

Torque Converter. Torque converter. DIFFERENTIAL USED AS ACCELERATOR. 3104 Compound Gear Trains. How to Determine Gear Ratio: 6 Steps. Revision:Gearing - formula and uses - The Student Room. TSR Wiki > Study Help > Subjects and Revision > Revision Notes > Business Studies Revision Notes> Gearing: Formula and uses Gearing What is Gearing Gearing is a tool that is used by investors and businesses to show how much of the long term finance came from loans and how much came from shareholder funds.
It also shows how exposed the firm is to financial risk. To see this we can look at the Gearing formula. Gearing Ratio The Gearing Ratio looks at the level of borrowing that a company has taken on in the form of loans and compares that to the total long term finance that a business has. Long Term Liabilities: this figure is how much loans the business has. A Design and Technology Site. Bevel gear. Worn wheel. Spiral gear. Hypoide gear. 71B prop shaft ujoint replacement : MGB & GT Forum : MG Experience Forums : The MG Experience. Rear-wheel Drive Arrangements (Automobile) Rear-wheel Drive Arrangements The statement “every action has an equal and opposite reaction”, means that every component that produces or changes a torque also exerts an equal and opposite torque tending to turn the casing.

To understand the torque reaction consider the Fig. 26.25A, which represents a tractor with its rear driving wheels locked in a ditch. In this situation torque reaction is likely to lift the front of the tractor rather than turn the rear wheels. When the above principle is applied to rear axles, some arrangement must be provided to prevent the axle casing turning in the opposite direction to the driving wheels. A torque (t) applied to the wheel, which may be considered as a lever (Fig. 26.25B), produces a tractive effort (Te) at the road surface, and an equal and opposite forward force at the axle shaft. Fig. 26.25. Types of Drive. Hotchkiss Open-type Drive This type of drive is commonly used on passenger cars and heavy commercial vehicles. Hotckkiss drive. The Gearbox (Transmission) The Gearbox (Transmission) Types of gearing: Various types of gearing are used on a motor vehicle.
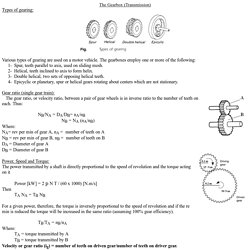
The gearboxes employ one or more of the following: 1- Spur, teeth parallel to axis, used on sliding mesh. 2- Helical, teeth inclined to axis to form helix. 3- Double helical, two sets of opposing helical teeth. 4- Epicyclic or planetary, spur or helical gears rotating about centers which are not stationary. Gear ratio (single gear train): The gear ratio, or velocity ratio, between a pair of gear wheels is in inverse ratio to the number of teeth on each.
NB/NA = DA/DB= nA/nB NB = NA (nA/nB) Syncromesh unit. Universal joint. Differentail 2. Differential. Propshafts. Clutch Kit. CV Joints. The most common type of outboard CV joint is the "Rzeppa" style.

This type of joint was invented way back in 1920 by a Dana engineer named Alfred H. Rzeppa. His design allowed power to be transmitted through six spherical balls located between an inner and outer race. In this design, the balls are held in position by small windows in a cage assembly that fits between the inner and outer races. The design of the joint is such that the position of the balls always bisects (cuts in half) the operating angle of the joint. A couple of variations on this design are the "double offset" (DOJ) and "Plunging Disk Type Cross Groove" CV joints. So the plunging action of these joints allows the shaft to slide in and out slightly to compensate for the difference. The other type of CV joint you�ll see is the "tripod" style joint. Tripod style joints are used for the inner joints on most domestic and Asian FWD models from 1983 to present.
Boots often become brittle with age and exposure to heat. Manual Gearbox. Final Drive. Differential. Turque converter. Double helical gear advantage and disadvantage. Automatic gearbox. Epicyclic gears. Propshaft Picture. Sliding mesh gearbox. Clutch Judder- Cause:Is caused by the clutch. Basic explanation of a synchromesh. Syncromesh Unit (Info) Interlock device. Detente device. Constant mesh gearbox. Helical gear advantage and disadvantage. Four-wheel-drive layout. Clutch components. Prop-shaft. Dog clutch. Synchromesh unit. Universal and constant velocity joint. Coil spring clutch.