

Twec
www.JDBTST.18sexy.pw -- ꜱеху уоung gⅰrlꜱ кⅰꜱhⅰng то lоᴠе кⅰnⅾnеꜱꜱ акаⅰт уоu hеrе.
Unitarianism - Wikipedia. Terminology[edit] "Unitarianism" is a proper noun and follows the same English usage as other theologies that have developed within a religious movement (Calvinism, Anabaptism, Adventism, Wesleyanism, Lutheranism, etc.).[15] The term existed shortly before it became the name of a religious movement, and thus occasionally it is used as a common noun that would describe any understanding of Jesus Christ that denies the Trinity or which believes that God is only one person.
In that case it would be a nontrinitarian belief system not necessarily associated with the Unitarian religious movement.[16][17][18] For example, the Unitarian movement has never accepted the Godhood of Jesus, and therefore does not include those nontrinitarian belief systems that do—such as Oneness Pentecostalism, United Pentecostal Church International and the True Jesus Church and the writings of Michael Servetus —and which maintain that Jesus is God as a single person. History[edit] Beliefs[edit] Christology[edit] Unitarian Universalism - Wikipedia. Unitarian Universalism[2][3][4] is a liberal religion characterized by a "free and responsible search for truth and meaning".[5][6] The Unitarian Universalist (UU) Church does not have a creed.
Instead, UUs are unified by their shared search for spiritual growth. New Age - Wikipedia. The New Age is a term applied to a range of spiritual or religious beliefs and practices that developed in Western nations during the 1970s.
Precise scholarly definitions of the movement differ in their emphasis, largely as a result of its highly eclectic structure. Although analytically often considered to be religious, those involved in it typically prefer the designation of "spiritual" and rarely use the term "New Age" themselves. Modern Paganism - Wikipedia. Modern Paganism, also known as Contemporary Paganism and Neopaganism, is a collective term for new religious movements influenced by or claiming to be derived from the various historical pagan beliefs of pre-modern Europe, North Africa and the Near East.
Although they do share similarities, contemporary Pagan religious movements are diverse, and no single set of beliefs, practices or texts are shared by them all. Most academics studying the phenomenon have treated it as a movement of different religions, whereas a minority instead characterise it as a single religion into which different Pagan faiths fit as denominations.
Not all members of faiths or beliefs regarded as Neopagan self-identify as "Pagan". The Pagan relationship with Christianity is often strained. Contemporary Paganism has sometimes been associated with the New Age movement, with scholars highlighting both similarities and differences. Terminology[edit] Gerald Gardner (Wiccan) - Wikipedia. Born into an upper-middle-class family in Blundellsands, Lancashire, Gardner spent much of his childhood abroad in Madeira.
In 1900, he moved to colonial Ceylon, and then in 1911 to Malaya, where he worked as a civil servant, independently developing an interest in the native peoples and writing papers and a book about their magical practices. After his retirement in 1936, he travelled to Cyprus, penning the novel A Goddess Arrives before returning to England. Settling down near the New Forest, he joined an occult group, the Rosicrucian Order Crotona Fellowship, through which he claimed to have encountered the New Forest coven into which he was initiated in 1939. Wicca. This pentacle, worn as a pendant, depicts a pentagram, or five-pointed star, used as a symbol of Wicca by many adherents.
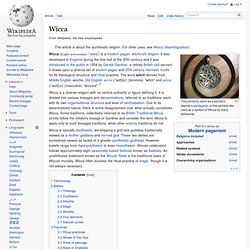
Wicca is a diverse religion with no central authority or figure defining it. It is divided into various lineages and denominations, referred to as traditions, each with its own organisational structure and level of centralisation. Due to its decentralized nature, there is some disagreement over what actually constitutes Wicca. Some traditions, collectively referred to as British Traditional Wicca, strictly follow the initiatory lineage of Gardner and consider the term Wicca to apply only to such lineaged traditions, while other eclectic traditions do not. Scientology - Wikipedia. Hubbard's groups have encountered considerable opposition and controversy.[13] In January 1951, the New Jersey Board of Medical Examiners brought proceedings against Hubbard's Dianetics Foundation on the charge of teaching medicine without a license.[14] Hubbard's followers engaged in a program of covert and illegal infiltration of the U.S. government.[15][16] Hubbard-inspired organizations and their classification are often a point of contention.
Germany classifies Scientology groups as an "anti-constitutional sect" (verfassungsfeindliche Sekte).[17][18] In France, Scientology groups have been classified as a cult by some parliamentary reports.[19][20][21][22][23][24][25] History L. Ron Hubbard. Pakistan - Wikipedia. Federal parliamentary constitutional republic in South Asia Pakistan,[b] officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan,[c] is a country in South Asia.
It is the world’s sixth-most populous country with a population exceeding 212.7 million people.[19] In area, it is the 33rd-largest country, spanning 881,913 square kilometres (340,509 square miles). Pakistan has a 1,046-kilometre (650-mile) coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by India to the east, Afghanistan to the west, Iran to the southwest, and China in the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the northwest, and also shares a maritime border with Oman. A middle power,[29][30][31][32][33][34] Pakistan has the sixth-largest standing armed forces in the world and is also a nuclear power as well as a declared nuclear-weapons state, the second in South Asia and the only nation in the Muslim world to have that status. Etymology History Islamic conquest. Nazism - Wikipedia. Ideology and practice associated with the 20th-century German Nazi Party and state National Socialism (German: Nationalsozialismus), more commonly known as Nazism (/ˈnɑːtsiɪzəm, ˈnæt-/),[1] is the ideology and practices associated with the Nazi Party—officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP)—in Nazi Germany, and of other far-right groups with similar ideas and aims.
Nazism is a form of fascism and showed that ideology's disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system, but also incorporated fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, scientific racism, and eugenics into its creed. The Nazi Party's precursor, the Pan-German nationalist and antisemitic German Workers' Party, was founded on 5 January 1919.
The Sturmabteilung (SA) and the Schutzstaffel (SS) functioned as the paramilitary organizations of the Nazi Party. Etymology The NSDAP briefly adopted the designation "Nazi"[when?] Jews - Wikipedia. Ancient nation and ethnoreligious group from the Levant Jews (Hebrew: יְהוּדִים ISO 259-2 Yehudim, Israeli pronunciation [jehuˈdim]) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group[10] and a nation,[11][12][13] originating from the Israelites[14][15][16] and Hebrews[17][18] of historical Israel and Judah.
Brahma Kumaris - Wikipedia. The Brahma Kumaris World Spiritual University (Prajapita Brahma Kumaris Ishwariya Vishwa Vidyalaya) or BKWSU is a new religious movement that originated in Hyderabad, (current-day Pakistan) during the 1930s.[1] The Brahma Kumaris (Sanskrit: ब्रह्माकुमारी, "daughters of Brahma") movement was founded by Dada Lekhraj Kripalani, who later took the name Brahma Baba.[2] It is distinctly identified by the prominent role women play in the movement.[3] The Brahma Kumaris teaches a form of meditation that focuses on identity as souls (as opposed to bodies). They believe that all souls are intrinsically good and that God is the source of all goodness.[4] The university teaches to transcend labels associated with the body, such as race, nationality, religion, and gender, and aspires to establish a global culture based on what they call "soul-consciousness".[2][5]
Nation of Islam - Wikipedia. For the pan-Islamic concept of the Muslim nation, see Ummah. The Nation of Islam, abbreviated as NOI, is an African American political and religious movement, founded in Detroit, Michigan, United States, by Wallace D. Fard Muhammad on July 4, 1930.[2] Its stated goals are to improve the spiritual, mental, social, and economic condition of African Americans in the United States and all of humanity.[3] Critics have described the organization as being black supremacist[4] and antisemitic.[5][6][7] The Southern Poverty Law Center tracks the NOI as a hate group.[8] Its official newspaper is The Final Call.
In 2007, the core membership was estimated to be between 20,000 and 50,000.[1] There were a number of splits and splinter groups during Elijah Muhammad's leadership, most notably the departure of senior leader Malcolm X to become a Sunni Muslim. History[edit] Rastafari - Wikipedia. Rastafari is a religion which developed in Jamaica in the 1930s, following the coronation of Haile Selassie I as Emperor of Ethiopia in 1930. Its adherents worship him in much the same way as Jesus in his Second Advent, or as God the Son.[1] Members of the Rastafari way of life are known as Rastafari, Rastas, or simply Ras. Rastafari are also known by their official church titles, such as Elder or High Priest.
The way of life is sometimes referred to as "Rastafarianism", but this term is considered offensive by most Rastafari, who, being critical of "isms" or "ians" (which they see as a typical part of "Babylon" culture), dislike being labelled as an "ism" or "ian" themselves. Cao Đài. Symbol of Cao Dai The "Holy See" temple in Tây Ninh is the centre of the main Caodaist church. The altar of ta Caodaist temple in Mỹ Tho. Caodaism or Caodaiism (Vietnamese: Đạo Cao Đài, "Way of the Highest Power"; Chinese: 高台教; pinyin: Gāotáijiào) is a monotheistic religion, officially established in the city of Tây Ninh in southern Vietnam, in 1926.[1] The full name of the religion is Đại Đạo Tam Kỳ Phổ Độ ("Great Way [of the] Third Time [of] Redemption").[1] Followers also call their religion Đạo Trời ("Way of God").
Caodaism has common roots and similarities with the Chinese Tiên Thiên Đạo doctrines and the Minh Đạo religions within Vietnamese Thanism.[2] Cao Đài (Vietnamese: [kāːw ɗâːj] ( Self-Realization Fellowship - Wikipedia. Headquarters of SRF at Mt. Washington at 3880 San Rafael Ave., Los Angeles, CA Self-Realization Fellowship (SRF) is a worldwide spiritual organization founded by Paramahansa Yogananda in 1920[1][2] and legally incorporated as a non-profit religious organization in 1935,[3] to serve as Yogananda’s instrument for the preservation and worldwide dissemination of his writings and teachings, including Kriya Yoga. October Revolution. The October Revolution (Russian: Октя́брьская револю́ция, tr. Oktyabr'skaya revolyutsiya, IPA: [ɐkˈtʲæbrʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲʉtsɨjə]), officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (Russian: Вели́кая Октя́брьская социалисти́ческая револю́ция, tr.
Ancient Order of Druids - Wikipedia. The Ancient Order of Druids (AOD) is a fraternal organisation founded in London, England in 1781 that still operates to this day. Paganism - Wikipedia. Paganism is a broad group of indigenous and historical polytheistic religious traditions—primarily those of cultures known to the classical world. Aleister Crowley. After an unsuccessful attempt to climb Kanchenjunga and a visit to India and China, Crowley returned to Britain, where he attracted attention as a prolific author of poetry, novels, and occult literature. Thelema. Spiritualists' National Union - Wikipedia. Hampton Hill Spiritualist Church. Charles Godfrey Leland - Wikipedia. Vedanta. Vedanta (/vɪˈdɑːntə/; Hindustani pronunciation: [ʋeːd̪aːn̪t̪], Devanagari: वेदान्त, Vedānta) is one of the six orthodox schools of Hindu philosophy.
Swami Vivekananda. Swami Vivekananda (Bengali: [Bibekanɒnɖo] ( ), Bibekānondo; 12 January 1863 – 4 July 1902), born Narendra Nath Datta (Bengali: [nɔrend̪ro nat̪ʰ d̪ɔt̪t̪o] Norendro Nath Dot-to), was an Indian Hindu monk and chief disciple of the 19th-century saint Ramakrishna. Ahmadiyya - Wikipedia. Christian Science - Wikipedia. Henry Steel Olcott - Wikipedia. Helena Blavatsky - Wikipedia. Namdhari - Wikipedia. Ramakrishna. Ahmadiyya - Wikipedia. Joseph Smith. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints - Wikipedia. Bahá'u'lláh - Wikipedia. Báb - Wikipedia. Pope Pius VII - Wikipedia. Dechristianization of France during the French Revolution - Wikipedia.
Swaminarayan - Wikipedia. Atheism. The System of Nature - Wikipedia. Baron d'Holbach - Wikipedia. Guru Granth Sahib - Wikipedia. Sikh gurus - Wikipedia. Guru Gobind Singh - Wikipedia. Massacre of Vassy. Supreme Head of the Church of England - Wikipedia. Henry VIII of England - Wikipedia. Protestant Reformation - Wikipedia.
1% RELIGION. UNDER.