

Regional Trade Agreements - goods (GATT) provisions. GATT: Article XXIV back to top Territorial Application — Frontier Traffic — Customs Unions and Free-trade Areas 1.
The provisions of this Agreement shall apply to the metropolitan customs territories of the contracting parties and to any other customs territories in respect of which this Agreement has been accepted under Article XXVI or is being applied under Article XXXIII or pursuant to the Protocol of Provisional Application. Each such customs territory shall, exclusively for the purposes of the territorial application of this Agreement, be treated as though it were a contracting party; Provided that the provisions of this paragraph shall not be construed to create any rights or obligations as between two or more customs territories in respect of which this Agreement has been accepted under Article XXVI or is being applied under Article XXXIII or pursuant to the Protocol of Provisional Application by a single contracting party. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
Paragraph 9 Paragraph 11. Stabex. The Stabex (from French Système de Stabilisation des Recettes d'Exportation) is the acronym for a European Commission compensatory finance scheme to stabilise export earnings of the ACP countries.
It was first introduced in the second Lomé Convention (1979) with the purpose of remedying the harmful effects of the instability of export revenue from agricultural products. Stabex (along with similar mechanism for the mineral products– Sysmin that was provided for in the third Lomé Convention (1984)) was abolished by Cotonou Agreement in 2000. Yaoundé Convention. The Yaoundé Convention was a convention signed in the city of Yaoundé, Cameroon between the EC and ASMM (African States, Madagascar and Mauritius).
The First Convention (1964-1969)[edit] The first association agreement between the EC and the 18 African ex-colonies that had recently gained independence, was signed in Yaoundé on 20 July 1963 and entered into force on 1 June 1964. It was mainly based on the previous treaty between the EC and its overseas territories and had a validity period of 5 years. The Second Convention (1971-1975)[edit] After the first treaty expired, a new one was signed on 29 July 1969. External links[edit] MEMBER STATES. ACP–EU development cooperation. ACP States Development cooperation between the European Union (EU) and the countries of the African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States (ACP) celebrated its 50th anniversary in 2007.
Although bilateral relations have always been and still remain one of the main features of modern development cooperation, it was the Treaty of Rome in 1957 which first established a collective European development policy. The Treaty of Rome granted associated status to 31 overseas collectivities and territories (OCTs) and provided for the creation of a European Development Fund (EDF) intended to grant technical and financial assistance to the countries which were still under European rule at the time.
More significantly, however, by means of the Treaty of Rome the six member states of the European Economic Community were expressing solidarity with the colonies and OCTs and committed themselves to contribute to their prosperity. Main actors[edit] Cotonou Agreement. ACP States Caribbean group East and South Africa group.
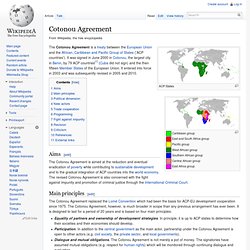
African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States. ACP States Caribbean group East and South Africa group Pacific group West African group Southern African group Central African group East Africa group The African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States (ACP) is a group of countries in Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific that was created by the Georgetown Agreement in 1975.
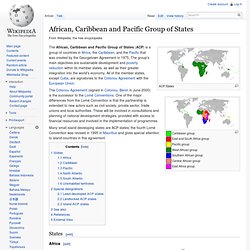
The Cotonou Agreement (signed in Cotonou, Benin in June 2000) is the successor to the Lomé Conventions. Many small island developing states are ACP states; the fourth Lomé Convention was revised in 1995 in Mauritius and gives special attention to island countries in this agreement. Commissaire européen au Commerce. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Le Commissaire européen pour le commerce extérieur est le membre de la Commission européenne responsable de la politique commerciale extérieure. Le commissaire est notamment la voix de l'Union européenne au sein d'organisations comme l'OMC. Liste des commissaires[modifier | modifier le code] Traité de Lisbonne. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Traité sur le fonctionnement de l'Union européenne. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Traité de Rome Voir le traité sur Wikisource Le même jour, les mêmes pays ont signé le traité Euratom. Toutes les ratifications ayant été acquises à la fin de l'année 1957, le traité a pu entrer en vigueur dès le . Il a institué le marché commun européen et a défini les bases de la politique agricole commune mise en œuvre en 1962. Contenu du traité[modifier | modifier le code] Le traité sur le fonctionnement de l'Union comprend sept parties, suivies de trente-sept protocoles et deux annexes. Les principes[modifier | modifier le code] La première partie contient : la définition du traité et son lien avec le traité sur l'Union européenne (article premier) ;la définition des compétences de l'Union : compétence exclusive, compétence partagée (articles 2 à 6) ;certains principes généraux de l'action de l'Union (article 7 à 17).
LexUriServ.