

ChemProt Server. The ChemProt 2.0 server is a ressource of annotated and predicted chemical-protein interactions.
The server is a compilation of over 1 100 000 unique chemicals with biological activity for more than 15000 proteins. ChemProt can assist in the in silico evaluation of small molecules (drugs, environmental chemicals and natural products) with the integration of molecular, cellular and disease-associated proteins complexes. You are welcome to read the "instructions" and "output format" in order to get more information about the different search options. For publication of results, please cite: ChemProt-2.0: Visual navigation in a disease chemical biology database.
View the abstracts. The chemical-protein information has been provided by: ChEMBL WOMBAT & WOMBAT-PK DrugBank PubChem BioassayKi Database BindingDB STITCH PharmGKB CTD IUPHAR The JME applet (Java Molecular Editor) used above has been provided by courtesy of dr Peter Ertl. VisANT: An integrative platform for network/pathway analysis. GOSTAR: Compound Centric Databases. COMPOUND CENTRIC DATABASES-- It includes data from Scientific Literature, Public Domain, FDA Product leaflets, and EPAR (European public assessment report) documents.
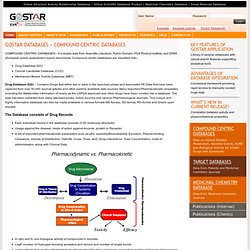
Compound centric databases are classified into-- Drug Database (DD)Clinical Candidate Database (CCD)Mechanism Based Toxicity Database (MBT) Drug Database (DD) – Contains Drugs that either are or were in the launched phase and associated PK Data that have been captured from over 50,000 Journal articles and other publicly available data sources. Many important Pharmacokinetic properties including the Metabolites information of nearly all the USFDA approved and other drugs have been curated into a database.
The data has been extracted from many standard books, online sources and various Pharmacological Journals. The Database consists of Drug Records This database offers the following possibilities: Characteristics of the available fields: This database offers the following utilities: In silico ADME/Tox: why models fail ? KEGG COMPOUND. KEGG COMPOUND Database KEGG COMPOUND is a collection of small molecules, biopolymers, and other chemical substances that are relevant to biological systems.
Each entry is identified by the C number, such as C00047 for L-lysine, and contains chemical structure and associated information, as well as various links to other KEGG databases and outside databases. KEGG COMPOUND is maintained in the KEGG LIGAND relational database. The classification of representative entries in KEGG COMPOUND is given in the following BRITE hierarchy file. Compounds with biological roles Biosynthetic Codes The structures of DNA, RNA, and proteins are determined by template-based syntheses of replication, transcription, and translation with the genetic code.
Peptides Peptide entries in KEGG COMPOUND are designated with "Peptide" in the first Entry line (see example here). DoseSim — Systems and Computational Biology Research Group. Assessing and improving the safety of chemicals and the efficacy of drugs depends on an understanding of the biodistribution, clearance, and biological effects of the chemical(s) of interest.

A promising methodology for the prediction of these phenomena is physiologically-based pharmacokineticpharmacodynamic (PBPK/PD) modeling, which centers on the prediction of chemical ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) and the biological effects of the chemical on the organism. A strength of this methodology is that it allows the inclusion and integration of various forms of information across multiple scales of biological organization and facilitates the extrapolation of results across routes of exposure, dosing levels, and species. It is also useful as the foundation for tools to (i) predict biomarker levels given a chemical dose or exposure (forward dosimetry) and (ii) reconstruct a dose given the levels of relevant biomarkers (reverse dosimetry).
Downloads. ACD/Percepta Predictors. Get an in-depth understanding of structure-property relationships with ACD/Labs' fully powered predictive models for physiochemical and ADME properties, and toxicity endpoints.

The predictors are a collection of expert modules built for comprehensive evaluation of structure-property relationships. The advanced algorithms that power these predictions have been built on the combined strengths of ACD/Labs and Pharma Algorithms (the companies merged in 2009). In the Percepta platform we have brought together our joint experience and expertise to provide the best from all models, and the fastest, most accurate predictions in almost two decades of development. We offer a broad collection of powerful prediction modules for physicochemical properties, ADME outcomes, and toxicity endpoints. Customize your own suite of tools by combining any number of modules below. *Trainable modules. Metabolism Prediction. Drug Adverse Reaction Target. In Silico drug repositioning - DDT - Liu, 2012. SuperTarget. SuperPred. STITCH: chemical association networks.
PharmGKB. Therapeutic Target Database. DrugBank. ADME/tox Filtering. Online XlogP calculations (computed with XScore, sw16.im.med.umich.edu/software/xtool).
A comparison of experimental versus calculated values for 109 compounds is shown here Salt removal: a tool to remove salts sometimes associated in compound description. Collections of compounds should be desalted before ADMETox filtering, otherwise some bias will be introduced for molecular weight calculation, logP calculation, etc. Test sets for virtual ligand screening These test sets include 6 different proteins (different folds and different nature of the binding pocket in term of open, close, polar, hydrophobe) : ER, factor Xa, HIVprotease, Neuraminidase, RNase and TK, all in PDB format with the PDB ID and corresponding ligands (active compound co-crystalized with these protein targets), about 10 ligands for each protein in Mol2 format.
These data can help to assess docking and scoring functions for a VLS project. Input: Molecules in SMILES or 2D/3D SDF format are required. Ref. Collections.