

The Reformation and art. The Protestant Reformation during the 16th century in Europe ushered in a new artistic tradition that embraced the Protestant agenda and diverged drastically from the southern European tradition and the humanist art produced during the High Renaissance.
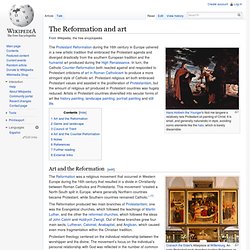
In turn, the Catholic Counter-Reformation both reacted against and responded to Protestant criticisms of art in Roman Catholicism to produce a more stringent style of Catholic art. Protestant religious art both embraced Protestant values and assisted in the proliferation of Protestantism, but the amount of religious art produced in Protestant countries was hugely reduced. Artists in Protestant countries diversified into secular forms of art like history painting, landscape painting, portrait painting and still life.
Medici: Godfathers of the Renaissance . Renaissance . Counter Reformation. Throughout the middle ages the Catholic Church sunk deeper into a pit of scandal and corruption.
By the 1520s, Martin Luther's ideas crystallized opposition to the Church, and Christian Europe was torn apart. In response, the Catholic Church set in motion the counter-reformation. An era of strict conformity and accompanying terror had begun. During the reign of Pope Leo X, discontent amongst Catholics in Europe was at an all-time high. THE REFORMATION AND COUNTER-REFO. By James Jackson Background At the beginning of the sixteenth century, the Catholic church, modeled upon the bureaucratic structure of the Holy Roman Empire, had become extremely powerful, but internally corrupt.

From early in the twelfth century onward there were calls for reform. Between 1215 and 1545 nine church-councils were held with church reforms as their primary intent. The councils all fail to reach significant accord. Counter-Reformation (religious history. Alternate titles: Catholic Reformation; Catholic Revival.
Comparing Medieval and Renaissance Music. By Rit Nosotro Comparative Essay Compare Medieval and Renaissance Music Thesis: Summary: The Medieval and Renaissance periods represent two distinct cultures and worldviews.

Unlike the Middle-Ages, several Renaissance scientists desired to learn about the earth apart from the idea of a Divine Creator, and philosophers brought in humanistic thinking. During the medieval era musical composition consisted of little movement in the notes themselves, and was, in a sense, plain. The years during the Renaissance mark a distinct change in the musical world. An obvious change occurred in the style of music itself, but what outside factors affected these two styles?
In conclusion, the Renaissance and Medieval time periods represent two different cultural, religious, and psychological views. Hopefully we will try and keep our focus as that of J.S. Quick Quiz:: 1. Www.wwnorton.com/college/music/concise-history-western-music4/ch/08/outline.aspx. Prelude.
(CHWM 152–53) The Reformation set in motion a rebellion against the authority of the Catholic Church. It brought new types of religious music, including chorales and chorale settings in the Lutheran Church and Psalters in Calvinist churches. The Catholic Church undertook its own internal program of reform, which likewise had important effects on church music.
I. Luther’s views Martin Luther (1483–1546) was a professor of biblical theology whose arguments that God offers salvation through faith alone and that religious authority comes from the Bible alone posed a challenge to the authority of the Catholic Church. II. Calvin’s views Jean Calvin (1509–1564) led a Protestant movement in France, the Low Countries, and Switzerland that rejected papal authority and accepted predestination. III. Council of Trent At the Council of Trent (1545–63), Catholic Church officials met to address abuses within the church. The Reformation. Unleashed in the early sixteenth century, the Reformation put an abrupt end to the relative unity that had existed for the previous thousand years in Western Christendom under the Roman Catholic Church.
The Reformation, which began in Germany but spread quickly throughout Europe, was initiated in response to the growing sense of corruption and administrative abuse in the church. It expressed an alternate vision of Christian practice, and led to the creation and rise of Protestantism, with all its individual branches. Images, especially, became effective tools for disseminating negative portrayals of the church (Satire on Popery, 53.677.5), and for popularizing Reformation ideas; art, in turn, was revolutionized by the movement.