

Prithashini
Skinner’s Operant Conditioning: Rewards & Punishments. The Growing Child- Teenager (13 to 18 Years) How much will my teen grow?
The teenage years are also called adolescence. This is a time for growth spurts and puberty changes (sexual maturation). A teen may grow several inches in several months, followed by a time of very slow growth. Then they may have another growth spurt. 9 Hurtful Things Parents Tell Teens. What Is Reinforcement in Operant Conditioning? One of the many different ways in which people can learn is through a process known as operant conditioning (also known as instrumental conditioning).1 This involves learning through reinforcement or punishment.

The type of reinforcement used can play an important role in how quickly a behavior is learned and the overall strength of the resulting response. Understanding Reinforcement. Examples of Positive Reinforcement. Whether you deal with young children at home or in the classroom, or you want to be a better manager of adults in the workplace, educational psychologists have studied ways to influence people to get the results you want.
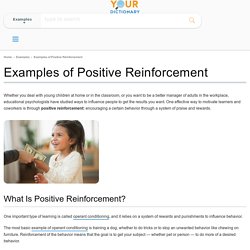
One effective way to motivate learners and coworkers is through positive reinforcement: encouraging a certain behavior through a system of praise and rewards. What Is Positive Reinforcement? Using Positive Reinforcement to Improve Behavior. When your child misbehaves, rewards might be the last thing on your mind.
But, positive reinforcement can be one of the most effective behavior modification techniques.1 You can use positive reinforcement to encourage prosocial behaviors, like sharing or following directions. And, you can use it to prevent misbehavior, like hitting and rule violations. Positive reinforcement can also be an effective way to encourage and motivate your child to be responsible, do their chores, get along with their siblings, or complete their homework assignments without arguing. How Positive Reinforcement Works. How Positive Reinforcement Improves Student Behavior. Children with learning disabilities are prone to behavior problems requiring the use of positive reinforcement.1 Having a learning disability can make a child worry that he is different from his peers, which can lead him to act out in the classroom, at home or both.

Some special needs students intentionally engage in bad behavior to avoid facing the classwork that they dread. They may lack the confidence to believe they can manage their learning disabilities. No matter the cause of worrisome behavior, positive reinforcement often helps motivate students to stop acting out in inappropriate ways. Learn more about using positive reinforcement as a behavior intervention method with this review. Why is positive reinforcement encouraged among parents? Negative reinforcement: Definition and examples. Negative reinforcement encourages specific behaviors by removing or avoiding negative consequences or stimuli.
It is different than punishment, which aims to discourage a specific behavior. Negative reinforcement has become a popular way of encouraging good behavior at school. Keep reading to learn more about how it works and how it differs from positive reinforcement and punishment. Negative reinforcement is the encouragement of certain behaviors by removing or avoiding a negative outcome or stimuli. The Study of Punishment in Psychology. Punishment is a term used in operant conditioning to refer to any change that occurs after a behavior that reduces the likelihood that that behavior will occur again in the future.

While positive and negative reinforcements are used to increase behaviors, punishment is focused on reducing or eliminating unwanted behaviors. Punishment is often mistakenly confused with negative reinforcement. The difference: Reinforcement increases the chances that a behavior will occur and punishment decreases the chances that a behavior will occur. Types of Punishment Behaviorist B. What Is Punishment Psychology, And Should You Use It? Updated February 01, 2021 Medically Reviewed By: Tanya Harell Source: rawpixel.com We were all punished when we were younger at one time or another.

However, it is how we are punished that can shape how we will behave in the future. Positive Punishment: What It Is, Benefits, and Examples. Positive punishment is a form of behavior modification.
In this case, the word “positive” doesn’t refer to something pleasant. Positive punishment is adding something to the mix that will result in an unpleasant consequence. The goal is to decrease the likelihood that the unwanted behavior will happen again in the future. What is Negative Punishment (Examples and Effectiveness)
In this article, we will review negative punishment, its definition, examples, and drawbacks.

American psychologist B.F. Skinner developed the theory of operant conditioning, which stated that a person or animal’s behavior could be increased or decreased by adding or removing appropriate stimuli after the behavior is exhibited. The difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning is that classical affects unconscious behavior, while operant affects conscious behavior. Negative Punishment Examples and Scenarios. Nobody ever wants their stuff taken away. That is the main concept behind negative punishment.
Using negative punishment example scenarios, gain an understanding of the concept and its effectiveness. Then, go on to explore the difference between positive and negative punishment. Exploring Negative Punishment The use of punishment is one way to deter or eliminate undesired behavior. Familytoday. Some days, it feels like all we do as parents is discipline our children, but do we understand what discipline really means? The goal of disciplining children is not to punish them for bad behavior. Rather, discipline is a tool to get the behavior we want. Ultimately, children who receive discipline become disciplined in the way they think, act and speak.
Discipline is a good thing, so long as it's not always about punishment. Positive and Negative Reinforcement.