to storage in honey. Dormice, ostrich meat and fresh fish: the surprising foods eaten in ancient Rome - HistoryExtra. We often think of the Mediterranean triad – bread, wine and olive oil – as the diet of most Romans, but in fact food in ancient Rome was much more diverse.
And within each food type there was a range of goods suited to fit every financial budget: cheap local plonk or expensive Falernian wine from the Bay of Naples; home grown pot-herbs or exotic seasonings from India, and traditional salted pork or the coveted salted tuna from Spain. Consumption practices in ancient Rome, too, ranged from the traditional to the truly exotic. Conversely, another myth surrounding Roman food and eating practices claims the Romans held elaborate banquets where bears, smelly fish sauce and even dormice were eaten. The exaggeration and perpetuation of these stories is primarily due to the fact that the Romans themselves were, on occasion, both fascinated and disgusted by their own eating habits, and so wrote them down. Food for sale. A LA MODE. Riciclaggio della memoria: Persecuzioni contro i cristiani e bugie "religiose" di convenienza, in verità i "cristiani" non furono mai perseguitati da Roma.
Ante Scriptum di Paolo D'ArpiniSul tema della "persecuzione" dei primi cristiani da parte delle autorità romane mi ero già espresso in altri articoli. 2009 Les « religions orientales » dans le monde grec et romain. La catégorie des "religions orientales" appartient au contexte épistémologique et culturel du début du XXe siècle. Archeologia, egittologia, storia. Animated GIFs Show 7 Ancient Ruins 'Reconstructed' The Classics Pages. You'll find well over 1000 pages of news, information, games and controversy about the life, literature, philosophy, art and archaeology of the ancient world of Greece & Rome. Search The Classics Pages (including "The Romans" - below) has a dedicated search engine, accessible from any page. Search now. Email The Classics Pages welcomes your emails - whether you want to comment, query or argue.
Bookshop. Bibliotheca Classica Selecta. Epigraphie. The Middle Ages: a study. Bisanzio. Byzance et l'Europe carolingienne. Anne Comnène. Anne Comnène (en grec : Άννα Κομνηνή, parfois transcrit Comnena ou Komnene[1]) est une historienne et princesse byzantine (1er ou 2 décembre 1083 à Constantinople[2] - v. 1153), premier enfant de l’empereur Alexis Ier (1058-1118) et de l’impératrice Irène Doukas (ou, selon l'usage grec, « Doukaina »). Dans le but de rapprocher les deux familles, elle fut fiancée peu après sa naissance à Constantin Doukas, fils que Marie d'Alanie avait eu de Michel VII. L'islam: pouvoirs, sociétés, cultures. Phantom time hypothesis. Did the Early Middle Ages Really Exist? L'ordre seigneurial.
L'affirmation de l'État monarchique. Templiers, Cathares & Co. Les Templiers. Ordre des Templiers. Chevalerie. Les «Guerres de religion» sont-elles des guerres de religion ? L’expression « guerres de religion » était inconnue des hommes et des femmes qui ont vécu aux XVIe et XVIIe siècles. Annalistes et chroniqueurs employaient d’autres formules pour désigner les troubles de leur temps.
En 1572, Jean Touchard parle de « guerres intestines ». Jean Heluïs, en 1573, évoque les « guerres civiles meües pour le fait de la religion ». Jean Le Frère, de Laval, la même année, emploie les termes « troubles et guerres civiles… pour le faict de la religion ». Un peu plus tard, dans son Histoire de la ville de Montauban (1668), Henry Lebret parle des « guerres de la religion », une expression assez proche de celle qui s’est imposée. L’Inquisition. Le pape (Sixte IV) et l'inquisiteur (Torquemada) par Jean-Paul Laurens. Medieval History. Moyen Age. Medieval world. The Labyrinth - Resources for Medieval Studies. Where the Middle Ages Begin. Western Civilization: Ancient and Medieval Europe. Free Online Ancient and Medieval History Courses from Top Universities.
10 Free Ancient and Medieval History Online Courses (Spring 2015) Tableau général des Croisades chrétiennes en Orient. XI ème SIECLE : - 1ère croisade : 1098 - 1099La conquête de Jérusalem par les croisés et le Rapport de Raimondo d'Aguilérec concernant la prise de Jérusalem. La peste del trecento. Medieval Wild Man relic discovered by treasure hunters has roots in ancient history. Au Moyen Âge, des amitiés très intéressées.