

Rome. Ancient Rome. In its approximately 12 centuries of existence, Roman civilization shifted from a monarchy to a classical republic and then to an increasingly autocratic empire.
Through conquest and assimilation, it came to dominate Southern and Western Europe, Asia Minor, North Africa, and parts of Northern and Eastern Europe. Rome was preponderant throughout the Mediterranean region and was one of the most powerful entities of the ancient world. It is often grouped into "Classical Antiquity" together with ancient Greece, and their similar cultures and societies are known as the Greco-Roman world. Ancient Roman society has contributed to modern government, law, politics, engineering, art, literature, architecture, technology, warfare, religion, language and society. The Forum Romanum. Leading statesmen of the Roman Republic. The Persians & Greeks: Crash Course World History #5. Republic vs. Democracy. Ancient Roman Laws. Since the days of the Law of the Twelve Tables, developed during the early republic, the Roman legal system was characterized by a formalism that lasted for more than 1.000 years.
Early Roman law was drawn from custom and statutes, but later during the times of the empire, the emperors asserted their authority as the ultimate source of law. Their edicts, judgments, administrative instructions, and responses to petitions were all collected with the comments of legal scholars. "What pleases the emperor has the force of law. " As the law and scholarly commentaries on it expanded, the need grew to codify and to regularize conflicting opinions. Roman Senate. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being founded in the first days of the city (traditionally founded in 753 BC).
It survived the overthrow of the kings in 509 BC, the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC, the split of the Roman Empire in 395 AD, the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD, and barbarian rule of Rome in the 5th, 6th, and 7th centuries. The Senate of the West Roman Empire continued to function until 603 AD. During the days of the kingdom, it was little more than an advisory council to the king.[1] The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the executive magistrates were quite powerful. Since the transition from monarchy to constitutional rule was probably gradual, it took several generations before the Senate was able to assert itself over the executive magistrates. The Roman Empire. List of Roman emperors. Augustus (Octavian), the first Roman Emperor of the Principate Era whose ascension ended republic rule at Rome.
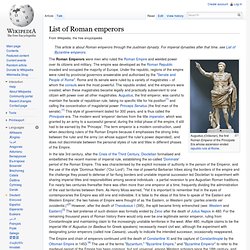
The Roman Emperors were men who ruled the Roman Empire and wielded power over its citizens and military. The empire was developed as the Roman Republic invaded and occupied the majority of Europe. Under the republic, regions of the empire were ruled by provincial governors answerable and authorised by the "Senate and People of Rome". Rome and its senate were ruled by a variety of magistrates – of whom the consuls were the most powerful. The republic ended, and the emperors were created, when these magistrates became legally and practically subservient to one citizen with power over all other magistrates. Legitimacy[edit] Lists of legitimate emperors are therefore partly influenced by the subjective views of those compiling them, and also partly by historical convention. Emperors after 395[edit] The situation in the West is more complex. The Principate[edit] The Dominate[edit] The Roman Empire. Or Republic. Or...Which Was It?: Crash Course World History #10.