

SunPower Sets Solar Cell Efficiency Record at 24.2% Timeline of solar cells. The timeline of solar cells begins in the 19th century when it is observed that the presence of sunlight is capable of generating usable electrical energy.
Solar cells have gone on to be used in many applications. They have historically been used in situations where electrical power from the grid is unavailable. A silicon solar cell or solar photovoltaic cell. 1800s[edit] 1900-1929[edit] 1930-1959[edit] 1960-1978[edit] 1980-1999[edit] 2000-present[edit] Photovoltaic World production, 1980-2007 (log scale). 2008 - New record achieved in solar cell efficiency. Solar Cell. Photoelectric/photovoltaic?? Solar power. How to use its energy. Solar Power is energy obtained by the sun in the form of light. ( When you are at the beach, you feel the sun as heat energy, but heat energy can't travel through space.

It is just light energy that gives the hot feeling) The sun is 150 million km from the earth and is 5 billion years old ( so don´t worry about sun death ). The temperature of the sun ranges from 6000 degrees Celsius at its surface to 10 million degrees Celsius at its centre. It takes about 8 minutes for the light energy to touch the earth. If we could "catch " the amount of solar energy that arrive every single day to earth and convert it into electrical energy, it would be enough to supply our energy needs for up to one a year. The photovoltaic effect. Russell Ohl. Russell Shoemaker Ohl (January 1898 - March 1987) was an American engineer who is generally recognized for patenting the modern solar cell (US Patent 2402662, "Light sensitive device").[1] Ohl was a notable semiconductor researcher prior to the invention of the transistor.[1] He was also known as R.S.
Ohl. Russell Ohl’s specialized area of research was into the behavior of certain types of crystals. He worked on materials research in the 1930s at AT&T's Bell Labs’ Holmdel facility, investigating diode detectors suitable for high-frequency wireless, broadcasting, and military radar. His work was only understood by a handful of scientists in the organization, one of whom was Dr. Solar power. Average insolation showing land area (small black dots) required to replace the world primary energy supply with solar electricity (18 TW or 568 Exajoule, EJ, per year).
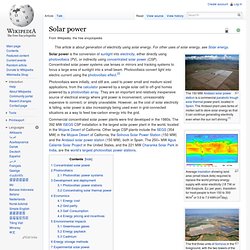
Insolation for most people is from 150 to 300 W/m2 or 3.5 to 7.0 kWh/(m2day). The first three units of Solnova in the foreground, with the two towers of the PS10 and PS20 solar power stations in the background. Solar power is the conversion of sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV), or indirectly using concentrated solar power (CSP). Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam. Photovoltaics convert light into electric current using the photovoltaic effect.[2] Photovoltaics were initially, and still are, used to power small and medium-sized applications, from the calculator powered by a single solar cell to off-grid homes powered by a photovoltaic array.
A. E. Becquerel. Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel (24 March 1820 – 11 May 1891), known as Edmond Becquerel, was a French physicist who studied the solar spectrum, magnetism, electricity and optics.
Photovoltaic effect. The photovoltaic effect is the creation of voltage or electric current in a material upon exposure to light.
The standard photovoltaic effect is directly related to the photoelectric effect, though they are different processes. When the sunlight or any other light is incident upon a material surface, the electrons present in the valence band absorb energy and, being excited, jump to the conduction band and become free. These highly excited, non-thermal electrons diffuse, and some reach a junction where they are accelerated into a different material by a built-in potential (Galvani potential). This generates an electromotive force, and thus some of the light energy is converted into electric energy. Photovoltaics. Photovoltaic SUDI shade is an autonomous and mobile station in France that provides energy for electric vehicles using solar energy.
Photovoltaics (PV) is a method of generating electrical power by converting solar radiation into direct current electricity using semiconductors that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic power generation employs solar panels composed of a number of solar cells containing a photovoltaic material. Mainstream materials presently used for photovoltaics include monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, and copper indium gallium selenide/sulfide. Due to the increased demand for renewable energy sources, the manufacturing of solar cells and photovoltaic arrays has advanced considerably in recent years.
Solar photovoltaics is a sustainable energy source.[1] In 2013, its fast-growing capacity increased by 36% to a running total of 136 GW, worldwide. Solar cell. Solar cells can be used in devices such as this portable monocrystalline solar charger.

A monocrystalline solar cell A solar cell (also called a photovoltaic cell) is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect. It is a form of photoelectric cell (in that its electrical characteristics—e.g. current, voltage, or resistance—vary when light is incident upon it) which, when exposed to light, can generate and support an electric current without being attached to any external voltage source, but do require an external load for power consumption.