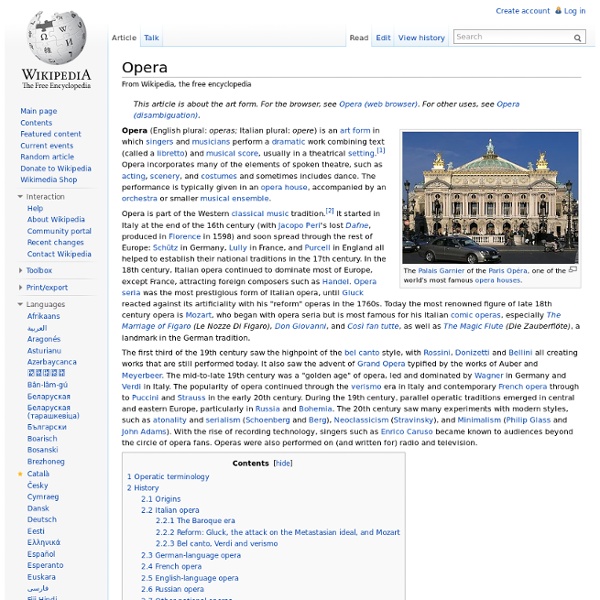
Opera
Opera (English plural: operas; Italian plural: opere) is an art form in which singers and musicians perform a dramatic work combining text (called a libretto) and musical score, usually in a theatrical setting.[1] Opera incorporates many of the elements of spoken theatre, such as acting, scenery, and costumes and sometimes includes dance. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble. Opera is part of the Western classical music tradition.[2] It started in Italy at the end of the 16th century (with Jacopo Peri's lost Dafne, produced in Florence in 1598) and soon spread through the rest of Europe: Schütz in Germany, Lully in France, and Purcell in England all helped to establish their national traditions in the 17th century. In the 18th century, Italian opera continued to dominate most of Europe, except France, attracting foreign composers such as Handel. Operatic terminology[edit] History[edit] Origins[edit]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Opera
The Baroque Era
As of July 1, 2013 ThinkQuest has been discontinued. We would like to thank everyone for being a part of the ThinkQuest global community: Students - For your limitless creativity and innovation, which inspires us all.
Baroque Era - Composers
As of July 1, 2013 ThinkQuest has been discontinued. We would like to thank everyone for being a part of the ThinkQuest global community: Students - For your limitless creativity and innovation, which inspires us all.
Music of the Baroque Era
General Characteristics of the Baroque The dominant trends in Baroque music correspond to those in Baroque art and literature. Among the general characteristics of Baroque art is a sense of movement, energy, and tension (whether real or implied). Strong contrasts of light and shadow enhance the dramatic effects of many paintings and sculptures. The term Baroque denotes the inner stylistic unity of the period.
Related: