

Vagus Nerve Anatomy. The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve.
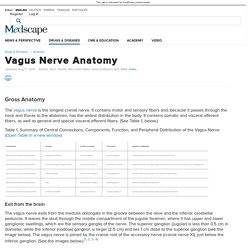
It contains motor and sensory fibers and, because it passes through the neck and thorax to the abdomen, has the widest distribution in the body. It contains somatic and visceral afferent fibers, as well as general and special visceral efferent fibers. (See Table 1, below.) MUSCLE TONE - SPINAL REFELXES. Muscles are always at least partially contracted.
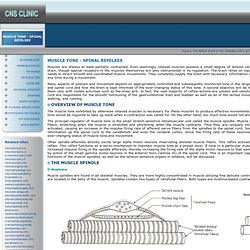
Even seemingly relaxed muscles possess a small degree of tension called resting muscle tonus or tone. This tone is ultimately controlled by impulses from the brain, though special receptors in the muscles themselves are also instrumental in its regulation. The brain relies on input from these receptors as well as those in tendons and joints to give it the information it needs to direct smooth and coordinated muscle movements. They constantly supply the brain with necessary information concerning the ever-changing tone in muscles as well as the present position of muscles at any time during a movement. Musom.marshall.edu/anatomy/grosshom/z_cranerv1.html. © 2005 zillmusom I.

OVERVIEW ‑ Cranial nerves vs. Musom.marshall.edu/anatomy/grosshom/z_cranerv1.html. Ocular Motor System (Section 3, Chapter 7) Neuroscience Online. 7.1 Introduction The simplicity of the motor systems involved in controlling eye musculature make them ideal for illustrating the mechanisms and principals you have been studying in the preceding material on motor systems.
They involve the action of few muscles and of well defined neural circuits. We use our eyes to monitor our external environment and depend on our ocular motor systems to protect and guide our eyes. The ocular motor systems control eye lid closure, the amount of light that enters the eye, the refractive properties of the eye, and eye movements. The visual system provides afferent input to ocular motor circuits that use visual stimuli to initiate and guide the motor responses. In this chapter we will start at the level of reflex responses and move onto more complex voluntary responses in the following lecture.
Ocular Motor System (Section 3, Chapter 7. CNs. Pterygopalatine Fossa. Cranial Nerve 4 & 6: Trochlear Nerve and Abducent Nerve. Anatomy.
Facial Nerve Video. Cranial Nerve 2, pg. 4. Vestibular evoked myogenic potential. Timothy C.
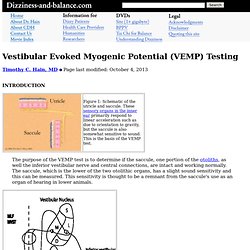
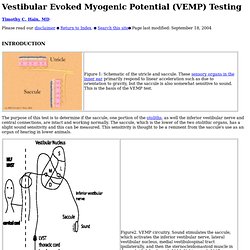
Hain, MD Page last modified: October 4, 2013 The purpose of the VEMP test is to determine if the saccule, one portion of the otoliths, as well the inferior vestibular nerve and central connections, are intact and working normally. The saccule, which is the lower of the two otolithic organs, has a slight sound sensitivity and this can be measured. This sensitivity is thought to be a remnant from the saccule's use as an organ of hearing in lower animals. The pathway supposed to account for the VEMP response is shown in figure 2 above. Methodology: VEMPs are recorded using an evoked response computer, a sound generator, and surface electrodes to pick up neck muscle activation or other muscles if this is of interest. The general rule of thumb with hearing and VEMP's is that conductive hearing loss obliterates VEMP's, and sensorineural hearing loss does little or nothing to VEMP's.
We think that binaural stimulation is generally a bad idea. Sound stimulus: Vestibular evoked myogenic potential. Timothy C.
Hain, MD Please read our disclaimer Return to Index. Search this site. Muscles of Facial Expression - Muscles of the Face, Head, and Neck. Diagram of the key muscles of human facial expression with interactive image for learning or revising them.
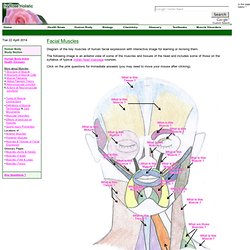
The following image is an anterior view of some of the muscles and tissues of the head and includes some of those on the syllabus of typical Indian head massage courses. Click on the pink questions for immediate answers (you may need to move your mouse after clicking). Glial Cells. Blue Histology. Anatomy of Olfactory and Optic nerves. Eye. Eye. File:ERP - optic cabling.jpg. Parasympathetic Pathways: Pupillary Light Reflex. Rednuclsubstnigra.jpg (260×303) Brain Atlas. Clarke's Nucleus. Www.tsdocs.org/downloads/CranialNerves.pdf. Cerebellar Afferent Fibers. Flocculonodular-lobe.png (319×174) Bony Labyrinth Model - Semicircular Canals. Medical Neuroscience - Motor pathways. Proprioceptors. Proprioception means "sense of self".
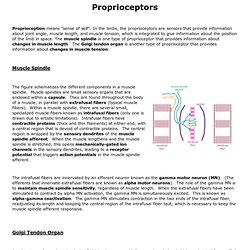
In the limbs, the proprioceptors are sensors that provide information about joint angle, muscle length, and muscle tension, which is integrated to give information about the position of the limb in space. Muscle spindles animation.