

Mathematics Illuminated. Trigonometric functions, such as sine and cosine, are useful for modeling sound waves, because they oscillate between values.
In the previous section, we looked at how to quantify different aspects of a sound wave mathematically. We saw that frequency, phase, and amplitude are the key quantifiable attributes that distinguish one wave from another. What of the actual wave itself? What is the mathematical function that represents a wave? Obviously, we need a relationship that exhibits periodic behavior, returning to the same position or value with regularity. NOTE: Throughout this discussion, we measure angles in units of radians. Sine, Cosine, Tangent. Three Functions, but same idea.
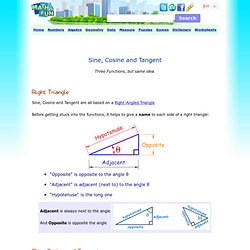
Right Triangle Sine, Cosine and Tangent are all based on a Right-Angled Triangle Before getting stuck into the functions, it helps to give a name to each side of a right triangle: Free Multiplication Games, Activities, & Resources. Fact Navigator. Multiplication stories. Greek Mathematics. As the Greek empire began to spread its sphere of influence into Asia Minor, Mesopotamia and beyond, the Greeks were smart enough to adopt and adapt useful elements from the societies they conquered.
This was as true of their mathematics as anything else, and they adopted elements of mathematics from both the Babylonians and the Egyptians. But they soon started to make important contributions in their own right and, for the first time, we can acknowledge contributions by individuals. By the Hellenistic period, the Greeks had presided over one of the most dramatic and important revolutions in mathematical thought of all time. The ancient Greek numeral system, known as Attic or Herodianic numerals, was fully developed by about 450 BCE, and in regular use possibly as early as the 7th Century BCE. But most of Greek mathematics was based on geometry. Review of CAMS & STAMS book collection from Curriculum Associates. Review by Maria Miller. How to help students with multiplication tables?
In this article I discuss some general principles in helping students with their multiplication tables: 1.
Why study the tables? 2. Learning tables in a structured manner3. Example: memorizing the table of 3 in five steps4. Why study the times tables? I feel that learning the multiplication tables is even more important than mastering addition and subtraction facts. Times Table. The Best Place to Get Your Math or Science Grade Up. BetterExplained. Millennium Mathematics Project. Visual Math Learning: A Free Online Tutorial for Teaching Math. The Official MURDEROUS MATHS Site.
ADDITION - PROCESS OF ADDING ONE TO FIVE OR MORE DIGIT NUMBERS AND WORD PROBLEMS. Resources for a Computer-Based Math Education: Key Resources, Videos, Press, and Other Links. Compass and straightedge constructions. Creating a regular hexagon with a ruler and compass Construction of a regular pentagon The idealized ruler, known as a straightedge, is assumed to be infinite in length, and has no markings on it and only one edge.
The compass is assumed to collapse when lifted from the page, so may not be directly used to transfer distances. (This is an unimportant restriction, as this may be achieved via the compass equivalence theorem.) More formally, the only permissible constructions are those granted by Euclid's first three postulates. Every point constructible using straightedge and compass may be constructed using compass alone. Compass and straightedge tools[edit] A compass The "compass" and "straightedge" of compass and straightedge constructions are idealizations of rulers and compasses in the real world: The modern compass generally does not collapse and several modern constructions use this feature.
Each construction must be exact. Each construction must terminate. The basic constructions[edit] Roman Numerals. The Romans were active in trade and commerce, and from the time of learning to write they needed a way to indicate numbers.

The system they developed lasted many centuries, and still sees some specialized use today. Roman numerals traditionally indicate the order of rulers or ships who share the same name (i.e. Queen Elizabeth II). They are also sometimes still used in the publishing industry for copyright dates, and on cornerstones and gravestones when the owner of a building or the family of the deceased wishes to create an impression of classical dignity. The Roman numbering system also lives on in our languages, which still use Latin word roots to express numerical ideas.
Free downloadable Maths Video Lecture courses. Blog : Twisted Architecture. I didn’t set out to tie knots in Norman Foster’s Hearst Tower or wrinkle his Gherkin, but I got carried away.
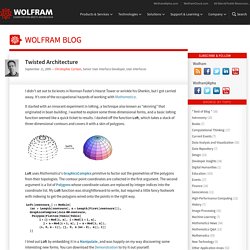
It’s one of the occupational hazards of working with Mathematica. It started with an innocent experiment in lofting, a technique also known as “skinning” that originated in boat-building. I wanted to explore some three-dimensional forms, and a basic lofting function seemed like a quick ticket to results. I dashed off the function Loft, which takes a stack of three-dimensional contours and covers it with a skin of polygons. Loft uses Mathematica‘s GraphicsComplex primitive to factor out the geometries of the polygons from their topologies. I tried out Loft by embedding it in a Manipulate, and was happily on my way discovering some interesting new forms. Even this trivial parameterization of a scaled and twisted half-sphere yields an amazing variety of forms, each of which suggests interesting avenues to explore.
I wondered how convincingly I could model the Gherkin in Mathematica. Free Computers Video Lecture courses. Upgrade Your Browser.