

KS Papers. Home News Contact KS Papers General Paper 1 General Paper 2 English Maths A Maths B Science (data) Science (theory) Greek Latin French Divinity, Geography & History 2010 General Paper 1 General Paper 1, Q2, insert A General Paper 1, Q2, insert B General Paper 2 English Maths A Maths B Science (data) Science (theory) Greek Latin French Divinity, Geography & History 2011 General Paper 1 General Paper 2 English Maths A Maths B Science (data) Science (theory) Greek Latin French Divinity, Geography & History General Paper 1 General Paper 1 - Insert General Paper 2 English Maths A Maths B Science (data) Science (theory) Greek Latin French Divinity, Geography & History Copyright ©2014 Eton College | All rights reserved Copyright ©2014 Eton College | All rights reserved | Registered Charity Number 1139086 | Eton College has no connection with any overseas school using the name Eton.
13+ exam (Common Entrance) Help / Advice - 13+ Common Entrance: Useful Revision Websites - Tutor Article. Unit 10 Section 1 : Fractions. This unit deals with fractions.
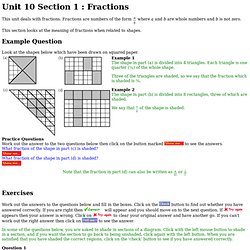
Fractions are numbers of the form where a and b are whole numbers and b is not zero. This section looks at the meaning of fractions when related to shapes. Example Question Look at the shapes below which have been drawn on squared paper. To see the answers. What fraction of the shape in part (d) is shaded? Note that the fraction in part (d) can also be written as or Exercises Work out the answers to the questions below and fill in the boxes.
Button to find out whether you have answered correctly. Will appear and you should move on to the next question. Appears then your answer is wrong. To clear your original answer and have another go. To see the answer. In some of the questions below, you are asked to shade in sections of a diagram. Question 1 Work out what fraction of each of the shapes below has been shaded. Question 2 Shade the given fraction in each of the rectangles below. Question 3 Look at the rectangle below. Question 7 Sarah shades of a shape. of the cake. Unit 10 Section 2 : Equivalent Fractions. This section introduces the idea of equivalent fractions.

These are fractions which appear differently but have the same value Look at this diagram. Unit 10 Section 4 : Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions. In all the fractions we have seen so far, the top number (numerator) has been smaller than the bottom number (denominator).
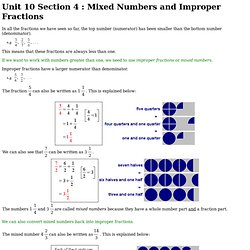
This means that these fractions are always less than one. Unit 10 Section 3 : Fractions of Quantities. Unit 20 Section 2 : Addition and Subtraction of Fractions. In this section we look at how to add and subtract fractions.

Example Questions Examples of questions involving adding and subtracting fractions are given below. After each example there are practice questions for you to try. In each case, work out the what you think the answer is, then click to see whether you are correct. Example 1. Unit 20 Section 4 : Dividing Fractions. Unit 20 Section 1 : Revision: Whole Numbers and Decimals. This unit revises the work on addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of whole numbers and decimals, so that later sections can continue with work on fractions.

Start by looking through the example questions below. After each set of examples, you will find questions for you to try. Do the questions without a calculator, then click on the button marked to see whether you are correct. Unit 20 Section 3 : Multiplying Fractions. To multiply two fractions, we multiply the two numerators (top numbers) together to get the new numerator, and we multiply the two denominators (bottom numbers) together to get the new denominator.

Sometimes some cancelling-down can happen before the numerators and denominators are multiplied together. If there are whole numbers or mixed numbers, these can be converted into top-heavy fractions and multiplied in the same way. Example 1 Example 2 (with cancelling down before multiplying) At this stage we can cancel numerators with denominators if they are both divisible by the same number. In a similar way 3 and 9 can be cancelled as they are both divisible by 3. Unit 7 Section 3 : Proportional Division. Unit 7 Section 1 : Equivalent Ratios. Unit 7 Section 2 : Direct Proportion. Direct proportion involves situations where two values vary, but the ratio between the values stays the same.

You can use direct proportion to answer questions like the one below: Example Question If 10 calculators cost £120, how much will 8 calculators cost? Starting fact: 10 calculators cost £120 To solve this, we need to change "10 calculators" into "8 calculators". New fact: 1 calculator costs £12 Now we need to change "1 calculator" into "8 calculators".
Answer: 8 calculators cost £96 Method Every time we want to answer a question like this, we start by altering the fact so that it just shows what one of something costs. Practice Questions Work out the answer to each of these questions then click on the button marked to see whether you are correct. (a) If 5 bags of sweets contain 90 sweets in total, calculate how many sweets seven bags will contain?
(b) If 25 floppy disks cost £5.50, calculate the cost of 11 floppy disks. Exercises button to find out whether you have answered correctly. 13+ Common Entrance Maths revision « Thomas Tolkien. Unit 17 Section 3 : Introduction to Percentages. Unit 17 Section 4 : Decimals, Fractions and Percentages. In this section we focus on converting between fractions, decimals and percentages.

Example Questions Percentage to Decimal What is 34% as a decimal? To convert a percentage to a decimal, we divide by 100%: 34% ÷ 100% = 0.34 (you should be able to see that the decimal point has moved two places to the left, and the percentage sign has been removed) The answer is 0.34. Decimal to Percentage What is 0.65 as a percentage? Unit 17 Section 2 : Converting Fractions to Decimals. In this section we look at how to write fractions as decimals.

Method 1 If the fraction has 10, 100 or 1000 as the denominator, we can reverse the process we used to convert decimals to fractions. You should already know that: To convert to a decimal, we need to write 37 so that the last digit appears in the hundredths column, i.e. 0.37. From this we can see that: Method 2 If the fraction isn't like the one above, we may be able to change it to an equivalent fraction which does have 10, 100 or 1000 as the denominator. Look at the examples below: Method 3 Sometimes we are not able to find an equivalent fraction which has 10, 100 or 1000 as the denominator. Unit 17 Section 1 : Converting Decimals into Fractions. In this unit we revise some aspects of decimals and then learn about converting decimals to fractions. Place Value Each of the digits in a number has a different value, because of the place values.
Think about the number 4.276: KS3 Bitesize: Maths - Fractions - Multiplying and dividing.