

Robert Becker Memorial Library. Nightly News: Seed libraries help future crops. Fun Things to Do in June 2013. SEED: The Untold Story. Nightly News: Seed libraries help future crops. Seeds The Game. JAHHM Seed Library Tutorial. Gene bank. Gene banks are a type of biorepository which preserve genetic material.
In plants, this could be by freezing cuts from the plant, or stocking the seeds. In animals, this is the freezing of sperm and eggs in zoological freezers until further need. With corals, fragments are taken which are stored in water tanks under controlled conditions.[1] Plant genetic material in a 'gene bank' is preserved at -196° Celsius in Liquid Nitrogen as mature seed (dry). In plants, it is possible to unfreeze the material and propagate it, however, in animals, a living female is required for artificial insemination. In an effort to conserve agricultural biodiversity, gene banks are used to store and conserve the plant genetic resources of major crop plants and their crop wild relatives.
Seedbank. Seedbank at the Western Regional Plant Introduction Station A seedbank (or seed bank) stores seeds as a source for planting in case seed reserves elsewhere are destroyed.
It is a type of gene bank. The seeds stored may be food crops, or those of rare species to protect biodiversity. The reasons for storing seeds may be varied. In the case of food crops, many useful plants that were developed over centuries are now no longer used for commercial agricultural production and are becoming rare. Seed library. The Seed Library of Los Angeles: checking out seeds at a monthly meeting.
A seed library is an institution that lends or shares seed. It is distinguished from a seedbank in that the main purpose is not to store or hold germplasm or seeds against possible destruction, but to disseminate them to the public which preserves the shared plant varieties through propagation and further sharing of seed.[1] Seed libraries usually maintain their collections through donations from members.[2] but may also operate as pure charity operations intent on serving gardeners and farmers.[3] A common attribute of many seed libraries is to preserve agricultural biodiversity by focusing on rare, local, and heirloom seed varieties.[4] Seed libraries use varied methods for sharing seeds, primarily by: While "lending" is straightforward, "returning" or re-depositing seeds presents a challenge, since the new seeds are not necessarily well-described, and may be hybrids.[5] References[edit]
Jane Addams Hull-House Museum. The Why Seed saving is the most secure way to ensure sustainable food systems and healthful food access.
By adapting this habit of conservation we are not only fostering biodiversity, but the notion of multiculturalism as well. Saving and planting seeds allows us to gather and conserve what we share culturally: food. Food access is an extensive issue that we currently face. Do we know where our food comes from? Do low-income families have the resources to obtain healthy food? The Heirloom Seeds Heirloom seeds are similar to family heirlooms. The History As a Jane Addams' Hull-House Seed Library, we aim to not only provide seeds, but a historical background of each plant. Sustainability Is there an alternative to purchasing food from big name grocery stores that conserves the unique spirit of neighborhoods, conserves the remaining diversity of our planet's seed stock, yet conforms to modern urban living?
Article. The new law in question [2] heralds the entry into Iraqi law of patents on life forms - this first one affecting plants and seeds.
This law fits in neatly into the US vision of Iraqi agriculture in the future - that of an industrial agricultural system dependent on large corporations providing inputs and seeds. In 2002, FAO estimated that 97 percent of Iraqi farmers used saved seed from their own stocks from last year's harvest or purchased from local markets. When the new law - on plant variety protection (PVP) - is put into effect, seed saving will be illegal and the market will only offer proprietary "PVP-protected" planting material "invented" by transnational agribusiness corporations.
The new law totally ignores all the contributions Iraqi farmers have made to development of important crops like wheat, barley, date and pulses. Its consequences are the loss of farmers' freedoms and a grave threat to food sovereignty in Iraq. Source: 16oct04 Related articles: Seed saving. Partial shelled popcorn seed saved for planting Open Pollination[edit] Open pollination is an important aspect of seed saving.
Plants that reproduce through natural means tend to adapt to local conditions over time, and evolve as reliable performers, particularly in their localities, known as landraces or "folk varieties. " Method[edit] Care must be taken, as training materials regarding seed production, cleaning, storage, and maintenance often focus on making landraces more uniform, distinct and stable (usually for commercial application) which can result in the loss of valuable adaptive traits unique to local varieties (Jarvis et al., 2000). Additionally, there is a matter of localized nature to be considered. Biological classification. The hierarchy of biological classification's eight major taxonomic ranks.
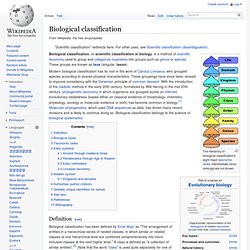
Intermediate minor rankings are not shown. Modern biological classification has its root in the work of Carolus Linnaeus, who grouped species according to shared physical characteristics. These groupings have since been revised to improve consistency with the Darwinian principle of common descent. With the introduction of the cladistic method in the early 20th century, formalized by Willi Hennig in the mid-20th century, phylogenetic taxonomy in which organisms are grouped purely on inferred evolutionary relatedness (based either on classical evidence of morphology, chemistry, physiology, ecology or molecular evidence or both) has become common in biology.[1] Molecular phylogenetics, which uses DNA sequences as data, has driven many recent revisions and is likely to continue doing so.
Biological classification belongs to the science of biological systematics.