

Laser is produced by a living cell. 13 June 2011Last updated at 01:42 By Jason Palmer Science and technology reporter, BBC News The single-cell lasers were less than 20 millionths of a metre across A single living cell has been coaxed into producing laser light, researchers report in Nature Photonics.
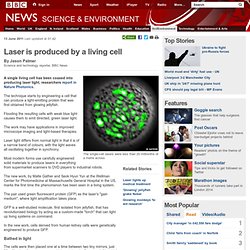
The technique starts by engineering a cell that can produce a light-emitting protein that was first obtained from glowing jellyfish. Flooding the resulting cells with weak blue light causes them to emit directed, green laser light. Total Internal reflection. Snell's law of Refraction. 169 years after its discovery, Doppler effect found even at molecular level. Whether they know it or not, anyone who's ever gotten a speeding ticket after zooming by a radar gun has experienced the Doppler effect – a measurable shift in the frequency of radiation based on the motion of an object, which in this case is your car doing 45 miles an hour in a 30-mph zone.
But for the first time, scientists have experimentally shown a different version of the Doppler effect at a much, much smaller level – the rotation of an individual molecule. Prior to this such an effect had been theorized, but it took a complex experiment with a synchrotron to prove it's for real. "Some of us thought of this some time ago, but it's very difficult to show experimentally," said T. Darrah Thomas, a professor emeritus of chemistry at Oregon State University and part of an international research team that today announced its findings in Physical Review Letters. But a similar effect can be observed when something rotates as well, scientists say. Physicists move closer to efficient single-photon sources. Public release date: 16-Mar-2011 [ Print | E-mail Share ] [ Close Window ] Contact: Charles E.

Bluecblue@aip.org 301-209-3091American Institute of Physics Washington, D.C. Silver bits channel nano light TRN 042303. Computer circuits and nanodevices are already smaller than that, and getting still smaller.

The key is figuring out how to guide near-field light, which forms a standing field rather than light's usual moving wave. Electromagnetic Radiation - The Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation. Visible light is a complex phenomenon that is classically explained with a simple model based on propagating rays and wavefronts, a concept first proposed in the late 1600s by Dutch physicist Christiaan Huygens.

Jablonski Diagram - Java Tutorial. Fluorescence activity can be schematically illustrated with the classical Jablonski diagram, first proposed by Professor Alexander Jablonski in 1935 to describe absorption and emission of light.
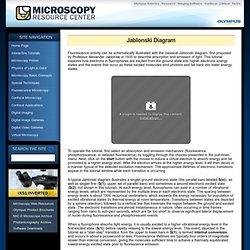
This tutorial explores how electrons in fluorophores are excited from the ground state into higher electronic energy states and the events that occur as these excited molecules emit photons and fall back into lower energy states. To operate the tutorial, first select an absorption and emission mechanism (fluorescence, phosphorescence, or delayed fluorescence) by toggling through the choices presented in the pull-down menu. Next, click on the start button with the mouse to induce a virtual electron to absorb energy and be promoted to a higher energy level. Basic Electromagnetic Wave Properties - Java Tutorial. Electromagnetic radiation is characterized by a broad range of wavelengths and frequencies, each associated with a specific intensity (or amplitude) and quantity of energy.
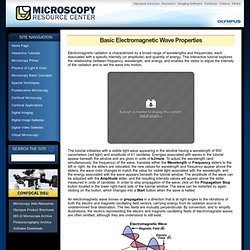
Electron Excitation and Emission - Java Tutorial. Electrons can absorb energy from external sources, such as lasers, arc-discharge lamps, and tungsten-halogen bulbs, and be promoted to higher energy levels.
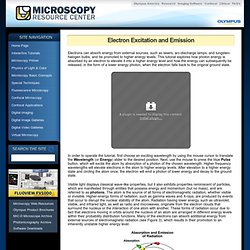
This tutorial explores how photon energy is absorbed by an electron to elevate it into a higher energy level and how the energy can subsequently be released, in the form of a lower energy photon, when the electron falls back to the original ground state. In order to operate the tutorial, first choose an exciting wavelength by using the mouse cursor to translate the Wavelength (or Energy) slider to the desired position. Electromagnetic Radiation - Java Tutorial. The Physics of Light and Color. Light is a complex phenomenon that is classically explained with a simple model based on rays and wavefronts.
The Olympus Microscopy Resource Center Microscopy Primer explores many of the aspects of visible light starting with an introduction to electromagnetic radiation and continuing through to human vision and the perception of color. Each section outlined below is an independent treatise on a limited aspect of light and color. We hope you enjoy your visit and find the answers to your questions. Review Articles Electromagnetic RadiationElectromagnetic radiation, the larger family of wave-like phenomena to which visible light belongs, is the primary vehicle transporting energy through the vast reaches of the universe.
Contributing Authors Mortimer Abramowitz - Olympus America, Inc., Two Corporate Center Drive., Melville, New York, 11747. Kenneth R. Matthew Parry-Hill, Brian O. The Physics of Color and Light - Light: Particle or a Wave? The exact nature of visible light is a mystery that has puzzled man for centuries.
Greek scientists from the ancient Pythagorean discipline postulated that every visible object emits a steady stream of particles, while Aristotle concluded that light travels in a manner similar to waves in the ocean. Even though these ideas have undergone numerous modifications and a significant degree of evolution over the past 20 centuries, the essence of the dispute established by the Greek philosophers remains to this day.