

File:Making of a DNA vaccine.jpg. Top 10 myths about HIV vaccine research. By Dr.
James KublinExecutive director of the HIV Vaccine Trials Network Today, December 1st, is World AIDS Day, and to mark the occasion the HIV Vaccine Trials Network, which is headquartered at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, would like to debunk the top 10 myths about HIV vaccine research. Myth No. 1: HIV vaccines can give people HIV. ViralZone: DsDNA virion. The Different Stages of HIV Infection. HIV infection can generally be broken down into four distinct stages: primary infection, clinically asymptomatic stage, symptomatic HIV infection, and progression from HIV to AIDS.
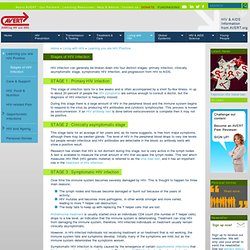
STAGE 1 : Primary HIV infection This stage of infection lasts for a few weeks and is often accompanied by a short flu-like illness. In up to about 20 percent of people the HIV symptoms are serious enough to consult a doctor, but the diagnosis of HIV infection is frequently missed. During this stage there is a large amount of HIV in the peripheral blood and the immune system begins to respond to the virus by producing HIV antibodies and cytotoxic lymphocytes. This process is known as seroconversion. Evolution from a virus's view. Resource library : Evo in the news : Evolution from a virus's viewDecember 2007 Where's the evolution?

To understand why some germs are virulent, we need to see the world from their point of view. To us, disease-causing viruses and bacteria may be evildoers — invaders of our bodies — who, if they can be said to have any aim at all, it is to do us harm. But shifting our perspective to their scale reveals these pathogens to be evolving populations of organisms like any other, whose habitat just happens to be the human body. As an example, consider a unique ecological challenge faced by many pathogens: appropriate habitats can be few and alarmingly far between. Droplet transmission — for example, being passed along when one host accidentally sneezes on another.
Pathogen lineages that fail to meet this challenge and never infect a new host are doomed. And that brings us back to Adenovirus-14. Read more about it. The 30th anniversary of quasispecies : Article : EMBO reports. The meeting on ‘Quasispecies: past, present and future’ took place between 17 and 18 November 2008, in Barcelona, Spain, and was organized by J.
Gómez, C. López‐Galíndez, M.A. Martínez & A. Mas. Introduction. Rule of 6ix: How dangerous are viral quasispecies? At around 1 mutation per 1,000 - 100,000 nucleotides per round of replication, RNA viruses have the highest mutation rate of anything seen in nature to date.
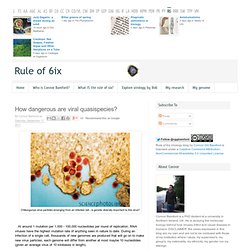
During an infection of a single cell, thousands of new genomes are produced that will go on to make new virus particles; each genome will differ from another at most maybe 10 nucleotides (given an average virus of 10 kilobases in length). This activity results in a 'swarm' of genome sequences that continuously sample sequence space and form what is known as a quasispecies, allowing the virus to adapt to it's complex environment; due to their general lack of proof-reading capability, large population sizes and mode of replication, these RNA viruses have an enormous bank of genetic diversity at their disposal. All those genome sequences uploaded to the public databases represent an average of the thousands of sequences isolated and fail to recognize their true diversity. But how important is it during an infection?
8. HIV variability. Plasma Viral Load Testing. What is a plasma viral load test?
A plasma viral load test (also called a PVL test) measures how much human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is in your blood. The amount of HIV in your blood is called your "viral load. " The lower the viral load, the less amount of the HIV virus. If your doctor knows your viral load, he or she can tell more about your risk of health problems caused by HIV infection. A PVL test helps your doctor determine if your current method of treatment is working or if it is time to change to different medicines.
Who needs a PVL test? PVL tests are intended for people who have already been diagnosed with HIV or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Because PVL tests can detect HIV faster than other tests, they're also used in newborn babies whose mothers have been diagnosed with HIV or AIDS. Pregnant women who may have had a recent exposure to HIV can also have a PVL test. PVL tests are not designed for people who want to know their HIV status. 1. VIROLOGY OF HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS. Julian W TANG, Paul KS CHAN.

Molecules of HIV. HIV, viral facts. Human Immunodeficiency Virus and HIV Disease, October 2001 Retroviruses.

Antiretroviral drug. HIV treatment has been proven so successful that in many parts of the world HIV has become a chronic condition in which progression to AIDS has become increasingly rare.
Anthony Fauci, head of the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has written "With collective and resolute action now and a steadfast commitment for years to come, an AIDS-free generation is indeed within reach. " In the same paper he notes that an estimated 700,000 lives were saved in 2010 alone due to antiretroviral therapy.[1] As another commentary in The Lancet noted, "Rather than dealing with acute and potentially life-threatening complications, clinicians are now confronted with managing a chronic disease that in the absence of a cure will persist for many decades"[2]
HIV Databases Review Article. Heinrich G. Göttlinger Department of Cancer Immunology and AIDS, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and Department of Pathology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115 Tel: (617) 632-3067; Fax: (617)632-3113; E-mail: heinrich_gottlinger@dfci.harvard.edu Introduction HIV-1 and other primate lentiviruses assemble at the plasma membrane and are released by budding from the cell surface. Landmarks of the HIV genome. Lentiviral Vectors Page 2. What is gene therapy?

The aim of gene therapy is to modify the genetic material of living cells for therapeutic purposes (Amado and Chen, 1999). Gene therapy involves the insertion of a functional gene or another molecule that contains and information sequence into a cell to achieve a therapeutic effect. Thus, the gene serves as a drug (Lasic, 1997). There are two types of gene therapy: somatic cell and germ line. Somatic cell gene therapy is the only technique now in use. Before 1996 scientists relied mainly on modified retroviruses such as Moloney murine leukemia virus when gene transfer into the chromosomes of target cells was needed, and adenovirus vectors when such integration was not needed. Back to Index. Dynamics of HIV-1 Assembly and Release. Quasispecies Theory and the Behavior of RNA Viruses.
A large number of medically important viruses, including HIV, hepatitis C virus, and influenza, have RNA genomes. These viruses replicate with extremely high mutation rates and exhibit significant genetic diversity. This diversity allows a viral population to rapidly adapt to dynamic environments and evolve resistance to vaccines and antiviral drugs. For the last 30 years, quasispecies theory has provided a population-based framework for understanding RNA viral evolution.