

Transmission Lines. Next: Normal Reflection and Transmission Up: Traveling Waves Previous: Energy Conservation A transmission line is typically used to carry high frequency electromagnetic signals over long distances: that is, distances sufficiently large that the phase of the signal varies significantly along the line (which implies that the line is much longer than the wavelength of the signal).

A common example of a transmission line is an ethernet cable. In its simplest form, a transmission line consists of two parallel conductors that carry equal and opposite electrical currents , where measures distance along the line. (See Figure 37.) Be the instantaneous voltage difference between the two conductors at position . And . Is the electric charge on one of the conducting sections, and the charge on the other, then charge conservation implies that . Transmission line, princeton.edu. Transmission line measurement, wikipedia.
Books (Transmission LInes) Lecture Powerpoints (Transmission Lines) Overhead power line, wikipedia. Overhead power line An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy along large distances.
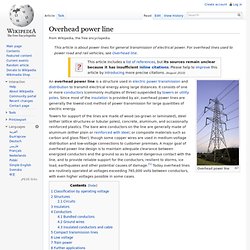
It consists of one or more conductors (commonly multiples of three) suspended by towers or utility poles. Since most of the insulation is provided by air, overhead power lines are generally the lowest-cost method of power transmission for large quantities of electric energy. Towers for support of the lines are made of wood (as-grown or laminated), steel (either lattice structures or tubular poles), concrete, aluminum, and occasionally reinforced plastics.
The bare wire conductors on the line are generally made of aluminum (either plain or reinforced with steel, or composite materials such as carbon and glass fiber), though some copper wires are used in medium-voltage distribution and low-voltage connections to customer premises. Classification by operating voltage[edit] High- and medium-voltage power lines in Łomża, Poland. Acoustic transmission line, wikipedia. The comparison between an acoustic duct and an electrical transmission line is useful in "lumped-element" modeling of acoustical systems, in which acoustic elements like volumes, tubes, pistons, and screens can be modeled as single elements in a circuit.
With the substitution of pressure for voltage, and volume particle velocity for current, the equations are essentially the same.[1] Electrical transmission lines can be used to describe acoustic tubes and ducts, provided the frequency of the waves in the tube is below the critical frequency, such that they are purely planar. Transmission Lines & Computer Engineering.
Distributed Parameter Trasmission Line Models. Transmission-line matrix method, wikipedia. The transmission-line matrix (TLM) method is a space and time discretising method for computation of electromagnetic fields.
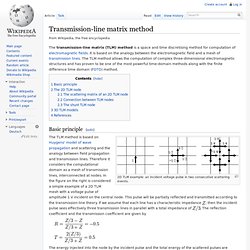
It is based on the analogy between the electromagnetic field and a mesh of transmission lines. The TLM method allows the computation of complex three-dimensional electromagnetic structures and has proven to be one of the most powerful time-domain methods along with the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method. Basic principle[edit] 2D TLM example: an incident voltage pulse in two consecutive scattering events. The TLM method is based on Huygens' model of wave propagation and scattering and the analogy between field propagation and transmission lines. . , then the incident pulse sees effectively three transmission lines in parallel with a total impedance of .
Velocity Of Propogation (Transmission Lines) Characteristic Impedence (Transmission Lines) Impedance Matching. Videos on Impedance Matching. Propagation constant, wikipedia. The propagation constant of an electromagnetic wave is a measure of the change undergone by the amplitude of the wave as it propagates in a given direction.
The quantity being measured can be the voltage or current in a circuit or a field vector such as electric field strength or flux density. The propagation constant itself measures change per metre but is otherwise dimensionless. In the context of two-port networks and their cascades, propagation constant measures the change undergone by the source quantity as it propagates from one port to the next. The propagation constant is expressed logarithmically, almost universally to the base e, rather than the more usual base 10 used in telecommunications in other situations. The quantity measured, such as voltage, is expressed as a sinusoidal phasor.
Alternative names[edit] The term propagation constant is somewhat of a misnomer as it usually varies strongly with ω. Definition[edit] where. Electricity & Magnitism (Physics) Electric power transmission, wikipedia. Two-circuit, single-voltage power transmission line; "Bundled" 4-ways Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to electrical substations located near demand centers.
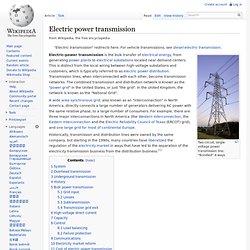
This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution. Transmission lines, when interconnected with each other, become transmission networks. The combined transmission and distribution network is known as the "power grid" in the United States, or just "the grid". In the United Kingdom, the network is known as the "National Grid". A wide area synchronous grid, also known as an "interconnection" in North America, directly connects a large number of generators delivering AC power with the same relative phase, to a large number of consumers. System[edit]