

Autodidacticism. Independent education without the guidance of masters Autodidacticism (also autodidactism) or self-education (also self-learning and self-teaching) is education without the guidance of masters (such as teachers and professors) or institutions (such as schools).
Generally, autodidacts are individuals who choose the subject they will study, their studying material, and the studying rhythm and time. Autodidacts may or may not have formal education, and their study may be either a complement or an alternative to formal education. Learning. Play has been approached by several theorists as the first form of learning.
Children experiment with the world, learn the rules, and learn to interact through play. Lev Vygotsky agrees that play is pivotal for children's development, since they make meaning of their environment through play. 85 percent of brain development occurs during the first five years of a child's life.[6] The context of conversation based on moral reasoning offers some proper observations on the responsibilities of parents.[7] Types of learning[edit] Non-associative learning[edit] Your Amazing Brain. List of common misconceptions. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.

Thought on Thinking. 49 Fascinating YouTube Videos to Learn About the Human Body. As any doctor, nurse practitioner or other health care professional knows, the body is an interesting system.
In many ways, it’s like a machine, with many complex parts. There is a lot to learn about the body and how it works, as well as how its different systems interact to create a larger system. Here are 49 interesting YouTube videos that can help you learn about the human body: Brain Your brain directs the rest of the body’s functions. How the Body Works: The Regions of the Brain: An interesting look at the different regions of the brain, and what they are responsible for.Brain Anatomy Function: How brain works? Nervous System. Sexology. Sexology is the interdisciplinary study of human sexuality, including human sexual interests, behaviors and function.[1] The term sexology does not generally refer to the non-scientific study of sexuality, such as political science or social criticism.[2][3] In modern sexology, researchers apply tools from several academic fields, such as biology, medicine, psychology, epidemiology, sociology and criminology.
Sexologists study sexual development (puberty), sexual orientation, sexual relationships and sexual activity, as well as document the sexualities of special groups; for example, child sexuality, adolescent sexuality, sexuality among the elderly and the disabled. The sexological study of sexual dysfunctions and disorders, including erectile dysfunction, anorgasmia, and pedophilia, are also common. History[edit] How to Live With an Unknowable Mind.
We know surprisingly little about our own personalities, attitudes and even self-esteem.

How do we live with that? How do you imagine your own mind? I sometimes picture mine as a difficult and contrary child; the kind that throws a stone at you for no reason and can’t explain itself. Or while at the beach it sits silent, looking miserable. Squashed Philosophers- Condensed Plato Aristotle Augustine Descartes Hume Marx Freud Copernicus Hobbes Sartre Ayer Sade Wittgenstein Einstein. Thou shalt not commit logical fallacies. SCHOPENHAUERS 38 STRATAGEMS, OR 38 WAYS TO WIN AN ARGUMENT - StumbleUpon. Arthur Schopenhauer (1788-1860), was a brilliant German philosopher.

These 38 Stratagems are excerpts from "The Art of Controversy", first translated into English and published in 1896. Carry your opponent's proposition beyond its natural limits; exaggerate it. Neuroscience of free will. Neuroscience of free will is the part of neurophilosophy that studies the interconnections between free will and neuroscience.
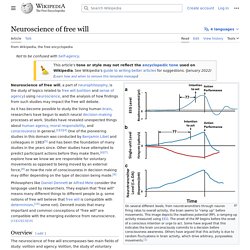
As it has become possible to study the living brain, researchers have begun to watch decision making processes at work. Findings could carry implications for our sense of agency and for moral responsibility and the role of consciousness in general.[1][2][3] Relevant findings include the pioneering study by Benjamin Libet and its subsequent redesigns; these studies were able to detect activity related to a decision to move, and the activity appears to begin briefly before people become conscious of it.[4] Other studies try to predict activity before overt action occurs.[5] Taken together, these various findings show that at least some actions - like moving a finger - are initiated unconsciously at first, and enter consciousness afterward.[6] Twenty-Five Ways To Suppress Truth: The Rules of Disinformation. Twenty-Five Ways To Suppress Truth: The Rules of Disinformation by H.

Michael Sweeney <HMS@proparanoid.com> (c) 1997, 2000, 2001 All rights reserved Permission to reprint/distribute hereby granted for any non commercial use provided information reproduced in its entirety and with author information in tact. For more Intel/Shadow government related info, visit the Author's Web site: Depressive realism. Evidence for[edit] Evidence against[edit] When asked to rate both their performance and the performance of another, non-depressed individuals demonstrated positive bias when rating themselves but no bias when rating others.

Criticism of the evidence[edit] Butterfly effect. In chaos theory, the butterfly effect is the sensitive dependency on initial conditions in which a small change at one place in a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state. The name of the effect, coined by Edward Lorenz, is derived from the theoretical example of a hurricane's formation being contingent on whether or not a distant butterfly had flapped its wings several weeks earlier. Although the butterfly effect may appear to be an unlikely behavior, it is exhibited by very simple systems. Language. A mural in Teotihuacan, Mexico (c. 2nd century) depicting a person emitting a speech scroll from his mouth, symbolizing speech Language is the human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, and a language is any specific example of such a system.
The scientific study of language is called linguistics. Languages evolve and diversify over time, and the history of their evolution can be reconstructed by comparing modern languages to determine which traits their ancestral languages must have had in order for the later developmental stages to occur. A group of languages that descend from a common ancestor is known as a language family. Gallifreyan Dictionary Wiki. Romaji.Me - English to Romaji, English to romanized Japanese translation. Alaska Native Language Archive. Eyak is not an Athabaskan language, but a coordinate sub-branch to Athabaskan as a whole in the Athabaskan-Eyak branch of the Athabaskan-Eyak-Tlingit language family. Eyak was spoken in the 19th century from Yakutat along the southcentral Alaska coast to Eyak at the Copper River delta, but by the 20th century only at Eyak.
It is now represented by about 50 people but no surviving fluent speakers. Eyaklanguageproject. How Language Works (Edition 3.0): Table of Contents. Learn the Hebrew Alphabet. IntroductionBy Jeff A. Benner Why Learn Hebrew? There are many reasons to learn Hebrew such as to read the Tenach (the Old Testament of the Bible written in Hebrew) in its original language or simply to learn how to pronounce Hebrew words such as those in Strong's Concordance without having to use the transliterations.
Probably the most advantageous reason to learn Hebrew is the ability to understand the original author's words, rather than through the translator's opinion of the author's words. Learning the Hebrew language can be both fun and exciting. Direction of Reading. Hebrew for Christians - Learn Hebrew for FREE! The Yiddish Handbook: 40 Words You Should Know. Learn to Read Hebrew Online Free. Translate English to Irish Gaelic Translations for Free. Skill. People need a broad range of skills in order to contribute to a modern economy. A joint ASTD and U.S. Department of Labor study showed that through technology, the workplace is changing, and identified 16 basic skills that employees must have to be able to change with it.[1] Labor skills[edit] Life skills[edit] Life skills are problem solving behaviors used appropriately and responsibly in the management of personal affairs.
People skills[edit] Free online speed reading software. How to Develop a Photographic Memory. How to Be Ambidextrous: 6 steps (with pictures) Edit Article. Lucid Dream Guru - Master the Art of Lucid Dreaming - StumbleUpon. Clear Mind Meditation Techniques. Micro Expressions - Research, Theory & Lying. How to Detect Lies - body language, reactions, speech patterns.
Interesting Info -> Lying Index -> How to Detect Lies. Eye Movement and Lying - How to detect lies. Interesting Info -> Lying Index -> Eye Direction & Visual Accessing Cues. Top 40 Useful Sites To Learn New Skills. The Beginner's Guide to Surviving on a Desert Island. Doom Survival Guide - SAS Survival Manual.