
Limited Time Lyapunov Exponents. Infinite and Finite Time Lyapunov Exponents and their use for Measuring the Stability of Orbits in the Outer Solar System Mark Lewis Infinite Time Lyapunov Exponents When Isaac Newton wrote the Principia, he had something of an itinerary other than simply advancing mankinds understanding of how the universe works.

There were definitely signs that pointed in the opposite direction. Poincarés approach to this problem was to see how small changes in the initial conditions propagated over time. The Lyapunov exponent is defined as the exponential rate at which nearby trajectories diverge. Where d(t) is the separation between the trajectories at time t, and d0 is their separation at time zero. Equation 1 is deceptively simple and could lead one to believe that the measuring of maximum Lyapunov exponents is a direct and easy process. One reason that Equation 1 is not directly usable is that when it is of interest, the system under consideration tends to be bounded. . Where . GEO Matlab. Chaos. Click here to go to Physics Virtual Bookshelf Click here to go to the UPSCALE home page.
James Gleick subtitled his popular book Chaos with Making a New Science. Note the word is "Science," not "Physics. " The sub-title is quite reasonable. However, much of the work on chaotic systems occurs in Physics departments. This is a non-technical survey of chaotic systems. The history of the study of chaotic systems exhibits a very common phenomenon in the sciences. The Three Body Gravitational Problem When Newton discovered (or "invented") the Universal Law of Gravitation, and invented (or "discovered") Newton's Laws of Motion, he then used these two discoveries to solve the problem of a planet such as the Earth in orbit around the Sun.
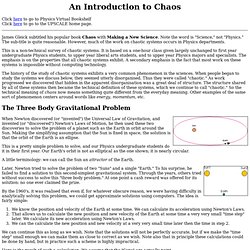
This is a pretty simple problem to solve, and our Physics undergraduate students do it in their first year. A little terminology: we can call the Sun an attractor of the Earth. Later, Newton tried to solve the problem of two "Suns" and a single "Earth. " Lorenz system. A sample solution in the Lorenz attractor when ρ = 28, σ = 10, and β = 8/3 The Lorenz system is a system of ordinary differential equations (the Lorenz equations) first studied by Edward Lorenz.
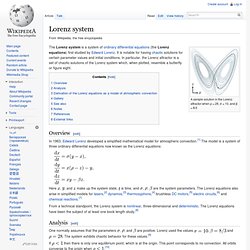
It is notable for having chaotic solutions for certain parameter values and initial conditions. In particular, the Lorenz attractor is a set of chaotic solutions of the Lorenz system which, when plotted, resemble a butterfly or figure eight. Overview[edit] In 1963, Edward Lorenz developed a simplified mathematical model for atmospheric convection.[1] The model is a system of three ordinary differential equations now known as the Lorenz equations: Here , and make up the system state, is time, and are the system parameters. Analysis[edit] One normally assumes that the parameters are positive. And . If then there is only one equilibrium point, which is at the origin.
A pitchfork bifurcation occurs at , and for two additional critical points appear at These correspond to steady convection. If . Attracteur de Lorenz. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
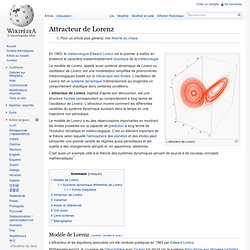
L'attracteur de Lorenz En 1963, le météorologue Edward Lorenz est le premier à mettre en évidence le caractère vraisemblablement chaotique de la météorologie. Le modèle de Lorenz, appelé aussi système dynamique de Lorenz ou oscillateur de Lorenz, est une modélisation simplifiée de phénomènes météorologiques basée sur la mécanique des fluides. L'oscillateur de Lorenz est un système dynamique tridimensionnel qui engendre un comportement chaotique dans certaines conditions. L'attracteur de Lorenz, baptisé d'après son découvreur, est une structure fractale correspondant au comportement à long terme de l'oscillateur de Lorenz. Le modèle de Lorenz a eu des répercussions importantes en montrant les limites possibles sur la capacité de prédiction à long terme de l'évolution climatique et météorologique.
C'est aussi un exemple utile à la théorie des systèmes dynamiques servant de source à de nouveau concepts mathématiques[1]. Dans ces équations, et. Attracteur. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
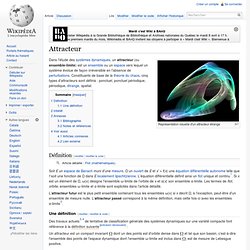
Représentation visuelle d'un attracteur étrange Définition[modifier | modifier le code] L'attracteur futur est le plus petit ensemble contenant tous les ensembles ω(x) si x décrit Ω, à l'exception, peut-être d'un ensemble de mesure nulle. L'attracteur passé correspond à la même définition, mais cette fois-ci avec les ensembles α-limite[2]. Une définition[modifier | modifier le code]
Lyapunov.