

Powering the Cell: Mitochondria « How Cells Divide. Share By Rick Groleau Posted 10.09.01 NOVA Most of the time, when a cell in our bodies divides, each new cell carries a complete set of chromosomes.
The cells involved with human reproduction, however, carry only half after division occurs. In this step-by-step explanation, learn about mitosis and meiosis, the two types of cell division. This feature originally appeared on the site for the NOVA program 18 Ways to Make a Baby. Cell Size and Scale. Some cells are visible to the unaided eye The smallest objects that the unaided human eye can see are about 0.1 mm long.
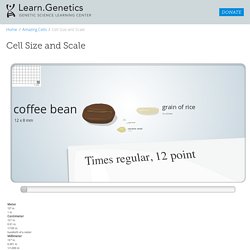
That means that under the right conditions, you might be able to see an ameoba proteus, a human egg, and a paramecium without using magnification. A magnifying glass can help you to see them more clearly, but they will still look tiny. Smaller cells are easily visible under a light microscope. Inside a Cell. Parts of the Cell - Cells Alive! For life all cells have basic needs.
Cells have diverged in their structure and function to accommodate these survival requirements. Here are some KEY TERMS to help you think, explore and search for similarities and significant differences that have become the characteristics of eukaryote (animal, plant) and prokaryotic (bacteria) cells. Examples might be searching: eukaryote prokaryote reproduction or animal plant cell energy. Reproduction / cell division Energy trapping, storage and consumption Form / shape / structure Cell specialization Compartmentalization of cell functions Communication within and beyond the cell Cell / organism survival. Small Movies of Cell Bio Topics. Interactive tutoring on the toughest topics in biology Have you ever wished for an effective tool to help your students visualize tough topics like a tour of the plant and animal cell, cellular respiration, photosynthesis, mitosis, meiosis, protein synthesis, or how neurons work?
Our new 3-minute animations allow instructors to show 3D, fluid movement and dramatic "zoom" sequences that bring difficult-to-teach biological concepts to life during lectures. The Cytoskeleton. Cells contain elaborate arrays of protein fibers that serve such functions as: establishing cell shape providing mechanical strength locomotion chromosome separation in mitosis and meiosisintracellular transport of organelles The cytoskeleton is made up of three kinds of protein filaments: Actin filaments (also called microfilaments) Intermediate filaments and Microtubules Actin Filaments Monomers of the protein actin polymerize to form long, thin fibers.
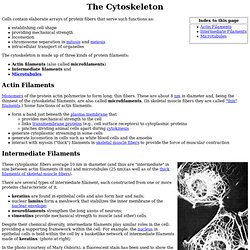
These are about 8 nm in diameter and, being the thinnest of the cytoskeletal filaments, are also called microfilaments. (In skeletal muscle fibers they are called "thin" filaments.) Fluid mosiac model. Membranes Organize Cellular Complexity. Membranes organize proteins and other molecules enabling the cell to run much more efficiently than if everything were floating freely. Mitochondrial membranes, for example, keep protein assembly lines together for efficient energy production.
And the lysosome safely holds enzymes that would destroy essential proteins if released into the cytoplasm. Transport Videos. Page Topics Brownian movement, Osmosis, Elodea Osmosis, Elodea Hypertonic, Elodea Hypotonic, Blood Isotonic, Blood Hypertonic, Blood Hypotonic,

Phagocytosis White blood cell, Shigella bacteria Live movie. DNA-RNA-Protein. DNA carries the genetic information of a cell and consists of thousands of genes.
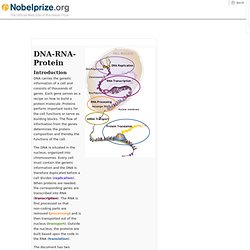
Each gene serves as a recipe on how to build a protein molecule. Proteins perform important tasks for the cell functions or serve as building blocks. The flow of information from the genes determines the protein composition and thereby the functions of the cell. From RNA to Protein Synthesis. Interactive Concepts-Catalysis. Protein Structure. Chemical Composition of the Human Body. Water Movie. It's All About Carbon. If you have questions about climate change, please e-mail them to All Things Considered or call the show at 202-898-2395.
When the subject is global warming, our mood is usually "uh-oh. " Which makes sense, because a warmer Earth will lead to all kinds of disruptions and expensive adjustments that we could do without. ChemHealthWeb. Assignment Discovery: Electron Shells" Elements, Compounds & Mixtures. CHEMICAL BONDS Song. Chemical Bonds. Selected by the SciLinks program, a service of National Science Teachers Association.

Copyright 2001. For an explanation of the significance of this logo go to: Because of the tendency of atoms to complete their outer energy shells with the stable number of electrons for each shell, atoms with incomplete shells have a tendency to gain electrons, lose electrons or share electrons. Atoms that have gained or lost electrons become ions. Oppositely charged ions form ionic bonds. Ionic bonds The following animation shows how ions of sodium and chlorine are formed. The oppositely charged ions in the animation will be attracted to each other and form an ionic bond. Covalent bonds Atoms can fill their outer shells by sharing electrons. In the animation, two hydrogen atoms share each other's electrons and form a molecule of hydrogen.
Covalent bonds can be nonpolar, or polar. Hydrogen bonds. Types of Bonds. Custom Search Bonding Links <-- Back to electronegativity Electronegativity Differences between atoms can be used to determine the type of bonding that occurs.
If the difference between 2 atoms is small (less than 1.7) the bond is covalent.