

Researchers see energy solution in artificial photosynthesis. Toshiba Corporate Research & Development Center : Toshiba Develops World's Highest Efficiency Artificial Photosynthesis Technology for Generation of Fuel and Feedstock from Carbon Dioxide. Toshiba Corporation today announced the development of a new technology that uses solar energy, the power of the sun, to generate carbon compounds from carbon dioxide and water, and to deliver a viable chemical feedstock or fuel with potential for use in industry.
Toshiba introduced the technology at the 2014 International Conference on Artificial Photosynthesis (ICARP2014) on 26 November, at the Awaji Yumebutai International Conference Center in Japan. Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, widely understood to be a major cause of global warming(Note 1), continue to increase. There are also concerns about the exhaustion of fossil fuels, which are spurring interest in adoption of renewable energy sources(Note 2). Artificial photosynthesis technologies that use solar energy to generate carbon compounds from carbon dioxide and water are seen as promising means to resolve both issues. (Note 1) IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (Synthesis Report), Ministry of the Environment. TU Delft: Solar fuels via artificial photosynthesis. To ensure a promising future for mankind, we need to find clean, renewable, and sustainable forms of energy production that can be large enough to power the growing global population.
One of the most attractive opportunities to accomplish this goal is to make SOLAR FUELS via artificial photosynthesis. Nature has developed an elegant system over 2 billion years that allows plants to store the energy from the Sun into chemicals such as sugar and oxygen. Using this exact design scheme, we research ways to convert solar energy, water, and CO2 into high energy density fuels such as H2 and CH4.
To accomplish this in a sustainable way, we only use earth abundant materials, and cheap, scalable fabrication techniques to make our devices. Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen with sunlight represents one of the few truly clean and sustainable energy sources. Several projects exist within the MECS group related to PEC research. CO2 Reduction. This Is How Good Solar-to-Fuel Conversion Can Be. In the artificial photosynthesis world, the recent buzz has been about new records set on water splitting by solar energy to make hydrogen.

However, a slightly newer, but similar, field of research is looking at another form of artificial photosynthesis—using solar energy to turn carbon dioxide into fuel. Such a technology would have the added benefit of removing a potent greenhouse gas from the atmosphere or preventing it from getting there in the first place. Researchers with the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory report today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that they have evaluated the potential efficiencies of this process for several different photoelectric cell configurations, catalysts, and fuel end products. The idea of using sunlight to consume CO2 and make fuel “has been around for awhile, but the challenges have been too great and there hasn't been a nationally focused effort,” Bell adds.
Artificial Photosynthesis: Creating fuel from sunlight. Researchers have made significant progress towards developing a process of Artificial Photosynthesis (AP) that could replace the use of fossil fuels in the future.
Artificial Photosynthesis is the industrial process of preparing fuels and chemicals from nothing more than carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. It is a vital process that would be the foundation of a world that would no longer need fossil fuels. In the latest issue of Advanced Energy Materials, researchers at Monash University have got a step closer to developing an AP process and have discovered a new way of converting carbon dioxide to methanol. Methanol is an extremely useful liquid fuel that could be used to run cars, heat homes or generate electricity in a fuel cell. Major Advance in Artificial Photosynthesis Poses Win/Win for the Environment. Artificial Photosynthesis Closer to Creating Fuel. The Caltech team looked at a different aspect of similar technology to make liquid fuel.
For that, his team at the Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at Caltech has shown how a special membrane could make artificial photosynthesis work without the risk of explosion from the volatile gases involved in the process. Artificial photosynthesis requires two light-sensitive electrodes: One oxidizes water molecules to form oxygen gas, protons and electrons, while the other electrode combines protons and electrons to generate hydrogen gas. A barrier must separate the two electrodes so the gas can enter a pipeline without exploding.
VIDEO: How Bionic Plants Will Change Everything! Why Solar Fuels — JCAP. Can high-tech photosynthesis turn CO2 into fuel for your car? Imagine having a fuel pump in your driveway that uses photosynthesis, the same process plants use to feed themselves, to turn carbon dioxide into fuel for your car.
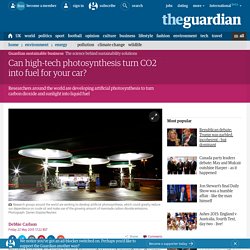
It’s not science fiction: research groups all over the world have been working to develop artificial photosynthesis, which could greatly reduce our dependence on crude oil and make use of the growing amount of manmade carbon dioxide emissions that contribute to climate change. The concept received a nod from US President Barack Obama when he mentioned “turning sunlight into liquid fuel” in his State of the Union speech in January. Despite carmakers’ efforts to roll out electric cars, liquid fuels aren’t likely to disappear any time soon. First of all, drivers are comfortable with – and accustomed to – their internal combustion engine vehicles and the process of finding gas stations and filling up a tank.
Speed bumps ahead However, there’s still a long way to go before the technology is ready for mass production.