

Glucose Molecule. Glucose a simple monosaccharide sugar, is one of the most important carbohydrates and is used as a source of energy in animals and plants.
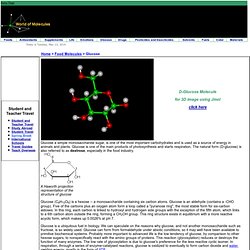
Glucose is one of the main products of photosynthesis and starts respiration. The natural form (D-glucose) is also referred to as dextrose, especially in the food industry. A Haworth projection representation of the structure of glucose Glucose (C6H12O6) is a hexose -- a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms. Glucose is an aldehyde (contains a -CHO group). Glucose is a ubiquitous fuel in biology. Chemically joined together, glucose and fructose form sucrose. The older name dextrose arose because a solution of D-glucose rotates polarised light towards the right. There are two enantiomers (mirror-image isomers) of the sugar -- D-glucose and L-glucose, but in living organisms only the D-isomer is found. D-Glucose has the same configuration at its penultimate carbon as D-glyceraldehyde.
What Is Calcium Carbide? American Chemical Society. Taaffeit. Tritium. Tritium (/ˈtrɪtiəm/ or /ˈtrɪʃiəm/; symbol T or 3H, also known as hydrogen-3) is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen.
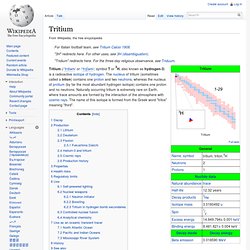
The nucleus of tritium (sometimes called a triton) contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of protium (by far the most abundant hydrogen isotope) contains one proton and no neutrons. Naturally occurring tritium is extremely rare on Earth, where trace amounts are formed by the interaction of the atmosphere with cosmic rays. The name of this isotope is formed from the Greek word "tritos" meaning "third". Decay[edit] While tritium has several different experimentally determined values of its half-life, the National Institute of Standards and Technology lists 4,500±8 days (approximately 12.32 years).[1] It decays into helium-3 by beta decay as in this nuclear equation: and it releases 18.6 keV of energy in the process.
Tritium is potentially dangerous if inhaled or ingested. Production[edit] Lithium[edit] Deuterium[edit] 17 8O + n → 14 6C + 4 2He Fission[edit] Tritium. Tritium page. Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen, used in research, fusion reactors and neutron generators.

The radioactive properties of tritium are very useful. By mixing tritium with a chemical that emits light in the presence of radiation, a phosphor, a continuous light source is made. This can be applied to situations where a dim light is needed but where using batteries or electricity is not possible or practical. Rifle sights and exit signs are two examples of where this phenomenon is commonly used. The phosphor sights help increase nighttime firing accuracy and the exit signs can be life saver if there is a loss of power. Virtual Textbook of Organic Chem. Protein. Education in Chemistry. Exhibition Chemistry Declan Fleming shows you how to capture your students’ imaginations with spectacular demonstrations Students should know that sulfuric acid can act in three main ways: as an acid, an oxidising agent and a dehydrating agent.

Demonstrations of the dehydrating properties of sulfuric acid are commonly given to audiences of 16–18 year olds (and to younger audiences for their visual appeal). Previously we looked at the most popular of these1 in which sulfuric acid dehydrates sucrose, causing a black carbon ‘snake’ to rise from the reaction vessel. The production of sulfur dioxide fumes indicates that oxidation processes also occur. A less common demonstration involves the dehydration of permanganic acid (HMnO4).
Kit 2 cm3 concentrated sulfuric acid (corrosive, oxidising) 1 g KMnO4 (irritant, oxidising) 2 watch glasses White tile Heat resistant mat Cotton wool ball (c.2 cm3) Glass rod (c.30 cm long) Preparation Work in a well-ventilated room. In front of the audience Disposal. Chemistry of Nitrogen. Isotopes Nitrogen has two naturally occurring isotopes, nitrogen-14 and nitrogen-15, which can be separated with chemical exchanges or thermal diffusion.
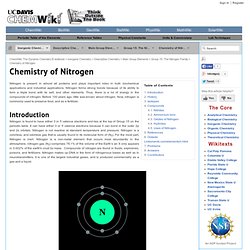
Nitrogen also has isotopes with 12, 13, 16, 17 masses, but they are radioactive. Nitrogen 14 is the most abundant form of nitrogen and makes up more than 99% of all nitrogen found on Earth. It is a stable compound and is non-radioactive. Nitrogen-14 has the most practical uses, and is found in agricultural practices, food preservation, biochemicals, and biomedical research. Compounds The two most common compounds of nitrogen are Potassium Nitrate (KNO3) and Sodium Nitrate (NaNO3). Nitrogen is an "unusually stable" compound, particularly because nitrogen forms a triple bond with itself. N-N (triple bond) → N2(g) enthalpy = +945.5 kJ 1/2 N2 + 1/2 O2 → NO(g) enthalpy = +86.55 kJ Figure: Picture of N2 For Nitrogen to follow the octet rule, it must have a triple bond. Nitrides 3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2. Your insight into science. The universe is a vast soup of interacting particles and energy.
The ways in which those interactions take place, as well as the structure and composition of matter, is the main focus of the field of chemistry. Our chemistry learning modules introduce you to the world of chemistry, exploring current research and scientific findings on concepts like the structure and function of atoms, forms of energy and its transfer, chemical bonding and reactions, and more. Summary Tracking the development of our understanding of the atomic structure of matter, this module begins with the contributions of ancient Greeks, who proposed that matter is made up of small particles.
The module then describes how Lavoisier's Law of Conservation of Mass and Proust's Law of Definite Proportions contributed to Dalton's modern atomic theory. Modern atomic theory has evolved dramatically from the 19th century view of the atom as a small, solid sphere resembling a billiard ball. This module introduces D. Crash Course - Chemistry. Chemistry.