

RFI- Joint Threat Warning System (JTWS) Ground SIGINT Kit - Mobile. Blarney (code name) BLARNEY is a communications surveillance program, started in 1978 and operated under FISA.[1][2] The collection takes place at top-level telecommunications facilities within the United States, choke points through which most traffic will flow, including wireless.
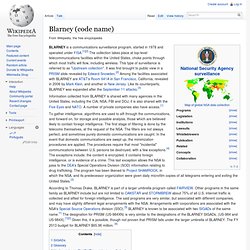
This type of surveillance is referred to as "Upstream collection". It was first brought to public view in a PRISM slide revealed by Edward Snowden.[2] Among the facilities associated with BLARNEY are AT&T's Room 641A in San Francisco, California, revealed in 2006 by Mark Klein, and another in New Jersey. Like its counterparts, BLARNEY was expanded after the September 11 attacks.[3] Information collected from BLARNEY is shared with many agencies in the United States, including the CIA, NSA, FBI and DOJ, it is also shared with the Five Eyes and NATO. A number of private companies also have access.[1] Blarney chart - top 10 collection SIGADs ^ Jump up to: a b c d "NSA Documents Show United States Spied Brazilian Oil Giant". STORMBREW. STORMBREW is a secret internet surveillance program of the National Security Agency (NSA) of the United States.
It was disclosed in the summer of 2013 as part of the leaks by former NSA contractor Edward Snowden. STORMBREW is an umbrella program involving surveillance of telecommunications. It falls under the category of "Upstream collection", meaning that data is pulled directly from fiber-optic cables and top-level communications infrastructure. There is also a SIGAD of the same name, which is described as a "key corporate partner. " That partner was identified on October 23, 2013 by the Washington Post -- quoting NSA historian Matthew Aid -- as Verizon.[1] Surveillance Detection Unit. Description[edit]
Fairview (surveillance program) Fairview is a secret mass surveillance programme run by the National Security Agency, aimed at collecting phone, internet and e-mail data in bulk from the computers and mobile telephones of foreign countries' citizens.[1] According to 2013 revelations by whistleblower Edward Snowden: The NSA partners with a large US telecommunications company...
[which] partners with telecoms in the foreign countries, [which] then allow the US company access to those countries' telecommunications systems, and that access is then exploited to direct traffic to the NSA's repositories.[2] According to the revelations, the NSA had collected 2.3 billion separate pieces of data from Brazilian users in January 2013 alone.[1] Several weeks earlier, Snowden had revealed that the NSA was also harvesting the telephone metadata and text messages from over a billion subscribers in China, however no precise program name was reported at the time.[3] 2nd FAIRVIEW presentation: Where SS0 is accessing your target.
Dropmire. Dropmire is a secret surveillance programme by the National Security Agency aimed at surveillance of foreign embassies and diplomatic staff, including those of NATO allies.
The programme's existence was revealed in June 2013 by whistleblower Edward Snowden in The Guardian newspaper. [1] The report reveals that at least 38 foreign embassies were under surveillance, some of which as far back as 2007. Earlier in the month, The Guardian had reported that the NSA spied on diplomats during the 2009 G-20 London Summit, but no precise program name was revealed at the time. [2] Diplomatic spying by the United States had been revealed as far back as 2010, when it was revealed that US agencies had spied on UN chief Ban Ki-moon – at the time, it was not known that this had been done as part of a systematic program. [3] XKeyscore. Logo for the XKeyscore program XKeyscore or XKEYSCORE (abbreviated as XKS) is a formerly secret computer system first used by the United States National Security Agency for searching and analyzing Internet data it collects worldwide every day.
The program has been shared with other spy agencies including Australia's Defence Signals Directorate, New Zealand's Government Communications Security Bureau and the German Bundesnachrichtendienst.[1] The program's existence was publicly revealed in July 2013 by Edward Snowden in The Sydney Morning Herald and O Globo newspapers, though the codename is mentioned in earlier articles, and like many other codenames can also be seen in job postings, and in the online resumes of employees.[2][3] The scope of XKeyscore[edit] XKeyscore is a complicated system and various authors have different interpretations about its actual capabilities. Boundless Informant. Boundless Informant or BOUNDLESSINFORMANT is a big data analysis and data visualization tool used by the United States National Security Agency (NSA).
ECHELON. ECHELON[needs IPA], originally a code-name, is now used in global media and in popular culture to describe a signals intelligence (SIGINT) collection and analysis network operated on behalf of the five signatory nations to the UKUSA Security Agreement[1] — Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Referred to by a number of other abbreviations, including AUSCANNZUKUS[1] and Five Eyes,[2][3][4] it has also been described as the only software system which controls the download and dissemination of the intercept of commercial satellite trunk communications.[5] It was created in the early 1960s to monitor the military and diplomatic communications of the Soviet Union and its Eastern Bloc allies during the Cold War, and was formally established in the year of 1971.[6][7] §Name[edit] Britain's The Guardian newspaper summarized the capabilities of the ECHELON system as follows: §History[edit] §Origins (1960s–1970s)[edit] §Expansion (1980s)[edit] Main Core. Main Core is the code name of a database maintained since the 1980s by the federal government of the United States.
Main Core contains personal and financial data of millions of U.S. citizens believed to be threats to national security.[1] The data, which comes from the NSA, FBI, CIA, and other sources,[1] is collected and stored without warrants or court orders.[1] The database's name derives from the fact that it contains "copies of the 'main core' or essence of each item of intelligence information on Americans produced by the FBI and the other agencies of the U.S. intelligence community. "[1] The Main Core database is believed to have originated with the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) in 1982, following Ronald Reagan's Continuity of Operations plan outlined in the National Security Directive (NSD) 69 / National Security Decision Directive (NSDD) 55, entitled "Enduring National Leadership," implemented on September 14, 1982.[1][2]
Turbulence (NSA) Turbulence is a United States National Security Agency (NSA) information-technology project started circa 2005.
It was developed in small, inexpensive "test" pieces rather than one grand plan like its failed predecessor, the Trailblazer Project. It also includes offensive cyber-warfare capabilities, like injecting malware into remote computers. The U.S. Congress criticized the project in 2007 for having similar bureaucratic problems as the Trailblazer Project.[1] According to Siobhan Gorman in a 2007 Baltimore Sun article, "The conclusion in Congress, two former government officials said, was that Turbulence was over budget, not delivering and poorly led, and that there was little or no strategy to pull it all together Trailblazer, the predecessor of Turbulence, had been cancelled in 2006 after a congressional investigation and a Defense Department's Inspector General's report found it over budget, wasteful, and ineffective.[1][3] Technical details of MUSCULAR, reference to TURMOIL.
Pinwale. Pinwale is the code name for an NSA collection and retrieval system for so-called "Digital Network Intelligence", including internet e-mail.[1][2] It is searchable by monitored NSA analysts. The existence of the system was first revealed by an NSA analyst who was trained in its use during 2005.[2] However, according to Homeland Security Today, Pinwale has in it much more than email, it also contains other forms of Internet data, and other forms of digital communications as well. Its software has built-in protections against collecting from any of the Five Eyes members. Unlike its successor XKeyscore, targets for PINWALE have to be approved beforehand by the FISC.[1] According to information obtained by The Guardian from Edward Snowden, Pinwale is part of a "multi-tiered system" to address the issue of NSA "collecting so much internet data that it can be stored only for short periods of time. " Pinwale consists of at least two known partitions referred to as "Sweet" and "Sour".[4]
MAINWAY. MAINWAY is a database maintained by the United States' National Security Agency (NSA) containing metadata for hundreds of billions of telephone calls made through the four largest telephone carriers in the United States: AT&T, SBC, BellSouth (all three now called AT&T), and Verizon.[1] The records include detailed call information (caller, receiver, date/time of call, length of call, etc.) for use in traffic analysis[5] and social network analysis,[6] but do not include audio information or transcripts of the content of the phone calls. The database's existence has prompted fierce objections. It is often viewed as an illegal warrantless search and a violation of the pen register provisions of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act and (in some cases) the Fourth Amendment of the United States Constitution.
Similar programs exist or are planned in other countries, including Sweden (Titan traffic database)[citation needed] and Great Britain (Interception Modernisation Programme). PRISM (surveillance program) Below are a number of slides released by Edward Snowden showing the operation and processes behind the PRISM program. It should be noted that the "FAA" referred to is Section 702 of the FISA Amendments Act ("FAA"), and not the Federal Aviation Administration, which is more widely known by the same FAA initialism.
Slide showing that much of the world's communications flow through the U.S. Details of information collected via PRISM Slide listing companies and the date that PRISM collection began Slide showing PRISM's tasking process Slide showing the PRISM collection dataflow Slide showing PRISM case numbers Slide showing the REPRISMFISA Web app Slide showing some PRISM targets. Slide fragment mentioning "upstream collection", FAA702, EO 12333, and references yahoo.com explicitly in the text. FAA702 Operations, and map FAA702 Operations, and map. Senator John McCain (R-AZ) Senator Dianne Feinstein (D-CA), chair of the Senate Intelligence Committee Senator Rand Paul (R-KY) Room 641A.
Coordinates: Room 641A is a telecommunication interception facility operated by AT&T for the U.S. President's Surveillance Program. Stellar Wind. Terrorist Surveillance Program. NSA warrantless surveillance (2001–07)