

Cristiano Ronaldo - Tested To The Limit. GCSE PE - Types of Feedback. ~Best Football Soccer Skills~ 2008/09. Nerds FC final game - short clip. Ronaldinho Cross Bar Ping Pong. Patersons Stadium - How Ridiculous. Feedback: Knowledge of Performance. One type of feedback most commonly used in skill acquisition studies is knowledge of performance (KP) and knowledge of results (KR).

KP refers to kinematic information about the actual execution of the movements performed (Gentile, 1972). The information provides a basis on which to assess the correctness of the movement, for example a sprinter sees a video replay of his or her performance during a training session. There are two common forms of KP feedback; video or verbal feedback and self directed strategies (Schmidt and Lee, 2005). Video and self directed attentional focusing may be critical to actively involving athletes in the learning process, such as identifying errors that the teacher believes to be important (Cutton and Landin, 2007). With the improvement of video analysis software available, coaches have been increasingly using video as a method of administering feedback.
Like this: Like Loading... Teaching games for understanding. Author: Shane Pill, Flinders University School of Education and President, SA Branch, Australian Council for Health, Physical Education and Recreation Issue:Volume 29 Number 2 Sports have traditionally been taught using the skill and drill or progressive part method.

Sports are broken down into their component skills and these are then taught. This technical approach, developed after World War 2, taught the skills isolated from the game and then the skills and the game are put back together. This method assumes there is only one right way to perform a skill, but we know from observation of elite sportspeople that frequently they don’t kick the ball or swing the racquet like the ideal model. Successful sport athletes often do not have perfect stylized technique, frequently having individual technique differences and successful unorthodoxies. This traditional technical approach begins with the question, “How is this skill performed?” Australian Coaches - Skill Acquisition. Skill Classification - Continuums. There is a large range of sporting activities each requiring a set of skills.
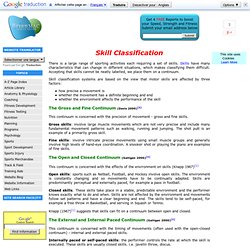
Skills have many characteristics that can change in different situations, which makes classifying them difficult. Accepting that skills cannot be neatly labelled, we place them on a continuum. Skill classification systems are based on the view that motor skills are affected by three factors: ASCA: The Premier Coaching Resource Worldwide. The Importance of “Self Confidence” in Achieving Your Swimming Goals By Wayne Goldsmith Belief is the knowledge that we can do something.

It’s the inner feeling that what we undertake, we can accomplish. For the most part, all of us have the ability to look at something and know whether or not we can do it. So, in belief there is power: our eyes are opened; our opportunities become plain; our visions become realities. - Unknown Have you said (or thought) any of the following in the past few months??? You are not alone. Swimmer says: “I can’t do it.” Swimmer says: “They are faster than me. Swimmer says: “I’m hopeless.” Personal Development, Health and Physical Education. Question 11 Written Paper Section I Question 11 - 2010 HSC Effective source of fuel for replenishing an athlete's energy store after completing a track event Question 11 Written Paper Section I Question 11 - 2002 HSC.
Stages Of Skill Acquisition: The Cognitive stage of skill acquisition. The first stage of skill learning is the cognitive stage.

The fundamental requirement here is that the athlete gains an understanding of the task required. This will necessitate knowing what to do and an insight about how to do it. Conceptualisation - or the generation of clear mental pictures of the task - is essential for good movement reproduction. Demonstrations, videos and information highlighting the important points can help guide the learner through the skill. However, coaches must be careful to avoid 'information overload', which would confuse the learner.It is expected that the learner will encounter problems, the number and magnitude of which will depend on the difficulty of the skill. (Above extract taken from: Third Edition, Outcomes 2 HSC Course, Personal Development, Health and Physical Education) Below: A great example of conceptualisation. Skill Development. When we choose to move, the action is controlled by the conscious brain using a collection of learned movements.

For the movement to progress successfully, the athlete requires information feedback. Types of skill There are a number of different types of skills: Cognitive - or intellectual skills that require thought processes Perceptual - interpretation of presented information Motor - movement and muscle control Perceptual motor - involve the thought, interpretation and movement skills How do we teach a new skill? The teaching of a new skill can be achieved by various methods: Verbal instructions Demonstration Video Diagrams Photo sequences The Learning Phases - Fitts & Posner Fitts and Posner (1967)[3] suggested that the learning process is sequential and that we move through specific phases as we learn.
The leaning of physical skills requires the relevant movements to be assembled, component by component, using feedback to shape and polish them into a smooth action. Schmidt's Schema Theory.