

Data networks, open system communications and security. Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) Download the Cloud Controls Matrix About the CSA Cloud Controls Matrix The Cloud Security Alliance Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) is specifically designed to provide fundamental security principles to guide cloud vendors and to assist prospective cloud customers in assessing the overall security risk of a cloud provider.
The CSA CCM provides a controls framework that gives detailed understanding of security concepts and principles that are aligned to the Cloud Security Alliance guidance in 13 domains. The foundations of the Cloud Security Alliance Controls Matrix rest on its customized relationship to other industry-accepted security standards, regulations, and controls frameworks such as the ISO 27001/27002, ISACA COBIT, PCI, NIST, Jericho Forum and NERC CIP and will augment or provide internal control direction for service organization control reports attestations provided by cloud providers. Online IP CIDR / VLSM Supernet Calculator. CIDR Calculator The CIDR Calculator enables CIDR network calculations using IP address, subnet mask, mask bits, maximum required IP addresses and maximum required subnets.

Results of the CIDR calculation provide the wildcard mask, for use with ACL (Access Control Lists), CIDR network address (CIDR route), network address in CIDR notation and the CIDR address range for the resulting CIDR network. VLSM CIDR Subnet Calculator. Administrative distance. Default administrative distances[edit] The following table lists the default administrative distances for various routing protocols used on Cisco routers.[3] Please note that:- An administrative distance of 255 will cause the router to disbelieve the route entirely and not use it.
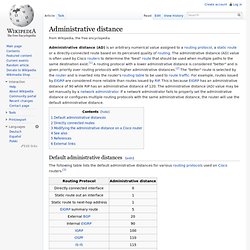
An administrative distance of 255 will cause the router to remove the route from the RIB and not use it.* Since IOS 12.2, the administrative distance of a static route with an exit interface is 1. Prior to the release of 12.2 it was in fact 0.Only the interface itself has an administrative distance of 0, since a route cannot be less than 1.Directly connected routes have an administrative distance of 1. Directly connected routes[edit] Please note that directly connected routes have an administrative distance of 1.
For example, the following commands could be issued at privileged exec mode on the router in order to verify that a static route has an administrative distance of 1. S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.31.0.1. Routing table. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol. The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP9) is an advanced distance-vector routing protocol that is used on a computer network to help automate routing decisions and configuration.
The protocol was designed by Cisco Systems as a proprietary protocol, available only on Cisco routers, but Cisco converted it to an open standard in 2013.[1] Open Shortest Path First. OSPF is perhaps the most widely used interior gateway protocol (IGP) in large enterprise networks.
IS-IS, another link-state dynamic routing protocol, is more common in large service provider networks. The most widely used exterior gateway protocol is the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), the principal routing protocol between autonomous systems on the Internet. Overview[edit] The OSPF routing policies to construct a route table are governed by link cost factors (external metrics) associated with each routing interface. Cost factors may be the distance of a router (round-trip time), network throughput of a link, or link availability and reliability, expressed as simple unitless numbers.
An OSPF network may be structured, or subdivided, into routing areas to simplify administration and optimize traffic and resource utilization. By convention, area 0 (zero) or 0.0.0.0 represents the core or backbone region of an OSPF network. IP Routing and Subnets. This article describes the basics of IP routing.
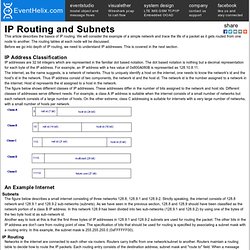
We will consider the example of a simple network and trace the life of a packet as it gets routed from one node to another. The routing tables at each node will be discussed. Before we go into depth of IP routing, we need to understand IP addresses. This is covered in the next section. Routing. Routing is the process of selecting best paths in a network.
In the past, the term routing was also used to mean forwarding network traffic among networks. However this latter function is much better described as simply forwarding. Internet Systems Consortium. Round-trip delay time. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority. Ephemeral port. The allocations are temporary and only valid for the duration of the communication session.
After completion of the communication session, the ports become available for reuse. [note 1] Since the ports are used on a per request basis they are also called dynamic ports. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) suggests the range 49152 to 65535 (215+214 to 216−1) for dynamic or private ports.[1] Many Linux kernels use the port range 32768 to 61000. [note 2] FreeBSD has used the IANA port range since release 4.6. In addition to the default range, all versions of Windows since Windows 2000 also allow the option to use a non-default port range with a maximum of 1024 to 65535.[7][8] Some Microsoft articles misleadingly list only this non-default range,[9] leading to a popular misconception that 1024 to 65535 is the default or required port range used. Time to live. IP packets[edit] DNS records[edit] TTLs also occur in the Domain Name System (DNS), where they are set by an authoritative name server for a particular resource record.
ARP spoofing. A successful ARP spoofing (poisoning) attack allows an attacker to alter routing on a network, effectively allowing for a man-in-the-middle attack.
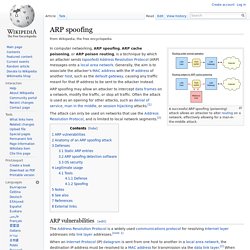
ARP spoofing may allow an attacker to intercept data frames on a network, modify the traffic, or stop all traffic. Often the attack is used as an opening for other attacks, such as denial of service, man in the middle, or session hijacking attacks.[1] The attack can only be used on networks that use the Address Resolution Protocol, and is limited to local network segments.[2] ARP vulnerabilities[edit]
RFC-Editor Webpage. CCNP Certification Training Site. Ip nat inside source static. Network address calculator and ip address calculator, javascript based. Show network, broadcast, first and last address for a given network: The netmask in "bits format" is also known as mask in CIDR format (CIDR=Classless Inter-Domain Routing). Subnet Mask Converter (dotted decimal to bits format) Subnet Mask Converter (bits format to dotted decimal) Number of required addresses to netmask converter.
Creating Your Own Custom Wireshark Dissector. Download source - 9.32 KB 1.0 Introduction Wireshark is a powerful open source tool used to dissect Ethernet packets. Have you ever wondered what it takes to implement your own custom dissector? Furthermore, have you attempted to learn Wireshark's API and found it difficult to understand? This article will attempt to demystify the development of your very own protocol dissector. 1.1 Requirements This article expects the reader to be familiar with structured C, TCP/IP. 2.0 Configure Wireshark Build Environment (Win32) The Wireshark developer's guide [^] features a section on setting up the Win32 environment, which I found to be invaluable. Step 1. If you do not have VS2005/VS2003 etc., you will need to download and install "Visual C++ 2005 Express Edition"[^].
Step 2. You must download and install the Platform SDK Server 2003 R2[^]. Step 3. This guide will not go into great details about the Cygwin package. Archive/unzip Devel/bison Devel/flex Interpreters/perl Utils/patch Web/wget Step 4. Online IP Subnet Calculator. IPv4_Subnetting Cheatsheet. Classless Inter-Domain Routing. A method for IP address allocation and routing IP addresses are described as consisting of two groups of bits in the address: the most significant bits are the network prefix, which identifies a whole network or subnet, and the least significant set forms the host identifier, which specifies a particular interface of a host on that network.
This division is used as the basis of traffic routing between IP networks and for address allocation policies. Whereas classful network design for IPv4 sized the network prefix as one or more 8-bit groups, resulting in the blocks of Class A, B, or C addresses, Classless Inter-Domain Routing allocates address space to Internet service providers and end users on any address-bit boundary. In IPv6, however, the interface identifier has a fixed size of 64 bits by convention, and smaller subnets are never allocated to end users. CIDR encompasses several concepts. Subnetting.org - Free Subnetting Questions and Answers Randomly Generated Online. Subnetting Secrets. Learn to Subnet – The Easy Way. The TCP/IP Guide.