

Optical fiber. A bundle of optical fibers Stealth Fiber Crew installing a 432-count fiber cable underneath the streets of Midtown Manhattan, New York City A TOSLINK fiber optic audio cable with red light being shone in one end transmits the light to the other end History[edit] Daniel Colladon first described this “light fountain” or “light pipe” in an 1842 article titled On the reflections of a ray of light inside a parabolic liquid stream.
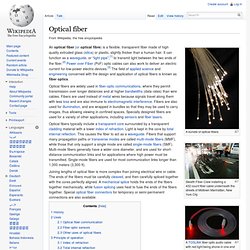
This particular illustration comes from a later article by Colladon, in 1884. Guiding of light by refraction, the principle that makes fiber optics possible, was first demonstrated by Daniel Colladon and Jacques Babinet in Paris in the early 1840s. Practical applications, such as close internal illumination during dentistry, appeared early in the twentieth century. A variety of other image transmission applications soon followed. NASA used fiber optics in the television cameras that were sent to the moon. Uses[edit] Fiber-optic communication. An optical fiber junction box.
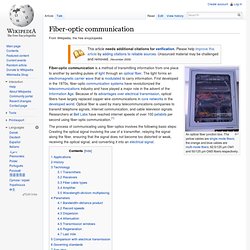
The yellow cables are single mode fibers; the orange and blue cables are multi-mode fibers: 62.5/125 µm OM1 and 50/125 µm OM3 fibers respectively. Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. How Fiber Optics Work" Diameter of an Optical Fiber. Topic index | author index | special index With the advent of the fiber-optic network, our world has entered into a new age of communications.
Optical fibers are extremely thin strands of glass, which are made up of many layers. They use laser light to carry information, sounds and images over very large distances. Optical communications systems have the capability of carrying thousands of telephone calls or television programs simultaneously, which is just one of their superior aspects in comparison to our current systems. Fiber-optic networks are quicker in transmitting data and make it possible to transmit this data further distances (up to 100 miles with out being quot;boosted"). Copper Wire and Its Limitations. Optical communications repeater. An optical communications repeater is used in a fiber-optic communications system to regenerate an optical signal by converting it to an electrical signal, processing that electrical signal and then retransmitting an optical signal.
Such repeaters are used to extend the reach of optical communications links by overcoming loss due to attenuation of the optical fibre and distortion of the optical signal. Such repeaters are known as optical-electrical-optical (OEO) due to the conversion of the signal. Repeaters are also called regenerators for the same reason. Classification of regenerators[edit] Optical regenerations are classified into 3 categories by the 3 R's scheme. [1] R : reamplification of the data pulse alone is carried out.2R : in addition to reamplification, pulse reshaping is carried out. All-optical regenerators[edit] An alternative method of regeneration is through all-optical without requirement to convert back and forth.
Fiber Optic History. By Jeff Hecht Reproduced from Fiber Optics Technician's Handbook, by Jim Hayes, Delmar Publishers, Albany, New York.

For the full history of fiber optics, see my book, City of Light: The Story of Fiber Optics, Oxford University Press, New York, 1999. (ISBN 0-19-510818-3) A book in the Sloan Foundation Technology series. For near-immediate gratification, order now from Amazon.com. Optical communication systems date back two centuries, to the "optical telegraph" that French engineer Claude Chappe invented in the 1790s. Alexander Graham Bell patented an optical telephone system, which he called the Photophone, in 1880, but his earlier invention, the telephone, proved far more practical.
In the intervening years, a new technology slowly took root that would ultimately solve the problem of optical transmission, although it was a long time before it was adapted for communications. Optical fibers went a step further. Kao took a long, hard look at fiber attenuation. "According to Dr. History of Fiber Optics. As far back as Roman times, glass has been drawn into fibers.
Yet, it was not until the 1790s that the French Chappe brothers invented the first "optical telegraph. " It was a system comprised of a series of lights mounted on towers where operators would relay a message from one tower to the next. Over the course of the next century great strides were made in optical science. John Tyndall, British physicist, demonstrated that light signals could be bent. In the 1840s, physicists Daniel Collodon and Jacques Babinet showed that light could be directed along jets of water for fountain displays.
Alexander Graham Bell patented an optical telephone system called the photophone in 1880. Sketch of a telephone system by Alexander Graham Bell. Doctors Roth and Reuss, of Vienna, used bent glass rods to illuminate body cavities in 1888. In the 1920s, John Logie Baird patented the idea of using arrays of transparent rods to transmit images for television and Clarence W. Semaphore line. A replica of one of Chappe's semaphore towers in Nalbach, Germany.
A semaphore telegraph, optical telegraph, shutter telegraph chain, Chappe telegraph, or Napoleonic semaphore is a system of conveying information by means of visual signals, using towers with pivoting shutters, also known as blades or paddles. Information is encoded by the position of the mechanical elements; it is read when the shutter is in a fixed position. The system was invented in 1792 in France by Claude Chappe, and was popular in the late 18th to early 19th century.[1][2][3] Semaphore lines were a precursor of the electrical telegraph. They were far faster than post riders for bringing a message over long distances, but far more expensive and less private than the electrical telegraph lines which would replace them.
Modern derivatives of the semaphore system include flag semaphore (a flag relay system) and the heliograph (optical telegraphy using mirror-directed sunlight reflections). Etymology[edit] History[edit] The History Of The Fibre Optic Cable.