

Homomorphic encryption. Homomorphic encryption is a form of encryption which allows specific types of computations to be carried out on ciphertext and generate an encrypted result which, when decrypted, matches the result of operations performed on the plaintext. There are several efficient, partially homomorphic cryptosystems, and a number of fully homomorphic, but less efficient cryptosystems. Although a cryptosystem which is unintentionally homomorphic can be subject to attacks on this basis, if treated carefully homomorphism can also be used to perform computations securely. Partially homomorphic cryptosystems[edit] In the following examples, the notation is used to denote the encryption of the message x.
Unpadded RSA[edit] If the RSA public key is modulus. Ciphertext. Symmetric key example[edit] Let be the plaintext message that Alice wants to secretly transmit to Bob and let be the encryption cipher, where is a secret key.
Alice must first transform the plaintext into ciphertext, , in order to securely send the message to Bob. Both Alice and Bob must know the choice of key, , or else the ciphertext is useless. Which is known as the decryption cipher, Types of ciphers[edit] The history of cryptography begins thousands of years ago and contains a variety of different types of encryption. Historical ciphers[edit] Historical pen and paper ciphers used in the past are sometimes known as classical ciphers.
Historical ciphers are not generally used as a standalone encryption solution because they are quite easy to crack. Transactions on Data Privacy. I2P. The software is free and open source and is published under multiple licenses. The name I2P is derived from Invisible Internet Project, which, in pseudo-mathematical notation, is represented as I²P. Technical design[edit] I2P is beta software since 2003.[3] Developers emphasize that there are likely to be bugs in the software and that there has been insufficient peer review to date.[4] However, they believe the code is now reasonably stable and well-developed, and more exposure can help development of I2P.
Many developers of I2P are known only under pseudonyms. While the previous main developer, jrandom, is currently on hiatus, others, such as zzz and Complication have continued to lead development efforts, and are assisted by numerous contributors.[6] Tor (anonymity network) Tor (previously an acronym for The Onion Router)[4] is free software for enabling online anonymity and censorship resistance.
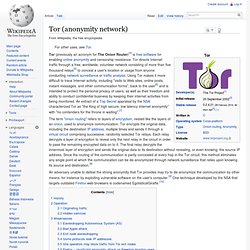
Tor directs Internet traffic through a free, worldwide, volunteer network consisting of more than five thousand relays[5] to conceal a user's location or usage from anyone conducting network surveillance or traffic analysis. Using Tor makes it more difficult to trace Internet activity, including "visits to Web sites, online posts, instant messages, and other communication forms", back to the user[6] and is intended to protect the personal privacy of users, as well as their freedom and ability to conduct confidential business by keeping their internet activities from being monitored. An extract of a Top Secret appraisal by the NSA characterized Tor as "the King of high secure, low latency Internet anonymity" with "no contenders for the throne in waiting".[7] Alice's Tor client picks a random path to destination server Steven J.
Syndie. Syndie is an open source cross-platform computer application to syndicate (re-publish) data (mainly forums) over a variety of anonymous and non-anonymous computer networks.
History[edit] Syndie has been in development since 2003 and ties in closely with the I2P network project, which is considered a parent project. Following the departure of lead developer Jrandom in 2007, work on syndie was paused, however as of 2013 active development has once again resumed. PISA Handbook. Editors: G.W. van Blarkom RE drs.

J.J. Borking dr.ir. J.G.E. Olk Printer: TNO-FEL, P.O. A draft version of the book is available here as a PDF document. Download the Handbook This is a very large PDF document (6.6 MB; 372 pages) so don't try to view it in your browser. Handbook of Privacy and Privacy-Enhancing Technologies About the Handbook The handbook was established within the PISA (Privacy Incorporated Software Agent) project supported by the European Union (project RTD IST-2000-26038). Objectives of the Handbook The objectives of the handbook on Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PET) and Intelligent Software Agents (ISAs) are: Livro Handbook_Privacy_and_PET_final.pdf. Tor. Transactions on Data Privacy. Artigo sobre taxonomia privacidade.
Information privacy. Information privacy, or data privacy (or data protection), is the relationship between collection and dissemination of data, technology, the public expectation of privacy, and the legal and political issues surrounding them.
Privacy concerns exist wherever personally identifiable information is collected and stored – in digital form or otherwise. Improper or non-existent disclosure control can be the root cause for privacy issues. Data privacy issues can arise in response to information from a wide range of sources, such as: The challenge in data privacy is to share data while protecting personally identifiable information. The fields of data security and information security design and utilize software, hardware and human resources to address this issue.