

Topological Data Analysis. Why this is important As the amount of information available increases exponentially, it becomes more important to find patterns in data than to find the reason for the patterns.
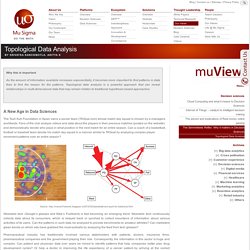
Topological data analysis is a powerful approach that can reveal relationships in multi-dimensional data that may remain hidden to traditional hypothesis based approaches A New Age in Data Sciences The Tsuh Kuh Foundation in Spain owns a soccer team (TKGoal.com) whose match day squad is chosen by e-managers worldwide. Fans of the club analyze videos and data about the players in their previous matches (posted on the website) and democratically decide who plays in what position in the next match for an entire season.
Source: Wearable tech (Google’s glasses and Nike’s Fuelband) is fast becoming an emerging trend. Pharmaceutical industry has traditionally involved various stakeholders with patients, doctors, insurance firms, pharmaceutical companies and the government playing their role. What and How of TDA? Source: Analyse des données. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
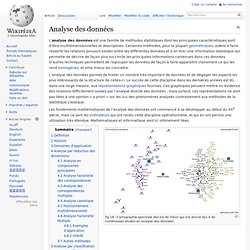
L’analyse des données permet de traiter un nombre très important de données et de dégager les aspects les plus intéressants de la structure de celles-ci. Le succès de cette discipline dans les dernières années est dû, dans une large mesure, aux représentations graphiques fournies. Ces graphiques peuvent mettre en évidence des relations difficilement saisies par l’analyse directe des données ; mais surtout, ces représentations ne sont pas liées à une opinion « a priori » sur les lois des phénomènes analysés contrairement aux méthodes de la statistique classique. Les fondements mathématiques de l’analyse des données ont commencé à se développer au début du XXe siècle, mais ce sont les ordinateurs qui ont rendu cette discipline opérationnelle, et qui en ont permis une utilisation très étendue.
Mathématiques et informatique sont ici intimement liées. Définition[modifier | modifier le code] Histoire[modifier | modifier le code] Exploratory data analysis. In statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach to analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often with visual methods.
A statistical model can be used or not, but primarily EDA is for seeing what the data can tell us beyond the formal modeling or hypothesis testing task. Exploratory data analysis was promoted by John Tukey to encourage statisticians to explore the data, and possibly formulate hypotheses that could lead to new data collection and experiments.
EDA is different from initial data analysis (IDA),[1] which focuses more narrowly on checking assumptions required for model fitting and hypothesis testing, and handling missing values and making transformations of variables as needed. EDA encompasses IDA. Overview[edit] Exploratory data analysis, robust statistics, nonparametric statistics, and the development of statistical programming languages facilitated statisticians' work on scientific and engineering problems. EDA development[edit] John W. Data Analysis. About the Course You have probably heard that this is the era of “Big Data”.
Stories about companies or scientists using data to recommend movies, discover who is pregnant based on credit card receipts, or confirm the existence of the Higgs Boson regularly appear in Forbes, the Economist, the Wall Street Journal, and The New York Times. But how does one turn data into this type of insight? Dessine-moi des data scientists. Récemment, la petite équipe d’Etalab, la mission en charge de l’ouverture des données publiques, s’est étoffée d’une poignée de personnes dont le métier est nimbé d’une aura de buzz en ce moment : des data scientists, qu’on pourrait traduire par “datalogue” ou “dataiste”, si ce n’était moins percutant que la version anglaise.
Pour faire simple, on peut partir de cette définition de Samuel Charron, data scientist chez Data Publica : Personne capable de valoriser la donnée : extraction, traitement, statistiques, analyse, visualisation, etc. Entre la nomination du premier administrateur général des données (AGD), Henri Verdier qui dirigeait déjà Etalab, et la passion pour les “smart cities”, l’exploitation des données dont regorgent les SI privés et publics, ouverte ou non, est devenue un gros enjeu, gage d’une meilleure efficacité et d’économies. Les data scientists sont donc présentés comme une fonction-clé. Et sont appelés à prendre pied dans les collectivités territoriales. Focus.